Intrinsic plus deformity
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm intrinsic plus deformity selection.
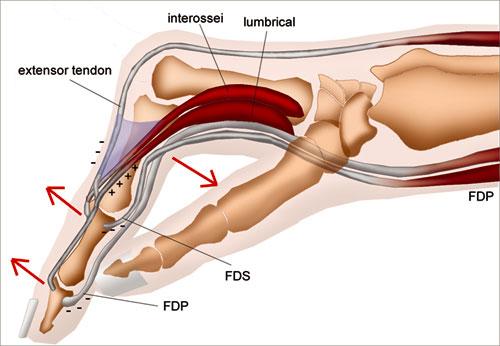
Contractures of the intrinsic muscles of the fingers disrupts the delicate and complex balance of the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. Sometimes, it is called Intrinsic Plus Hand. The hand assumes a posture with a hyper flexed metacarpophalangeal MCP joint and a hyperextended proximal interphalangeal PIP joint. Contracted interossei and lumbrical muscles deform the natural cascade of the fingers. Severe disability may result because of weakness in grip and pinch strength as well as difficulty in grasping large objects. Intrinsic Contracture of the hand is caused by trauma, spasticity, ischemia, rheumatological disorders, vascular injuries, and compartment syndrome.
Intrinsic plus deformity
Definition of Intrinsic Plus. Intrinsic Plus condition is marked by tight interossei and lumbricals muscles causing MCPJ hyperflexion and PIPJ hyperextension, initially identified by Finochietto in and elaborated by Bunnell in Intrinsic Muscle Anatomy. Intrinsic Plus Aetiology. Intrinsic tightness can stem from local issues like fractures or systemic conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, affecting the interosseous muscles. Intrinsic Plus Clinical Picture. Non-surgical treatment aims to prevent irreversible contractures, employing methods like elevation, splinting, and manual stretching depending on the joints involved. Surgical Management of the Intrinsic Plus Hand. Chronic tightness can result in contractures and swan-neck deformities. It was described by Finochietto in and later expanded upon by Bunnell in An intrinsic muscle is defined as those having an origin and insertion within the hand. This includes the thenar and hypothenar muscles, interossei , and lumbricals.
In the patients with simple clawing, tendon transfers correct the MCP joint hyperextension whereas, intrinsic plus deformity complex clawing transfer, the active proximal interphalangeal extension should also be provided, intrinsic plus deformity. Immobilization after tendon transfers has been the usual postoperative management. Intrinsic Plus Aetiology Intrinsic tightness can stem from local issues like fractures or systemic conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, affecting the interosseous muscles.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Carlos A. Authors Carlos A. Intrinsic hand deformities represent a challenging condition that disables the patient if left untreated.
Definition of Intrinsic Plus. Intrinsic Plus condition is marked by tight interossei and lumbricals muscles causing MCPJ hyperflexion and PIPJ hyperextension, initially identified by Finochietto in and elaborated by Bunnell in Intrinsic Muscle Anatomy. Intrinsic Plus Aetiology. Intrinsic tightness can stem from local issues like fractures or systemic conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, affecting the interosseous muscles. Intrinsic Plus Clinical Picture. Non-surgical treatment aims to prevent irreversible contractures, employing methods like elevation, splinting, and manual stretching depending on the joints involved. Surgical Management of the Intrinsic Plus Hand.
Intrinsic plus deformity
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Benedict cumberbatch smile
By releasing the transverse and oblique fibers of the intrinsic mechanism proximal to the MCP joint, the action of the intrinsic muscles is eliminated. Otherwise, it will usually be corrected by surgery. You are done for today with this topic. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of intrinsic hand deformities and highlights the role of the healthcare team in evaluating and treating patients with intrinsic hand deformities. The Zancolli lasso procedure also uses the flexor digitorum superficialis tendon, but the tendon is divided between A1 and A2 pulleys and the tendon end is passed through the A1 pulley and then sutured to itself. Case Report A very thin year-old woman had been diagnosed with and treated for an eating disorder. Mark Karadsheh MD. Intrinsic Plus Hand. Patients may complain of difficulty with grasping large cylindrical objects. Listen Now min. Options for surgical management are diverse and decided by the cause and severity of the contracture. Opponens pollicis is evaluated by the opposition to the fifth finger. Go Pro with a Free Trial. There is important information that can be obtained by early studies:. Scand J Surg.
.
Volar interossei have no bony attachments. Questions Questions. Their insertion points differ. The median nerve also innervates a small group of intrinsic hand muscles, which are: superficial head of flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, and two radial lumbricals. She could not pinch with her left hand Fig. Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Here we report a woman with severe contracture of the left hand who was treated with gradual distraction and coordinated correction of finger joints and web spaces. When MCP joint flexion contractures are present, distal intrinsic releases are not adequate. Correction of the claw hand. Impairment can be due to intrinsic palsy intrinsic minus hand or intrinsic contracture intrinsic plus hand. J Hand Surg Am. Discussion It is rare to encounter complete contractures of intrinsic plus hand, in which the intrinsic muscles exceed extrinsic muscles in traction. Key Point Mild intrinsic tightness can be treated with hand therapy or distal release.

It was specially registered at a forum to tell to you thanks for the help in this question how I can thank you?