Sf4 molecular geometry
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Sulfur sf4 molecular geometry located in Group 16 of the periodic table and has six valence electrons.
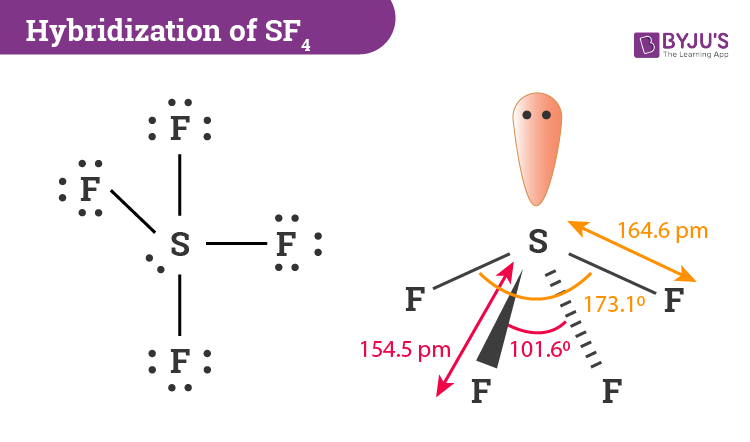
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown.
Sf4 molecular geometry
.
Sulphur Tetrafluoride contains 34 valence electrons, out of which it forms four covalent bonds and one lone pair of electrons on the core atom in its Lewis structure.
.
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula S F 4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds , [3] some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. Of sulfur's total of six valence electrons , two form a lone pair. One of the three equatorial positions is occupied by a nonbonding lone pair of electrons. Consequently, the molecule has two distinct types of F ligands, two axial and two equatorial. It is typical for the axial ligands in hypervalent molecules to be bonded less strongly. Further contrasting with SF 4 , SF 6 is extraordinarily inert chemically. The 19 F NMR spectrum of SF 4 reveals only one signal, which indicates that the axial and equatorial F atom positions rapidly interconvert via pseudorotation.
Sf4 molecular geometry
Within the context of VSEPR theory , you can count electrons to determine the electron geometry "parent" geometry. Sulfur : 6 valence electrons Fluorine : 7x4 valence electrons Total : 34 valence electrons. You can put sulfur in the middle because fluorine tends to make single bonds. Therefore, you can put 6x4 on each fluorine, 2x4 to account for four single bonds, and 2 for the last 2 valence electrons available. As a result, you have 5 electron groups, so the electron geometry would be trigonal bipyramidal.
Fiesta sonic
Sulfur will use four valence electrons to bond with the four fluorine atoms. Ans : Not all ligands peripheral groups in trigonal bipyramidal molecules or complexes are equidi Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. Get all the important information related to the JEE Exam including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc. SF 4 isomerised temperature- or solvent-dependently, switching between states in which the nonbonding electron pair is equatorial with two fluorines and states in which the electron pair and one fluorine are axial. In comparison, the other three fluorines are equatorial. In the 2p-orbitals, four hybrid orbitals overlap, whereas the fifth has just one pair. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. According to this theory, the central sulfur atom has a steric number of 5. Atoms and X-Rays Important Questions. As a result, electrons from the 3p orbital are excited to the 3d orbitals in the excited state of sulphur, leaving four orbitals available for bonding with fluorine atoms. Dash lines represent the four S-F single covalent bonds. Ans : Draw the SF
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms.
SF 4 isomerised temperature- or solvent-dependently, switching between states in which the nonbonding electron pair is equatorial with two fluorines and states in which the electron pair and one fluorine are axial. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. JEE Advanced Syllabus. When the electrons are separated by merely 90 degrees, the quantity of repulsion is substantially larger. Valence bond and hybridisation are not connected to the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR hypothesis, even though they are commonly taught together. A trigonal bipyramid produces the see-saw structure. It has five valence atomic orbitals forming five sp3d hybridized orbitals — one 3s orbital, three 3p orbitals, and one 3d orbital. Enthalpy of Neutralisation. Table of Content. JEE Coaching Centres. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown. You may use the steric number to determine how many hybrid orbitals an atom possesses.

Has casually come on a forum and has seen this theme. I can help you council.