Aerosol optical thickness
They are provided on the NEO web site as 1-day measurements and 8-day and 1-month composites. There are many applications for aerosol optical thickness data: " 1 Atmospheric correction of remotely sensed surface features 2 Monitoring of sources and sinks of aerosols 3 Monitoring of volcanic eruptions and forest fire 4 Radiative Transfer Model 5 Air Quality 6 Health and Environment 7 Earth Radiation Budget 8 Climate Change" 1 "Aerosol particles are aerosol optical thickness to scientists because they represent an area of great uncertainty in their efforts to understand Earth's climate system, aerosol optical thickness.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 04 December
Aerosol optical thickness
This post contains formulas! Aerosols play a great role in the atmospheric effects. Aerosols are particles suspended in the atmosphere, which can be of several types: sand or dust, soot from combustion, sulfates or sea salt, surrounded by water… Their size ranges between 0. Their quantity is also extremely variable : rain can suddenly reduce their abundance known as « aerosol optical thickness ». The abundance variations result in great variations of observable reflectances from one day to the next, and it is therefore necessary to know the quantity and type of aerosols, in order to correct their effects. Unfortunately, to correct the effects of aerosols, there is no global aerosol observation network, and the only available data are local observations from the few hundred points of Aeronet network. Therefore, this network can not be used operationally to correct the satellite images over large areas. Weather forecast models just start predicting the amounts of aerosols , based on satellite observations and modeling of sources and sinks and of the transport of aerosols by the winds, but these data do not seem to have sufficient accuracy yet to be used for the atmospheric correction of images. Our atmospheric correction method, named MACCS, is therefore based on an estimate of aerosol optical depth from the images themselves. To understand how this method works, one must already understand the effects of aerosols on radiation. We have seen in this post, that the effects of diffusion can be modelled as follows assuming the corrected gas absorption :. We seek to know the surface reflectance, but for each measurement made at the top of the atmosphere, there are three unknowns to be determined. To separate the effects of the atmosphere and surface effects, we must use other information. We can therefore deduce the atmospheric reflectance and using a radiative transfer model, the aerosols optical thickness AOT. However, this method assumes that there is a very dark area in the image which is not always the case , and that the reflectance of the dark surface is known.
This method is too complex to be explained in detail here, aerosol optical thickness, interested readers can refer to [Hagolle ]. Note that the optical depth of a given medium will be different for different colors wavelengths of light.
In physics , optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material. Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power through the material. Spectral optical depth or spectral optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. The use of the term "optical density" for optical depth is discouraged. In chemistry , a closely related quantity called " absorbance " or "decadic absorbance" is used instead of optical depth: the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, that is the optical depth divided by ln Optical depth measures the attenuation of the transmitted radiant power in a material. Attenuation can be caused by absorption, but also reflection, scattering, and other physical processes.
The aerosol quantity determined by most instruments is the aerosol optical depth AOD. This is related to the amount of light aerosols scatter or absorb in a column through the atmosphere specifically, it is the vertically-integrated aerosol extinction , and is also sometimes referred to as aerosol optical thickness AOT. AOD depends on wavelength; a common reference wavelength reported by satellite data products is nm. This is related to the aerosol particle size. Roughly speaking , values less than 1 suggest an optical dominance of coarse particles e. For health purposes, people are often interested in the mass of aerosols of a certain size at ground level. This is often referred to by the term 'particulate matter' PM and separated by size. Terms such as PM 1 , PM 2.
Aerosol optical thickness
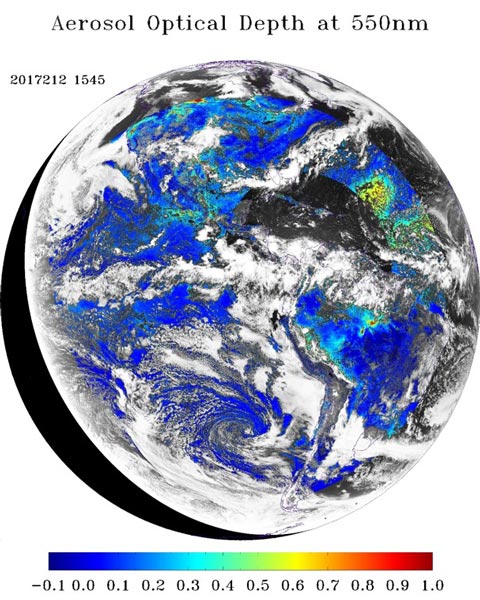
An aerosol optical depth product has been recently added. Aerosol optical depth is a measure of the extinction of the solar beam by dust and haze. In other words, particles in the atmosphere dust, smoke, pollution can block sunlight by absorbing or by scattering light.
Plus size casual outfits with sneakers
Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. The combination of the two methods retains the best of the two basic methods. Unfortunately, to correct the effects of aerosols, there is no global aerosol observation network, and the only available data are local observations from the few hundred points of Aeronet network. They characterized by rapidly growing economies with the largest urban and industrial agglomerations and the highest density of population Fig. In the Yangtze River Delta density of population is also high. Weather forecast models just start predicting the amounts of aerosols , based on satellite observations and modeling of sources and sinks and of the transport of aerosols by the winds, but these data do not seem to have sufficient accuracy yet to be used for the atmospheric correction of images. Hi Olivier,Thanks for this article. Results of regression showed that satellite products often correlate well with one another, but struggle from slope or Y-intercept biases. With that Gui, K. Also, apparently, the highest aerosol concentration was caused by their generation as a result of direct emissions from various anthropogenic activity and formation of secondary hygroscopic particles at high relative humidity 22 ,
In the maps shown here, dark brown pixels show high aerosol concentrations, while tan pixels show lower concentrations, and light yellow areas show little or no aerosols. Black shows where the sensor could not make its measurement. Aerosol optical depth is the degree to which aerosols prevent the transmission of light by absorption or scattering of light.
Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. At the same time, it is obvious that satellite measurements of MODIS AOD over various regions showed good results, delivering quite precise values of optical depth under conditions of most typical atmospheric aerosol loads, making it possible to carry out the analysis of trend constituents of multiannual time series. High AOD values are attributed to hygroscopic growth of aerosols, formation of secondary aerosols and pollutants as a result of agricultural biomass combustion after crop harvesting in the adjacent districts, which entails pollutants accumulation in this region. They generally tend to work better on vegetated areas rather than in arid areas. Atmospheric aerosol is the most common in natural conditions type of disperse system, consisting of solid and liquid particles, suspended in the atmosphere. These daily "data are produced at the spatial resolution of a In the Pearl River Delta density of population constitutes over 1, people per km 2 and the highest density in the mainland of this region is found in Shenzhen 5, people per km 2 , Dongguan 3, people per km 2 , Foshan 1, people per km 2 and Guangzhou 1, people per km 2 Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. This task is performed by 9 cameras, carrying out survey in 9 different directions nadir, Enregistrer mon nom, mon e-mail et mon site dans le navigateur pour mon prochain commentaire. Li, L. However, the highest values were found at Beijing data points of and Taihu data points of stations Fig. Swath constitutes kilometers. Such good results may be characterized by unique features in MISR instrument, which make it possible to ensure a better view and study of spectral response characteristics to obtain aerosol optical properties over various surfaces due to the use of its polygonal and multispectral view capabilities.

What necessary words... super, an excellent phrase