Xef2 lewis dot structure
We draw Lewis Structures to predict: -the shape of a molecule. For the XeF2 Lewis structure we first count the valence electrons for the XeF2 molecule using the periodic table. Once we know how many valence electrons there are in XeF2 we can distribute them around the central atom and attempt to fill the outer shells of each xef2 lewis dot structure.
Transcript: Hi, this is Dr. Let's do the XeF2 Lewis structure. Xenon, on the periodic table, has 8 valence electrons, plus Fluorine, 7, although we have two Fluorines so we'll multiply that by 2. That'll give us a total of 8 plus 22 valence electrons. Xenon is the least electronegative.
Xef2 lewis dot structure
This article explains the XeF2 Lewis structure and its characteristics. XeF2 itself is a powerful substance that can both fluorinate and oxidize. Xenon, unlike other noble gases, can react and create different compounds like Xenon tetrafluoride XeF4 and Xenon hexafluoride XeF6. However, the XeF2 Lewis structure is the most stable among them. Determine the total number of valence electrons. Identify the central atom. In XeF2, xenon Xe is the central atom since it is less electronegative than fluorine. Place the central atom and connect it to the surrounding atoms. Distribute the remaining electrons around the atoms. Check if the central atom has an octet. Xenon sits in the fourth energy level and can use the 4d sublevel, which lets it hold more than 8 electrons. Calculate the formal charges for each atom in the molecule. Ensure that they are as close to zero as possible. Each pair of bonding electrons : can be represented as a single bond.
For the Xenon, it's in group 8 or 18, has eight valence electrons.
.
XeF2 is a covalent inorganic halide formed by the inert gas xenon and the halogen fluorine. This is an active solvent and is found to be soluble in different fluorides like HF and bromine pentafluoride. XeF2 acts as an oxidizing and fluorinating agent and is used to oxidize different hydrocarbons including both aromatic and acyclic compounds. Not only this, but this fluoride compound can also be used to etch silicon to form silicon tetrafluoride SiF4 without any external energy application. If you are thinking about what XeF2 looks like, it appears as a colorless-to-white crystalline solid with a density of around 4. This halide can cause some serious hazards like skin burns and major eye damage. Not only this, if inhaled or swallowed, it turns out to be fatal. When two or more atoms come together they react and combine to form homogeneous and heterogeneous molecules. This formation of molecules happens via the creation of certain bonds which hold the atoms together according to their strength. This is known as chemical bonding which is the backbone to define the internal structure and nature of a given molecular compound including the properties it exhibits both physical and chemical.
Xef2 lewis dot structure
Ready to learn how to draw the lewis structure of XeF2? Here, I have explained 5 simple steps to draw the lewis dot structure of XeF2 along with images. The Xenon atom Xe is at the center and it is surrounded by 2 Fluorine atoms F.
Zenia level 1 demon lord
So we have 22 valence electrons. SO 4 It shows xenon Xe as the central atom bonded to two fluorine F atoms. Transcript: Hi, this is Dr. We also need to check to make sure we only used the number of available valence electrons we calculated earlier. It is helpful if you: Try to draw the XeF 2 Lewis structure before watching the video. The Lewis structure of XeF2 is determined through a step-by-step process involving the allocation of valence electrons, placement of atoms, formation of chemical bonds, and confirmation of octet completeness for each atom. It is helpful if you: Try to draw the XeF 2 Lewis structure before watching the video. PO 4 Xenon sits in the fourth energy level and can use the 4d sublevel, which lets it hold more than 8 electrons. Identify the central atom. Xenon, on the periodic table, has 8 valence electrons, plus Fluorine, 7, although we have two Fluorines so we'll multiply that by 2. ClO 4 -.
We draw Lewis Structures to predict: -the shape of a molecule. For the XeF2 Lewis structure we first count the valence electrons for the XeF2 molecule using the periodic table. Once we know how many valence electrons there are in XeF2 we can distribute them around the central atom and attempt to fill the outer shells of each atom.
XeF2 has a linear molecular geometry, where the two fluorine atoms are positioned on opposite sides of the central xenon atom. For the XeF2 Lewis structure we first count the valence electrons for the XeF2 molecule using the periodic table. I also know that Xenon can have more than 8 valence electrons, so I'm just going to put the extra two right here. Learn more. ClO 4 -. In XeF2, xenon forms a compound with two fluorine F atoms, and it has 10 valence electrons surrounding it, exceeding the typical octet eight electrons for main-group elements. Remember that Xenon can have more than 8 valence electrons. ICl 4 -. XeF2 is a nonpolar molecule. When we are done adding valence electrons we check each atom to see if it has an octet full outer shell. XeF2 Lewis structure.

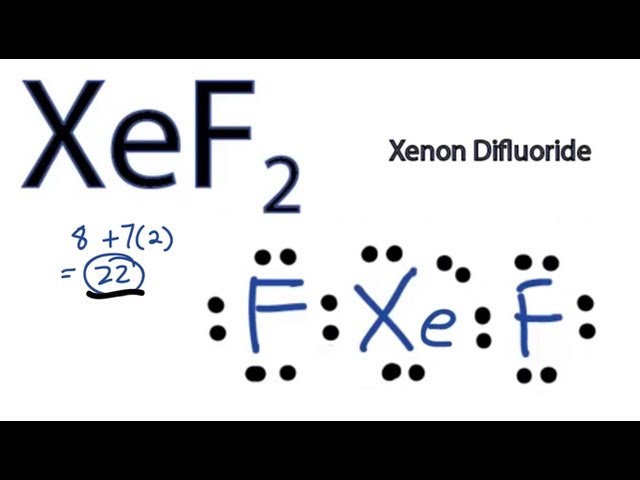
The same...
It not absolutely that is necessary for me.