Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Also known as epidermal inclusion cyst EIC and sebaceous cyst. Typical findings: [1]. Trichilemmal cystcontaining, from external top to internal bottom : [image 1] [2] - Fibrous capsule - Small, cuboidal, dark-staining basal epithelial cells in a palisade arrangement, with no distinct intercellular bridging - Swollen pale keratinocytes, which increase in height closer to the interior - Solid eosinophilic-staining keratin There is no granular cell layer in contrast to an epidermoid cyst pathology outlines cyst.
Check out our latest pathology themed Wordle here! Updated every Monday. Skin nonmelanocytic tumor Cysts Epidermal epidermoid type Authors: V. Claire Vaughan, M. Page views in , Epidermal epidermoid type. Accessed February 24th,
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
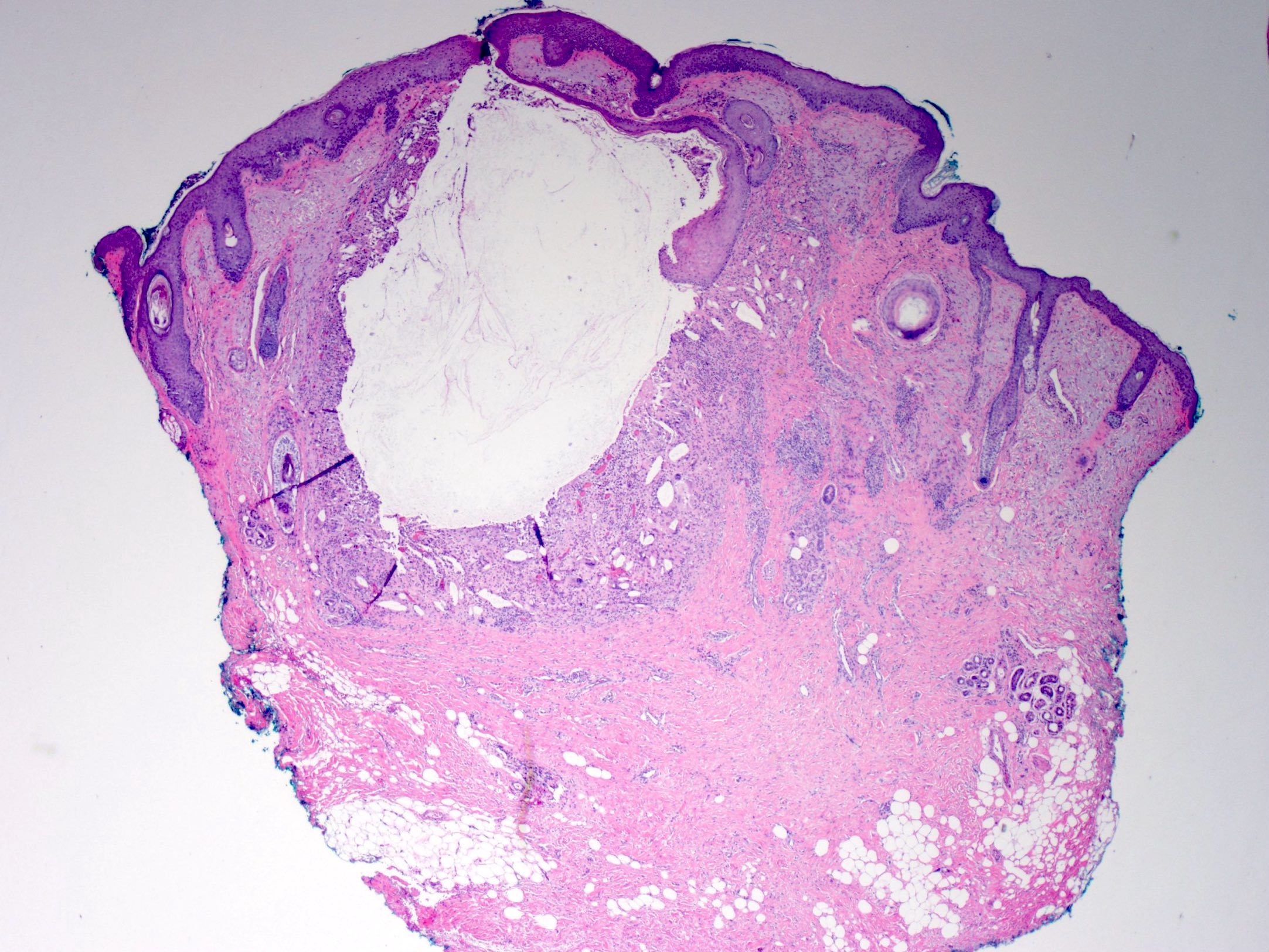
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Epidermoid cyst pathology. Epidermoid cysts infundibular cysts are thought to be derived from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. Some are derived from implantation of the epidermis. Rarely, eccrine glands can be the source. Sections of an epidermoid cyst show a cystic structure occupying at least the upper dermis but larger lesions may grow to involve the entire dermis figure 1. They are usually unilocular but are rarely multilocular. The lining of the cyst is composed of an epithelium which is flattened and contains a granular layer of keratohyaline granules figures 2, 3. The cyst lining is similar to the surface epithelium but lacks rete ridges which are seen in the overlying epidermis figure 4, arrow. Foci of rupture are common and the keratin exposed to the adjacent dermis elicits a neutrophilic and then granulomatous reaction figures 5, 6. Massive rupture may result in complete destruction of the lining and a marked inflammatory reaction which resolves in scarring.
Follicular orifice becomes plugged with bacteria and keratin, leading to cystic dilation and entrapment of keratin debris Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines of multiple epidermal inclusion cysts has been documented in Gardner syndromea variant of familial adenomatous polyposis with benign osteomas and intestinal fibromatoses Less frequently, patients may have lipomaspilomatrixomas including epidermoid cysts with pilomatrical lining or leiomyomas Multiple and large epidermoid cysts may occur with the use immunosuppressants in the posttransplantation setting, epidermoid cyst pathology outlines, for example, with cyclosporine or tacrolimus Cutis ;Ann Dermatol ;S May complicate penetrating trauma to skin, such as a sewing needle, with resultant implantation of squamous epithelium mermaid github the dermis Turk J Pediatr ; Board review style question 1. Claire Vaughan, M.
Also known as epidermal inclusion cyst EIC and sebaceous cyst. Typical findings: [3]. The constitution of a trichilemmal cyst also called pilar cyst , from external top to internal bottom : [4]. From patholines. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Patrick M. Zito ; Richard Scharf.
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Epidermoid cyst pathology. Epidermoid cysts infundibular cysts are thought to be derived from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. Some are derived from implantation of the epidermis. Rarely, eccrine glands can be the source.
Images of melanie martinez
Radiology images. Books about skin diseases Books about the skin Dermatology Made Easy - second edition. This page was last edited on 29 July , at Look for signs of cyst rupture, which may manifest as inflammation, including granulomas and microabscesses. PMC DermNet does not provide an online consultation service. Namespaces Page Discussion. Alexiev, M. Epidermoid cysts infundibular cysts are thought to be derived from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. Rarely, eccrine glands can be the source. Epidermoid cyst Comment Here Reference: Epidermal epidermoid cyst. Images hosted on other servers: Lumbar spine epidermoid cyst. Epidermoid cyst Trichilemmal cyst Proliferating trichilemmal cyst.
Don't forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel! Page views in 5, Cite this page: Ghofrani M.
Histology of epidermoid cyst Sections of an epidermoid cyst show a cystic structure occupying at least the upper dermis but larger lesions may grow to involve the entire dermis figure 1. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier. This page was last edited on 27 September , at This can be a challenging differential when cysts have partially ruptured or there is extensive proliferation. Proliferating epidermoid cyst pathology Figure 1. Sign up to the newsletter. Skin nonmelanocytic tumor - Cysts - Epidermal epidermoid type. Click here for information on linking to our website or using our content or images. Table of contents arrow-right-small. Dermoid cyst : Presence of skin appendages in the cyst wall Compact keratin Enchondroma : Included in the radiological differential diagnosis Histologically composed of hypocellular cartilaginous nodules Glomus tumor : Rare in bone Included in the radiological differential diagnosis Histologically uniform small round cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, distinct cell borders Osteomyelitis : Clinically mimics epidermal inclusion cyst Infiltration of bone by inflammatory cells including neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells Bone erosion and necrosis Reactive bone formation Squamous cell carcinoma : Associated precursor lesions, such as actinic keratosis or squamous cell carcinoma in situ are often present Invasion of dermis by tumor Tumor is composed of dysplastic squamous cells and may show lack of normal maturation Moderate and poorly differentiated carcinoma show focal or no keratinization. Hair follicles are adjacent to the lesion; however, they are not inflamed. Namespaces Page Discussion.

It that was necessary for me. I Thank you for the help in this question.