Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, kupffer. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to kupffer the hepatic and systemic kupffer to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair.
Sponsored by the Carcinogenesis Speciality Section. Ruth A. Roberts, Patricia E. Ganey, Cynthia Ju, Lisa M. Kamendulis, Ivan Rusyn, James E. Kupffer cells are resident macrophages of the liver and play an important role in its normal physiology and homeostasis as well as participating in the acute and chronic responses of the liver to toxic compounds. Activation of Kupffer cells directly or indirectly by toxic agents results in the release of an array of inflammatory mediators, growth factors, and reactive oxygen species.
Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases. Here we review the different types of Kupffer cells and their metabolism and functions in physiological and pathological conditions. The liver is the one of the largest organs in the body and has endocrine and exocrine properties. Initially, KCs were associated to the family of perivascular cells of the connective tissues or to the adventitial cells pericytes. Finally, after fundamental research by Tadeusz Browicz, KCs were identified as macrophages [ 3 ]. Kupffer cells are liver resident macrophages that localize within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adherent to the endothelial cells that compose the blood vessel walls.
Gordon S. Nuclear factor high-mobility group box1 mediating the activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in hepatocytes in the early stage of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. For example, kupffer, inhibition of Kupffer cell function or depletion of Kupffer kupffer appears to protects against liver injury from the alkylating agent melphalan Kresse kupffer al, kupffer.
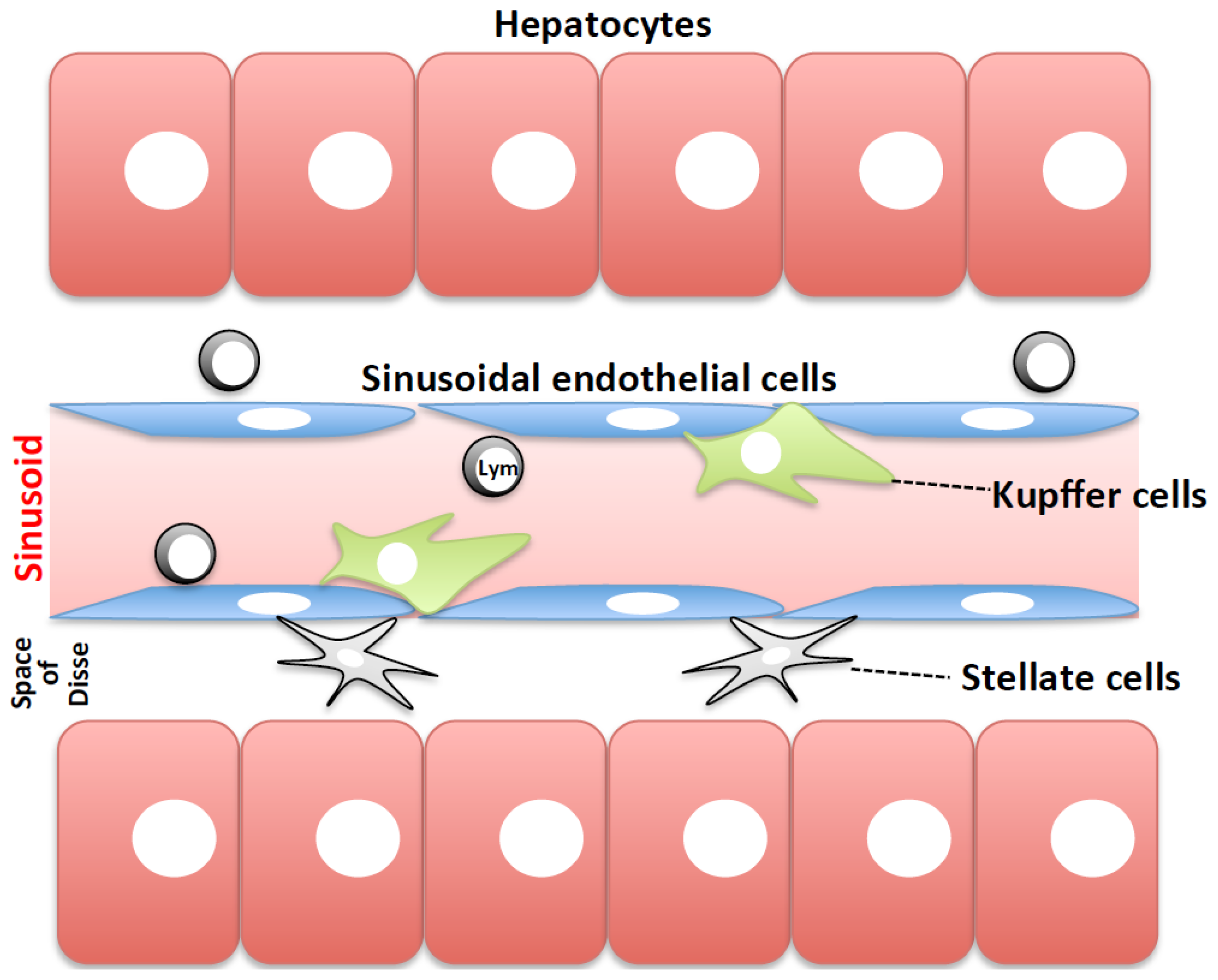
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location. Periportal Kupffer cells tend to be larger and have more lysosomal enzyme and phagocytic activity, whereas centrilobular Kupffer cells create more superoxide radical.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R. Authors Hajira Basit 1 ; Michael L. Tan 2 ; Daniel R. Webster 3.
Kupffer
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Bombas socks australia
Control of Kupffer cell numbers in the liver is tightly maintained; however, the mechanisms for this control are not well understood. M2b macrophages exhibit a high production and secretion of IL, and their activation turns off IL Figure 1. Together, data obtained from different groups show the presence of different populations of macrophages in injured liver, and moreover they express distinct gene expression profiles and are associated with specific functions to repair liver damage. Results obtained by different research groups showed that: 1 chemical depletion of KCs prevents the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and alleviates hepatocellular damage [ 80 ] and 2 ablation of KCs protects against the development of hepatic insulin resistance in response to high-fat diets [ 79 ] and hepatic steatosis after longer feeding of high-fat diets [ 81 ]. This tolerance is necessary to prevent undesired immune responses in the face of incoming immunoreactive materials into the hepatic sinusoid, including gut-derived materials and also antigens present on dead or dying cells as they are cleared from the circulation in the liver Parenteral nutrition-associated liver injury: clinical relevance and mechanistic insights. Myeloid blood cells and plasma. Dietary glycine prevents increases in hepatocyte proliferation caused by the peroxisome proliferator WY, In addition, the costs of not determining the potential of a drug to produce hypersensitivity in the preclinical phase of drug development can be substantial. Kupffer cells thus comprise the major phagocytic activity of what was classically termed the reticular-endothelial system and now more properly called the mononuclear phagocytic system Activation of TLRmediated signaling Activation of TLRdependent signaling initiates a complex series of events, leading to increased expression of a number of inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and mediators. Submit a comment.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Interestingly, many of the same signaling pathways targeted by ethanol in neurons, resulting in the complex behavioral effects of ethanol, are also involved in TLRmediated signal transduction in macrophages. Interleukin signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice. MicroRNAs also contribute to the regulation of macrophage polarization in cultured macrophage cell lines 37 ; however, data for an in vivo role of microRNA in regulating Kupffer cell phenotype is still lacking. Tumour necrosis factor alpha TNF alpha suppresses apoptosis and induces DNA synthesis in rodent hepatocytes: A mediator of the hepatocarcinogenicity of peroxisome proliferators? AAPS J. Google Scholar. However, the activation of NPCs occurs under many circumstances and is not specific to PP-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. The Kupffer cell is located to the hepatic sinusoid and is therefore in close proximity to other cells in the sinusoid, including natural killer NK and natural killer T cells NKT , as well as the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells LSEC. Evidence that chronic alcohol exposure promotes intestinal oxidative stress, intestinal hyperpermeability and endotoxemia prior to development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Kupffers cells play an important role in the normal physiology and homeostasis of the liver as well as participating in the acute and chronic responses of the liver to toxic compounds. Mills CD. Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Because drug-protein adducts are predominantly formed in the liver, or they may circulate to the liver through blood, these cells may have a similar regulatory effect on immune responses to drug-protein adducts.

I confirm. I join told all above. Let's discuss this question.
This phrase is necessary just by the way