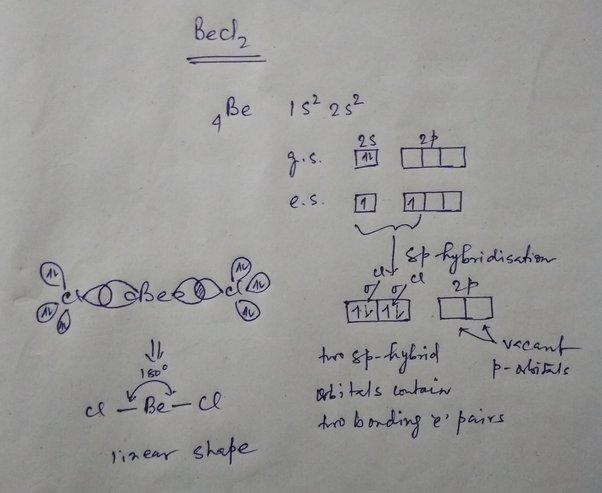
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Views: 5, Connect with our Chemistry tutors online and get step by step solution of this question. Are you ready to take control of your learning?
Submitted by Marilyn R. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Theoretical Physical Chemistry Revision Notes. The Shapes of Molecules and Ions and bond angles related to their Electronic Structure - mainly inorganic molecules on this page. Part 1 from diatomic molecules to polyatomic molecules. All by structure and chemical bonding revision notes All my advanced A level inorganic chemistry notes Index of all my GCSE level chemistry notes The shapes and bond angles of a variety of molecules are described, explained and discussed using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory and patterns of shapes deduced for 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 groups of bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons in the valence shell of the central atom of the molecule or ion. So, this page is all about how to work out molecule shapes and work out bond angles is described and explained! Sub-index for 'shapes of molecules' pages. Consider bonding pairs and lone non-bonding pairs of electrons as charge clouds that repel each other remember that like electrical charges repel. In deducing the shape of free radicals, a single electron can be treated as a lone pair to a reasonable approximation. These pairs of bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons in the outer shell of atoms arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimise this repulsion. We are talking about the electron clouds or more precisely, the orbitals that these bonding and non-bonding pairs of electrons occupy. This effectively means to produce a range of as wide as possible angles between adjacent orbitals. These maybe lone pair - lone pair , bond pair - lone pair or bond pair - bond pairs of electrons.
One of the limitations of Lewis structures is that they depict molecules and ions in only two dimensions.
Submitted by Brian S. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. Predict the shape of the following molecule o ion: AsH4 trigonal pyramidal trigonal planar linear tetrahedral bent.
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. This theory is very simplistic and does not account for the subtleties of orbital interactions that influence molecular shapes; however, the simple VSEPR counting procedure accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
To use the VSEPR model, one begins with the Lewis dot picture to determine the number of lone pairs and bonding domains around a central atom. For example, in either the hypervalent or octet structure of the I 3 - ion above, there are three lone pairs on the central I atom and two bonding domains. We then follow these steps to obtain the electronic geometry :. The molecular geometry is deduced from the electronic geometry by considering the lone pairs to be present but invisible. The most commonly used methods to determine molecular structure - X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, and electron diffraction - have a hard time seeing lone pairs, but they can accurately determine the lengths of bonds between atoms and the bond angles. The table below gives examples of electronic and molecular shapes for steric numbers between 2 and 9. We are most often concerned with molecules that have steric numbers between 2 and 6. From the Table, we see that some of the molecules shown as examples have bond angles that depart from the ideal electronic geometry. We can rationalize this in terms of the last rule above.
Priceline warragul
The methyl radical CH 3. All electrons shown on the left dot and cross diagram. COCl 2 below and the carbonate ion CO 3 2- are also trigonal planar, no lone pairs, but involve single and double bonds. At the same time, the repulsion would decrease in order of: triple bond-single bond, double bond-single bond, and single bond-single bond if the central atom E has multiple bonds. More Than Just We take learning seriously. I haven't introduced this APPENDIX 1 summary here at the start - its too much in one go, but when you have studied a variety of examples of deducing molecule shapes and bond angles take a good look at it and you should then fully appreciate point 4. Ans: The molecules are said to have a linear shape if the central atom is bonded to two other atoms at an angle of o. Despite consisting of the same electrons, the shapes of species may vary from one another. With four nuclei and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular structure is based on a trigonal bipyramid with a missing equatorial vertex; it is described as a seesaw. Phosphorus has five valence electrons and each chlorine has seven valence electrons, so the Lewis electron structure of PCl 5 is. H2S: This molecule has two atoms bonded to the central S atom, with two lone pairs.
Drawing and predicting the BeCl2 molecular geometry is very easy. Here in this post, we described step by step method to construct BeCl2 molecular geometry. A three-step approach for drawing the BeCl2 molecular can be used.
Housecroft, Catherine E. More Than Just We take learning seriously. The Lewis electron structure is. This can be overlooked by exam boards in their marking schemes and 'stuff' you find on the internet! Prior to protonation, you have five crosses of nitrogen's valence electrons and three dots for the bonding hydrogen electrons. Lone pair electrons are also taken into account. Four Electron Groups One of the limitations of Lewis structures is that they depict molecules and ions in only two dimensions. It can be concluded that the Lewis electron-pair theory is not the most suitable one for finding a number of lone pairs and structures of molecules, whereas the VSEPR model is most likely to be used to determine the structure of molecules. Algebra Chemistry Prealgebra. This effectively means to produce a range of as wide as possible angles between adjacent orbitals. The molecule has three atoms in a plane in equatorial positions and two atoms above and below the plane in axial positions. Introduction The shapes of the molecules is determined mainly by the electrons surrounding the central atom. Due to the arrangement of the bonds in molecules that have V-shaped, trigonal pyramidal, seesaw, T-shaped, and square pyramidal geometries, the bond dipole moments cannot cancel one another. This gives a stable 'octet' of electrons around both the nitrogen and boron atoms.

I am sorry, it not absolutely that is necessary for me. Who else, what can prompt?
By no means is not present. I know.
It doesn't matter!