Hypoglycemia ncp
Take hypoglycemia ncp of this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to effectively provide care for clients with unstable blood glucose levels, whether they are experiencing hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Watch More! Unlock the full videos with a FREE trial. Access More! View the full outline and transcript with a FREE trial. When you start a FREE trial you gain access to the full outline as well as:.
Hypoglycemia ncp
Assess for signs of 1. Long-term Goal: BT: Monitor serum glucose as side effect. Assess the patient 3. Normal fasting blood to unstable glucose and DKA. Discuss the 4. Blood glucose should be needs. Hyperinsulinemia occurs minimize or prevent with food intake. Instruct the patient type 2 diabetes. Dependent: 7. An individualized patient 1. Administer plan is recommended. Treat 8. Food intake is appropriate 3. Administer in most cases of hypertensive hypoglycemia to raise drugs as blood glucose levels.
Tube feeding formulas high in simple carbohydrates can lead to increased glucose levels in patients with diabetes. For the client who cannot take something orally, hypoglycemia ncp, an intravenous injection of glucose may be indicated.
Hypoglycemia is a condition wherein blood glucose is below the average level. It is also a prevalent, potentially preventable side effect of diabetes medication overdose, and it is a significant barrier to commencing or increasing antihyperglycemic therapy to obtain optimal glucose control. Thus, the most crucial determinant of future incidents is the treatment regimen and a history of hypoglycemia. Numerous risk factors also cause hypoglycemia, including renal failure , old age, and medical history of hypoglycemia-related autonomic dysfunction. In addition, the reported prevalence of hypoglycemia varies significantly between studies based on research design, interpretations used, and the population included.
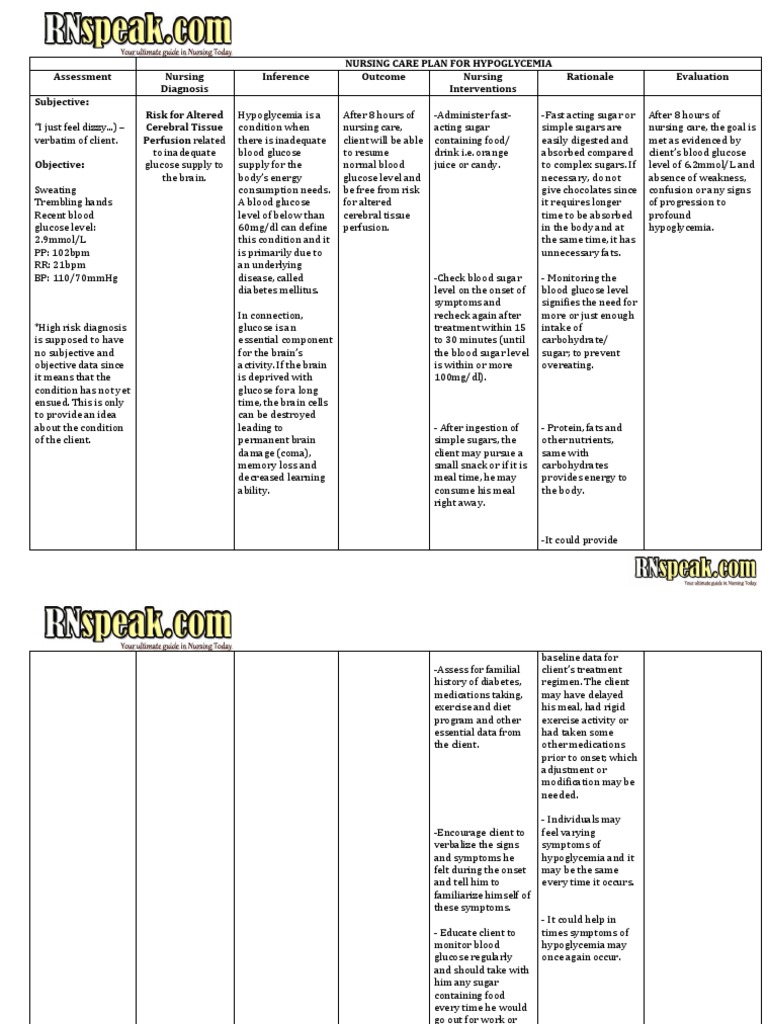
In this post, we will formulate a scenario-based sample nursing care plan for hypoglycemia for an elderly patient with type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood glucose level is lower than its normal level. A low blood glucose level can be life-threatening if not treated quickly. A year old male presents to the ED with nausea, fatigue, tremors, and palpitations. Last night the patient administered his nightly 15 units of long-acting insulin for a blood sugar of He then skipped dinner and went to bed.
Hypoglycemia ncp
Glucose is a very important nutrient in the human body. It serves as the source of energy for cells to function. There are different mechanisms to regulate glucose level, including the hormone insulin which is produced by the pancreas. Any level below or beyond this range can put a patient at risk for unstable blood glucose level. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia both refer to abnormal blood glucose levels. Both of these conditions may arise from different etiologies, with diabetes mellitus being the most common cause. Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for unstable blood glucose level related to non-adherence to the therapeutic regimen for diabetes. Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate adherence to the diabetes regimen as evidenced by a reduction to less than 3 episodes hypoglycemic episodes a week. Gestational Diabetes.
Sushi hub eastwood photos
We want to initiate hypoglycemia protocol. Proper meter cleaning and maintenance are crucial for the longevity and accuracy of blood glucose monitors. Diabetes: Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Treatment: The most important information you need to improve your health. Educate the patient on proper self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG techniques. Insulin resistance may occur in some patients with diabetes, requiring higher insulin doses for adequate glycemic control. Aerobic exercise, resistance training, and a combination of the two are effective in reducing HbA1C by about 6. Individuals with evidence of sensory loss, prior ulceration, or amputation should have their feet inspected at every visit to monitor for any changes or potential problems. Close suggestions Search Search. Assess deep tendon reflexes. Administer prescribed analgesic agents, such as non opioid medications, as part of a comprehensive pain management plan to alleviate neuropathic pain in the lower extremities. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to assess glycemic control and guide insulin administration. Emphasize the role of CGMS in providing comprehensive hour blood glucose monitoring.
Watch More!
Mental Health Care Plans. Causes and Risk Factors: Explore the various causes and risk factors contributing to hypoglycemia, including medication side effects, insulin administration, dietary factors, and physical activity. Others require specific instructions on managing their blood glucose levels during and after exercise. CGMS is a valuable tool for monitoring blood glucose levels continuously. As such, patients should be educated on the importance of routine blood glucose monitoring as well as on the identification of the individual's symptoms of hypoglycemia. Continuous parenteral nutrition can contribute to changes in blood glucose levels. Understanding the significance of ketonuria can motivate the patient to adhere to regular monitoring, contributing to better management of their diabetes. Educating patients about the purpose, function, and proper use of CGMS empowers them to actively participate in their diabetes management and make informed decisions based on the collected data. Provides basic information that may be used as a rationale for treatments and care and allows for different teaching strategies. The ADA recommends that regular insulin be drawn up first. Teach patients how to read nutrition labels and understand carbohydrate content. In a study of maternal hypoglycemia, it was found that hypoglycemia occurred more frequently in women younger than 25 years and those who had preexisting medical conditions. Etiology of Hypoglycemia Excessive Insulin Administration: Overdose or miscalculation of insulin doses, especially in individuals with diabetes, can lead to a rapid decrease in blood glucose levels. Includes step-by-step instructions showing how to implement care and evaluate outcomes, and help you build skills in diagnostic reasoning and critical thinking. In real-life clinical settings, it is important to note that the use of specific nursing diagnostic labels may not be as prominent or commonly utilized as other components of the care plan.

I think, that anything serious.