Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
A patient prescribed spironolactone is demonstrating ECG changes and complaining of muscle weakness. The nurse realizes this patient is exhibiting signs of which electrolyte imbalance? Hypocalcemia refers to low levels of calcium in the blood, which can present with symptoms like muscle cramps, numbness, and tingling. However, this choice is not relevant to the patient's symptoms in the scenario, hyperkalemia ecg changes ati.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Leslie V. Simon ; Muhammad F.
Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
Use this EKG interpretation cheat sheet that summarizes all heart arrhythmias in an easy-to-understand fashion. An EKG uses electrodes attached to the skin to detect electric currents moving through the heart. These signals are transmitted to produce a record of cardiac activity. Arrhythmia or dysrhythmia are disturbances in the normal cardiac rhythm of the heart which occur as a result of alterations within the conduction of electrical impulses. These impulses stimulate and coordinate atrial and ventricular myocardial contractions that provide cardiac output. Ever wonder how nurses and doctors can read ECG papers with ease? How do they differentiate atrial tachycardia from atrial fibrillation, or how even to know what atrial fibrillation or tachycardia is? Sinus tachycardia is a heart rate greater than beats per minute originating from the sinus node. Causes of sinus tachycardia may include exercise, anxiety , fever , drugs, anemia , heart failure , hypovolemia , and shock. Sinus tachycardia is often asymptomatic. Management, however is directed at the treatment of the primary cause. Carotid sinus pressure carotid massage or a beta-blocker may be used to reduce heart rate. It has the following characteristics.
Valve surgery Digoxin toxicity. Gastrointestinal cation exchangers such as patiromer may be helpful, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency who cannot receive immediate dialysis. Irregular PR interval.
The normal cardiac action potential may be altered by electrolyte imbalance , owing to changes in intra- and extracellular electrolyte concentrations. Some electrolyte imbalances are clinically negligible from an electrophysiological standpoint , whereas others may be life-threatening. The most common and clinically most relevant electrolyte imbalances concern potassium, calcium and magnesium. Note that some patients may exhibit combined electrolyte imbalance. The ECG may be used to estimate the severity of electrolyte imbalances and to judge whether there is a risk of serious arrhythmias. This is possible because there is a correlation between the severity of electrolyte imbalance and the visible ECG changes.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Nowadays, electrocardiogram ECG changes are one of the valuable diagnostic clues for recognizing abnormalities. Potassium is one of the essential electrolytes in cardiac cells, and its variations affect ECG. Potassium disorders, including hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in authoritarian states, may lead to heart dysfunctions and could be life-threatening, and urgent interventions are needed in this conditions.
Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
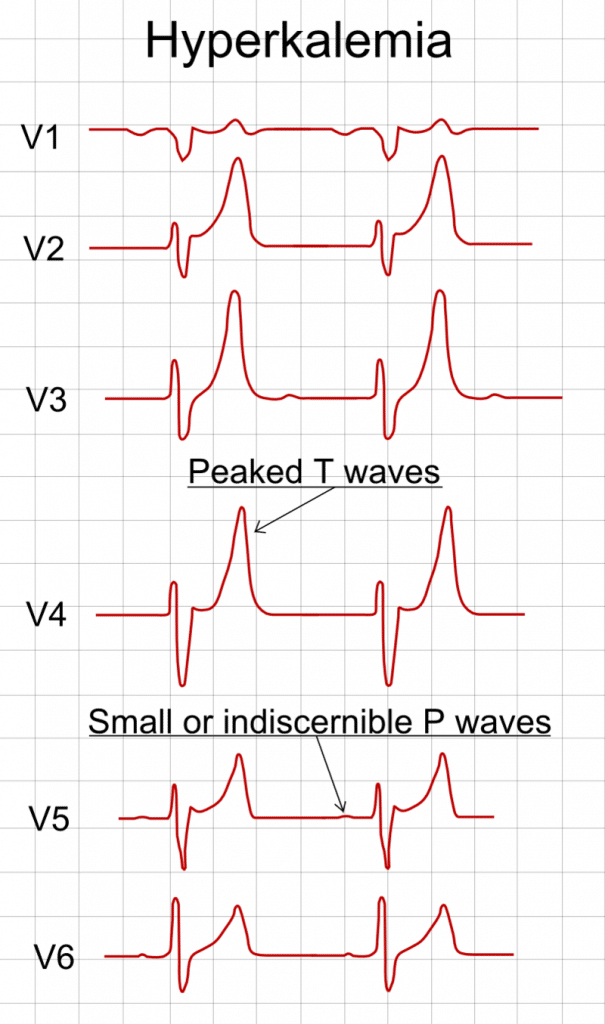
The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in T wave amplitude. Note: Serum potassium level may not correlate closely with ECG changes. Patients with a relatively normal ECG can suffer sudden hyperkalaemia cardiac arrest. In any patient who has suffered a bradycardia PEA arrest, suspect and treat for hyperkalaemia. Potassium is vital for regulating the normal electrical activity of the heart. Increased extracellular potassium reduces myocardial excitability, with depression of both pacemaking and conducting tissues. Progressively worsening hyperkalaemia leads to suppression of impulse generation by the SA node and reduced conduction by the AV node and His-Purkinje system, resulting in bradycardia and conduction blocks and ultimately cardiac arrest. Suspect hyperkalaemia in any patient with a new bradyarrhythmia or AV block, especially patients with renal failure, on haemodialysis, or taking any combination of ACE inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics and potassium supplements. For an excellent review of the management of hyperkalaemia, check out this podcast by Scott Weingart.
Lisandro martínez
Recent Activity. If patient is stable, drug therapy may include calcium channel blockers, beta-adrenergic blocks, or antiarrhythmics. Comment on this article. Patients may complain of weakness, fatigue, palpitations, or syncope. Management, however is directed at the treatment of the primary cause. Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing. Two cases of hyperkalemia. Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, and its use can lead to increased potassium levels in the blood hyperkalemia , which can affect the heart's electrical activity and cause muscle weakness. They seem too small to be printed and legible. Severe coronary artery disease , anterior wall MI, acute myocarditis. The three types are first degree, second degree and third degree. Management includes atropine, epinephrine, and dopamine for bradycardia.
Federal government websites often end in.
Manifestations include hypotension , angina , and heart failure. Could you please try it again? Atrial and ventricular rhythms are irregular. Management includes atropine, epinephrine, and dopamine for bradycardia. I would really appreciate your help on this. Using tourniquets and excessive fist pumping during blood draw also increases the risk. If patient is stable, drug therapy may include calcium channel blocker, beta-adrenergic blockers, or antiarhythmics. AV blocks are conduction defects within the AV junction that impairs conduction of atrial impulses to ventricular pathways. The management of hyperkalemia is multidisciplinary because of its potential to induce cardiac arrest and severe weakness. Heart failure, tricuspid or mitral valve disease, pulmonary embolism, cor pulmonale, inferior wall MI, carditis. While generally safe to consume even in large quantities by patients with normal potassium homeostasis, these foods should be avoided in patients with severe renal disease or other underlying conditions or medications predisposing them to hyperkalemia.

You are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.