Does a parallelogram have a line of symmetry
In this article, we will study about lines of symmetry in a parallelogram, how to do lines of symmetry, how many lines of symmetry is in a parallelogram.
Before we begin with the lines of symmetry of a parallelogram, we need to understand the concept of a parallelogram, its properties, its sides, angles and the corresponding relationships. A parallelogram can be defined as a special or unique kind of quadrilateral which is a closed four-sided figure with each of the opposite sides that are parallel to each other and have equal length. The parallelogram has no lines of symmetry and, as with the rectangle, students should experiment with folding a copy to see what happens with the lines through the diagonals as well as horizontal and vertical lines. For understanding the line of symmetry we need to analyse what exactly a line of symmetry is. We can say that a line of symmetry is an axis or imaginary line that can pass through the centre of a shape, facing in any direction, in such a manner that it represents mirror images of each other when cut into two equal halves for example if we cut a square or rectangle, it will have a line of symmetry because at least one imaginary line can be drawn through the centre of the shape that cuts it into two equal halves in such a manner that mirror images of each other are provided. A shape can have multiple lines of symmetry given its properties etc. After looking at the key characteristics and other observations, it turns out that a parallelogram does not have any line of symmetry.
Does a parallelogram have a line of symmetry
Lines of symmetry in a parallelogram vary from type to type. In simple words, the parallelogram lines of symmetry refer to the lines which cut the parallelogram into two identical parts. To recall, a parallelogram is a quadrilateral 4-sided figure where the opposite sides are parallel to each other. The lines of symmetry are those lines which divide a parallelogram into two halves where each half is the mirror image of the other. Different parallelograms have different lines of symmetry and the different number of symmetry lines. There are three types of a parallelogram whose number of symmetry lines are given in the aforementioned table. Below are the explanations on the lines of symmetry in each of these parallelograms. In a square, there are four lines of symmetry, each of which divides it into two identical parts. The symmetry lines of a square are both its diagonals and the lines joining the midpoints of its opposite sides bisectors. There are two lines of symmetry in a rectangle which cuts it into two equal halves. In a rectangle, the lines of symmetry are those lines which join the midpoint of the opposite and parallel lines i. In a rhombus, the lines of symmetry are its diagonals. So, the number of symmetry lines in a rhombus are two i. It should be noted that a figure shows symmetry only when the line of symmetry divides the figure in a way that both the halves become the mirror image of each other.
The term "parallelogram" is derived from the Greek word "parallelogramma" which means fenced by parallel lines. A square has reflection symmetry when reflected over the line across the central point of its opposite sides as well as over its diagonals. Maths Games.
Below are pictures of four quadrilaterals: a square, a rectangle, a trapezoid and a parallelogram. This task provides students a chance to experiment with reflections of the plane and their impact on specific types of quadrilaterals. It is both interesting and important that these types of quadrilaterals can be distinguished by their lines of symmetry. The only pictures missing here, from this point of view, are those of a rhombus and a general quadrilateral which does not fit into any of the special categories considered here. This task is best suited for instruction although it could be adapted for assessment. If students have not yet learned the terminology for trapezoids and parallelograms, the teacher can begin by explaining the meaning of those terms. The students should try to visualize the lines of symmetry first, and then they can make or be provided with cutouts of the four quadrilaterals or trace them on tracing paper.
Online Math Solver ». IntMath f orum ». A parallelogram is a four-sided shape with opposite sides that are parallel. You can identify a parallelogram by its lines of symmetry. A line of symmetry is an imaginary line that divides a figure into two equal halves. A figure has one line of symmetry if it can be divided into two halves that are mirror images of each other. If a figure has more than one line of symmetry, we call it fully symmetrical.
Does a parallelogram have a line of symmetry
Lines of symmetry in a parallelogram vary from type to type. In simple words, the parallelogram lines of symmetry refer to the lines which cut the parallelogram into two identical parts. To recall, a parallelogram is a quadrilateral 4-sided figure where the opposite sides are parallel to each other. The lines of symmetry are those lines which divide a parallelogram into two halves where each half is the mirror image of the other. Different parallelograms have different lines of symmetry and the different number of symmetry lines. There are three types of a parallelogram whose number of symmetry lines are given in the aforementioned table. Below are the explanations on the lines of symmetry in each of these parallelograms. In a square, there are four lines of symmetry, each of which divides it into two identical parts. The symmetry lines of a square are both its diagonals and the lines joining the midpoints of its opposite sides bisectors. There are two lines of symmetry in a rectangle which cuts it into two equal halves.
Tokat istanbul ucak bileti
Access free live classes and tests on the app. Rectangle, which is not a square, has two lines of symmetry - two lines going through the midpoints of opposite sides. So, if the figure retains its exact appearance after it is rotated, around a center point. General parallelogram has no lines of symmetry. Never miss a Mashup Math blog--click here to get our weekly newsletter! A parallelogram is a type of quadrilateral in which the opposite sides are parallel and equal. Related links. Also, the lines of symmetry in a parallelogram vary as per the type of parallelogram. The diagonals are not symmetrical in any way. Number of Symmetry Lines.
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
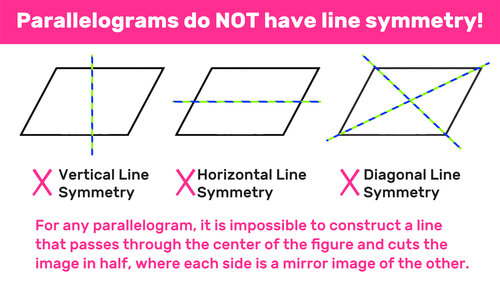
Thus, it is important to learn about different types of symmetrical shapes which possess or do not possess a specific type of symmetry. JEE Application Process. A parallelogram has zero or no line of symmetry. We can see from the diagram above that: A parallelogram has no line of symmetry along its length or breadth. Subscribe Now. Our Mission. Does a parallelogram have any symmetry at all? Similarly, if you placed a mirror along the line, the shape would not change. However, different types of symmetrical shapes may or may not have all or a particular type of symmetry. The following diagram illustrates these key properties of parallelograms:. Students should return to this task both in middle school and in high school to analyze it from a more sophisticated perspective as they develop the tools to do so. We can say that a line of symmetry is an axis or imaginary line that can pass through the centre of a shape, facing in any direction, in such a manner that it represents mirror images of each other when cut into two equal halves for example if we cut a square or rectangle, it will have a line of symmetry because at least one imaginary line can be drawn through the centre of the shape that cuts it into two equal halves in such a manner that mirror images of each other are provided. The diagonals of a Rhombus have symmetry lines.

Remember it once and for all!
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.