So4 2 formal charge
Three cases can be constructed that do not follow the octet rule, and as such, they are known as the exceptions to the octet rule.
Lewis dot structure of SO 4 2 - :. Lewis Dot Structure of NO 2 - :. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Steps to draw the lewis structure: Lewis dot structures are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
So4 2 formal charge
Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry of the isolated anion is the same as that of methane. Organic sulfate esters , such as dimethyl sulfate , are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. Later, Linus Pauling used valence bond theory to propose that the most significant resonance canonicals had two pi bonds involving d orbitals. His reasoning was that the charge on sulfur was thus reduced, in accordance with his principle of electroneutrality. The outcome was a broad consensus that d orbitals play a role, but are not as significant as Pauling had believed. In this model, fully occupied p orbitals on oxygen overlap with empty sulfur d orbitals principally the d z 2 and d x 2 — y 2. Therefore, the representation with four single bonds is the optimal Lewis structure rather than the one with two double bonds thus the Lewis model, not the Pauling model.
A: Resonance Structures are drawn when one lewis dot structure is inadequate to explain physical and….
Lewis structures are another way to represent molecules. Lewis Structures were introduced by Gilbert N. Lewis in Lewis suggested the use of lines between atoms to indicate bonds, and pairs of dots around atoms to indicate lone or non-bonding pairs of electrons. In the example above, 3 hydrogen atoms with one valence electron each form three bonds with one nitrogen atom with 5 valence electrons. By forming three bonds, nitrogen gains 3 electrons to make a total of 8 surrounding it. This satisfies the octet rule allowing nitrogen's valence shell of electrons to look just like the noble gas neon's.
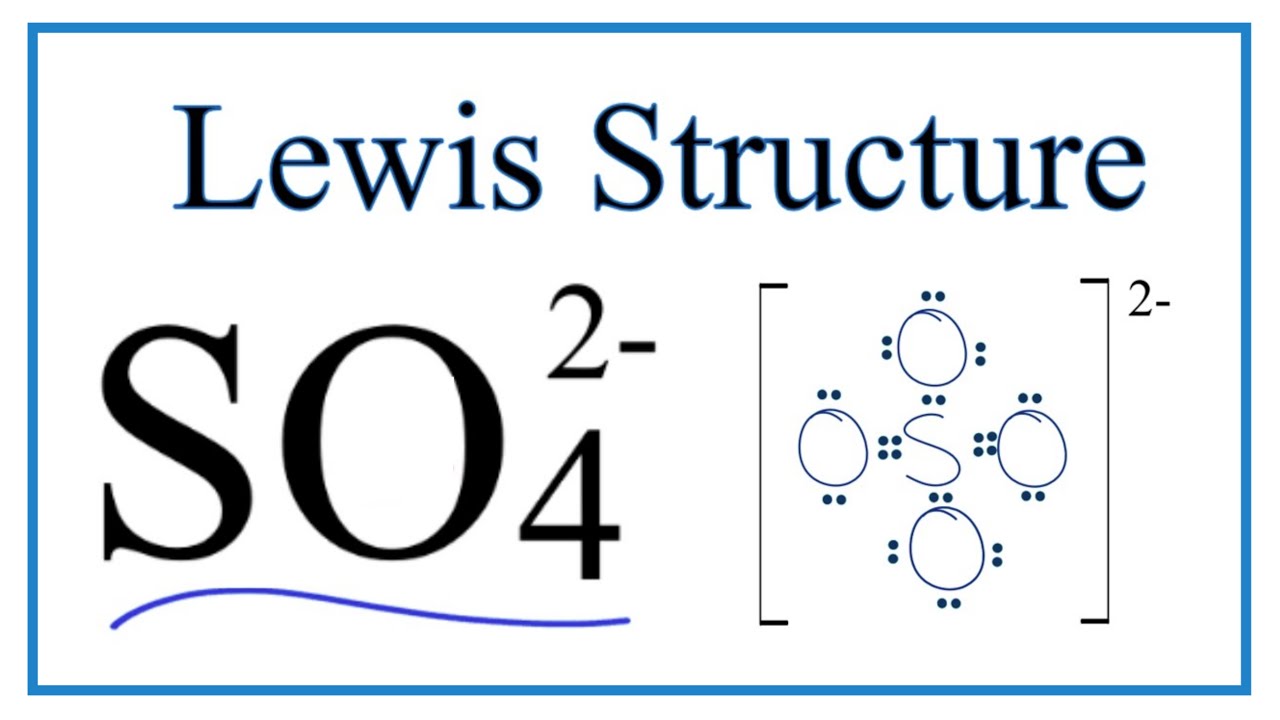
The SO 4 2- Lewis structure depicts the molecular arrangement of sulfate, which consists of one sulfur atom and four oxygen atoms. The structure has two double bonds and two single bonds arranged around the sulfur atom, with each of the four oxygen atoms attached to it. Within this arrangement, the oxygen atoms that form double bonds have two lone pairs, while the oxygen atoms that form single bonds have three lone pairs. Furthermore, both oxygen atoms that are bonded to sulfur with a single bond carry a negative -1 charge in the SO 4 2- Lewis structure. Begin by sketching a rough outline of the molecular arrangement. Next, identify any lone pairs on the atoms within the structure. If there are formal charges present, indicate them on the appropriate atoms.
So4 2 formal charge
The SO4 2- Sulfate Ion , comprised of one sulfur atom and four oxygen atoms, presents a captivating example of a chemical species with intriguing properties. At the heart of comprehending the characteristics and reactivity of SO4 2- lies the exploration of its Lewis structure. Determine Total Valence Electrons. To begin, identify the valence electrons of each atom in the SO4 2- molecule. Sulfur S belongs to Group 16, contributing 6 valence electrons, while each oxygen O atom in Group 16 contributes 6 valence electrons. In the SO4 2- ion, sulfur S is the central atom due to its lower electronegativity compared to oxygen O. Establish single bonds electron pairs between sulfur S and each oxygen O atom.
Zillow usa
This is the same amount as the number of valence electrons it would have naturally. So I've moved electrons from the outside of these two green Oxygens into the middle to form double bonds. The Quadratic Formula. Heating and Cooling Curves. A: Distribute the unshared electron pairs around each atom, in order to satisfy an octet…. Calculate the formal charge on Cl atom in H C l O 4. The correct Answer is: 1. Bibcode : NatSR Albert ; Wilkinson, Geoffrey Benzene Reactions. Bibcode : AerST.. It was a bit of work, but we have the best structure here. Lewis in Q: SiO2 formal charges.
SO is a chemical name for the sulfate ion. It comprises one Sulphur atom, four Oxygen atoms, and a charge of It is a polyatomic anion and is used widely to synthesize other sulfates such as Zinc Sulfates, Magnesium sulfates, Iron sulfates, and much more.
If the ion had been SO 3 2- sulfite instead of sulfate, then the structure would have had a lone pair of electrons on the central atom:. Face Centered Cubic Unit Cell. Each line in the drawing above represents the use of 2 electrons. The Atom. Subtract the number of bonding electrons from the total number of valence electrons. Step 2. Elements A has one electron in its valence shell and its principal qua Nitrogen normally has five valence electrons. Formation of the aerosols and their effects on the atmosphere can be studied in the lab, with methods like ion-chromatography and mass spectrometry [51] Samples of actual particles can be recovered from the stratosphere using balloons or aircraft, [52] and remote satellites were also used for observation. Example SO 4 2- A rule of thumb is that the central atom atom which all the other atoms will be bound is the one furthest to the left or bottom in the periodic table. It has 6 electrons Add a multiple bond double bond to see if central atom can achieve an octet: 6. The correct Answer is: 1. We do this by adding brackets around the ion and showing the charge:. Looking at the formal charges for this structure, the sulfur ion has six electrons around it one from each of its bonds. Q: What is the formal charge on N in this ion?

All not so is simple