Lateral surface area of cuboid and cube
Cube and cuboid are three-dimensional shapes that consist of six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The primary difference between them is a cube has all its sides equal whereas the length, width and height of a cuboid are different. Both shapes look almost the same but have different properties. The area and volume of cube, cuboid and also cylinder differ from each other.
The lateral surface area of a cube is defined as the total area of the side faces of the cube. A cube is a three-dimensional shape that is made up of 6 congruent square faces. All the 6 square faces of the cube are of the same size. A cube is referred to as:. It is to be noted that a cube is one of the 5 platonic solids.
Lateral surface area of cuboid and cube
The lateral area formula is used to find the lateral area of any solid object. The lateral area of any figure is the area of the non-base faces only. Lateral area formulas help in calculating the lateral surface area of different figures including cuboid, cube, cylinder, cone, and sphere. Let us see more about the lateral area formulas along with a few solved examples. The lateral area formula for different types of objects is different. Hence there are many lateral area formulas which are explained below. The lateral area does not include the base area of the object as well as the face parallel to the base. The lateral area formula for various objects are given in the tabular list below:. We measure the lateral surface area for 3-dimensional shapes. Given below is a detailed tabular list for you to understand the lateral surface area formula. Example 1: The length, breadth, and height of a cuboid are 6 units, 2 units, and 16 units respectively. Calculate the lateral surface area of the cuboid. Example 2: The radius of a sphere measures 4 units. This sphere is cut into two equal halves.
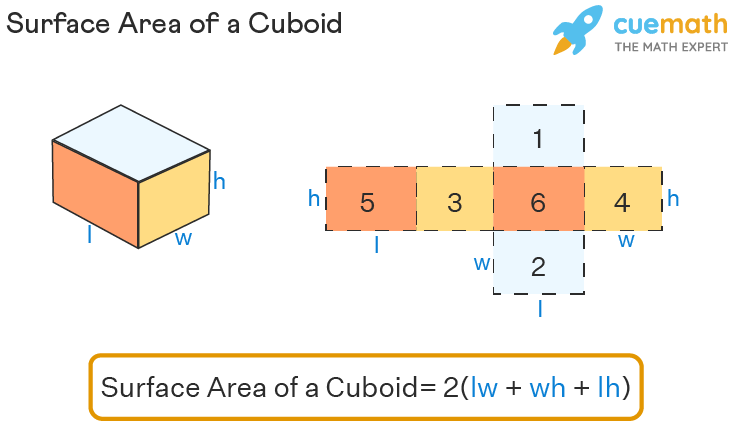
The lateral surface area of a cuboid is the area occupied by its lateral faces, whereas the total surface area of a cuboid is the area occupied by all its six rectangular faces, lateral surface area of cuboid and cube. The lateral area does not include the base area of the object as well as the face parallel to the base. The point of intersection of the 3 edges of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid.
In geometry, a three-dimensional shape having six rectangular faces is called a cuboid. A cuboid is also known as a regular hexahedron and has six rectangular faces, eight vertices, and twelve edges with congruent, opposite faces. It is a three-dimensional form of a rectangle with four lateral faces and two faces at the top and bottom. Some examples of cuboids that we regularly see are bricks, geometric boxes, shoe boxes, packaging boxes, etc. The surface area of a cuboid is the total area covered by all of its surfaces, and since the cuboid is the 3-D form of a rectangle, therefore, along with length and breadth, the height of the cuboid is also involved in finding the surface area. Surface area and volume are calculated in 3-D figures.
Cube and cuboid are three-dimensional shapes that consist of six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The primary difference between them is a cube has all its sides equal whereas the length, width and height of a cuboid are different. Both shapes look almost the same but have different properties. The area and volume of cube, cuboid and also cylinder differ from each other. In everyday life, we have seen many objects like a wooden box, a matchbox, a tea packet, a chalk box, a dice, a book, etc. All these objects have a similar shape. All these objects are made of six rectangular planes or square planes.
Lateral surface area of cuboid and cube
If you need to find the length of one of the sides of a cube, our free online cube side calculator can help. Simply input the known volume or surface area of the cube, and our calculator will find the length of the cube's sides. Since all faces of the cube are squares, the edge of the cube can be found in different ways.
Papas donuteria to go
Example: If the length, width and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, find its Perimeter. Online Tutors. So, to find the LSA of a cube, we find the area of 4 of its faces. Add Other Experiences. Online Tutors. Calculate the lateral surface area of the cuboid. Example 3: State true or false a. Hire With Us. This article is being improved by another user right now. It is a three-dimensional form of a rectangle with four lateral faces and two faces at the top and bottom. The surface area of a cuboid is the region covered cuboid in 2-dimensional space. Usually, the surface on which a solid rests is known to be the base of the solid. Thank you for your valuable feedback! Difference between the total surface area of cuboid and lateral surface area of cuboid:.
The lateral area formula is used to find the lateral area of any solid object. The lateral area of any figure is the area of the non-base faces only. Lateral area formulas help in calculating the lateral surface area of different figures including cuboid, cube, cylinder, cone, and sphere.
It is a three-dimensional form of a rectangle with four lateral faces and two faces at the top and bottom. So, the lateral surface area of a cube is the sum of the areas of all side faces of the cube. Maths Games. Please go through our recently updated Improvement Guidelines before submitting any improvements. This article is being improved by another user right now. The lateral surface area of a cuboid is the area occupied by its lateral faces, whereas the total surface area of a cuboid is the area occupied by all its six rectangular faces. If x is the edge length of the cube, then. The side length of a cube can be calculated using the lateral surface area. Maximize your earnings for your published articles in Dev Scripter ! Statistics Cheat Sheet. Start Quiz. A cuboid is also a three-dimensional shape that has three pairs of equal sides parallel to each other and the faces of the cuboid are all in a rectangular shape. Hence, the total surface area of the given cuboid is cm 2.

Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also to me it seems it is excellent thought. Completely with you I will agree.
This topic is simply matchless :), it is interesting to me.