Aminoacyl-trna
Thank you for visiting nature.
Past events. These enzymes are not gentle with tRNA molecules. The enzyme shown in red firmly grips the anticodon loop shown in yellow , spreading the three bases widely apart for better recognition. At the other end, the enzyme unpairs one base at the beginning of the chain, seen curving upward here, and kinks the long acceptor end of the chain into a tight hairpin, seen here curving downward. This places the 2' hydroxyl on the last nucleotide in the active site, where ATP colored white and the amino acid not present in this structure are bound.
Aminoacyl-trna
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Synthetases help to ensure accurate translation of the genetic code by using both highly accurate cognate substrate recognition and stringent proofreading of noncognate products. While alterations in the quality control mechanisms of synthetases are generally detrimental to cellular viability, recent studies suggest that in some instances such changes facilitate adaption to stress conditions. Beyond their central role in translation, synthetases are also emerging as key players in an increasing number of other cellular processes, with far-reaching consequences in health and disease. The biochemical versatility of the synthetases has also proven pivotal in efforts to expand the genetic code, further emphasizing the wide-ranging roles of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family in synthetic and natural biology. The product of this reaction, an aminoacyl-tRNA aa-tRNA , is delivered by elongation factors to the ribosome to take part in protein synthesis. The discovery of the aaRSs and their role in protein synthesis began in the 50s and 60s when it was reported that amino acids were required to undergo an activation process in order to take part in protein synthesis Hoagland ; Zamecnik et al. The discovery of tRNA Hoagland et al. AaRSs fulfill two extremely important roles in translation: not only do they provide the building blocks for protein synthesis, they are also the only enzymes capable of implementing the genetic code Woese et al. A total of 23 aaRSs have been described so far, one for each of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids except for lysine, for which there are two plus pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase PylRS and phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase SepRS , enzymes with a more restricted distribution that are only found in some bacterial and archaeal genomes Cusack et al. It is also worth noting that in eukaryotes the protein synthesis machineries of mitochondria and chloroplasts generally utilize their own, bacterial-like sets of synthetases and tRNAs that are distinct from their cytosolic counterparts Tzagoloff et al.
A common novel function within human aaRSs is providing additional regulation of biological processes. Springer, Dordrecht. Most cells make twenty different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, aminoacyl-trna for each type of amino acid, aminoacyl-trna.
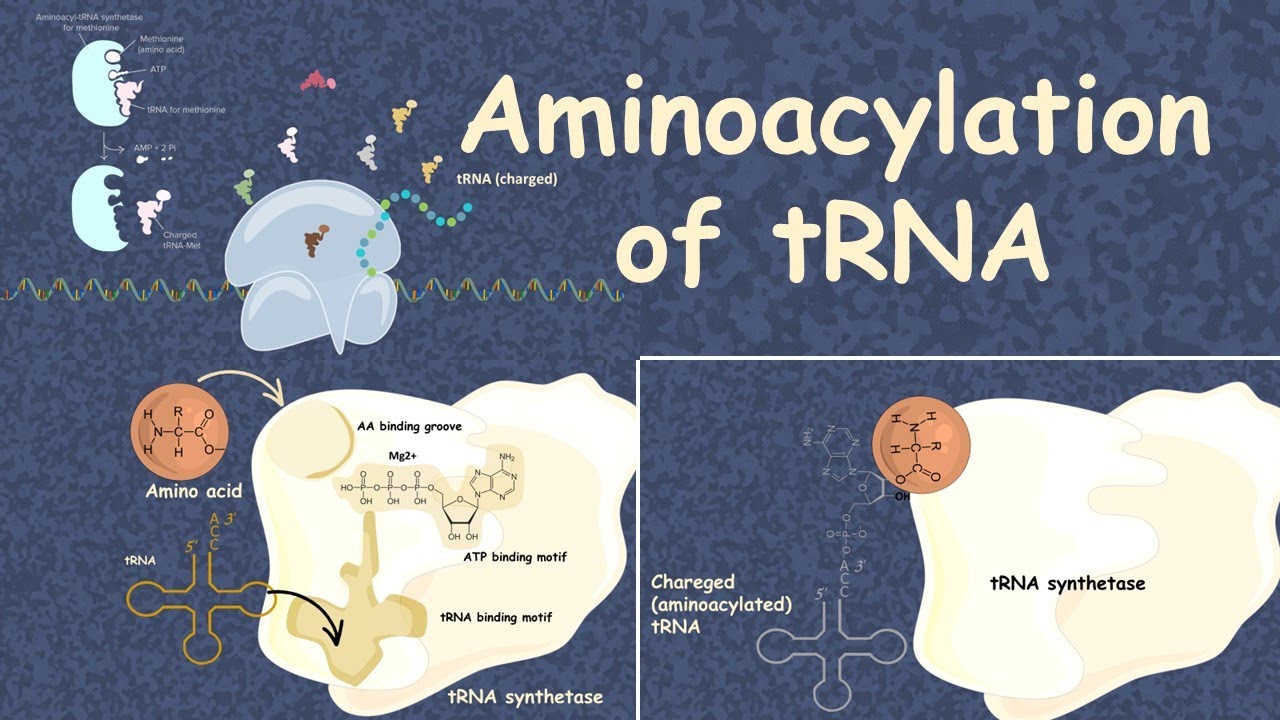
It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide , according to the genetic code. The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid or its precursor to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate PPi. Summing the reactions, the highly exergonic overall reaction is as follows:. Some synthetases also mediate an editing reaction to ensure high fidelity of tRNA charging.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases ARSs are essential enzymes for protein synthesis with evolutionarily conserved enzymatic mechanisms. Despite their similarity across organisms, scientists have been able to generate effective anti-infective agents based on the structural differences in the catalytic clefts of ARSs from pathogens and humans. However, recent genomic, proteomic and functionomic advances have unveiled unexpected disease-associated mutations and altered expression, secretion and interactions in human ARSs, revealing hidden biological functions beyond their catalytic roles in protein synthesis. These studies have also brought to light their potential as a rich and unexplored source for new therapeutic targets and agents through multiple avenues, including direct targeting of the catalytic sites, controlling disease-associated protein—protein interactions and developing novel biologics from the secreted ARS proteins or their parts. This Review addresses the emerging biology and therapeutic applications of human ARSs in diseases including autoimmune and rare diseases, and cancer. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution.
Aminoacyl-trna
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. This typical function has been well recognized over the past few decades. However, accumulating evidence reveals that ARSs are involved in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes apart from translation.
Patrick kearney riverdale
Read Edit View history. The modular structure of Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase as both an enzyme and a regulator of gene expression. Ultrastructure of the eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex derived from two dimensional averaging and classification of negatively stained electron microscopic images. The latter activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Drosophila macrophages and acted as a chemoattractant to recruit macrophages to loser cells, thereby eliminating these apoptotic cells from healthy tissues. Jones, C. This relatively low accuracy during protein synthesis at the ribosome is the result of two different events: mismatching of the mRNA:tRNA duplex and mischarging of the tRNA with a near- or noncognate amino acid. Chen, J. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Functional association between three archaeal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79 : — Site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids into Escherichia coli recombinant protein: methodology development and recent achievement. It is understood that aa-tRNAs may function as donors of amino acids necessary for the modification of lipids and the biosynthesis of antibiotics. Diversity-oriented synthesis yields novel multistage antimalarial inhibitors. Noh, K. As genetic efficiency evolved in higher organisms, 13 new domains with no obvious association with the catalytic activity of aaRSs genes have been added.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code.
Participation of aaRSs in transcription or translation process is often achieved via hairpins and loops in the nucleic acid sequence that folds into cloverleaf-like structures that mimics those of the tRNA substrate. B Cysteine. An editing mechanism for the methionyl-tRNA synthetase in the selection of amino acids in protein synthesis. More importantly, ARSs act as regulators and signaling molecules in various immune diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and tumor immunity. Mutational isolation of a sieve for editing in a transfer RNA synthetase. Keller, T. Numerous genetic mutations are associated with CMT and, interestingly, these mutations are found in several aaRSs for reviews, see Boczonadi et al. Can the safety and drug resistance of potential anti-infective compounds that target pathogen ARSs be resolved? J Mol Biol : 83— Read Edit View history. Another contribution to the accuracy of these synthetases is the ratio of concentrations of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and its cognate tRNA. By analyzing the crystal structures of both human and bacterial ThrRS-borrelidin complexes, the researchers found that a single borrelidin not only occupied three substrate-binding sites for threonine, ATP and tRNA in the ThrRS catalytic domain, but also extended into a fourth orthogonal pocket. Adaptive translation as a mechanism of stress response and adaptation. Functional class I and II amino acid-activating enzymes can be coded by opposite strands of the same gene.

0 thoughts on “Aminoacyl-trna”