Which of the following describes a lysosome
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Submitted by Michael K. Solved by verified expert. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. Which of the following cell organelles function in supporting cellular structures and in generating movements of organelles, chromosomes, and secretory vesicles?
Which of the following describes a lysosome
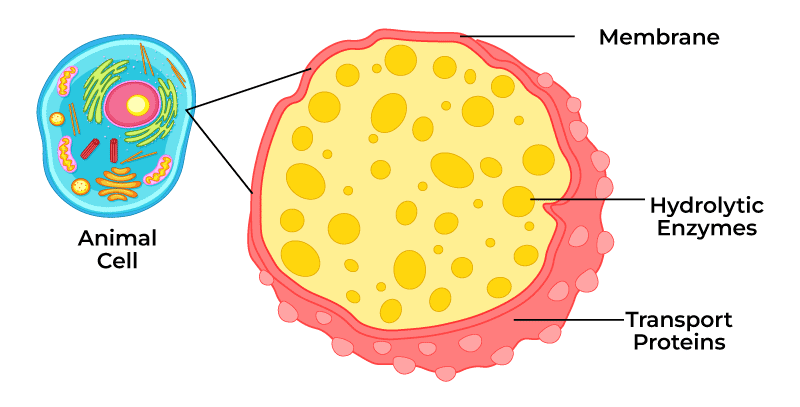
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. They may be used to destroy invading viruses and bacteria. If the cell is damaged beyond repair, lysosomes can help it to self-destruct in a process called programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Now, the lysosome is a specific type of organelle that's very acidic. So that means that it has to be protected from the rest of the inside of the cell. It's a compartment, then, that has a membrane around it that stores the digestive enzymes that require this acid, low-pH environment. Those enzymes are called hydrolytic enzymes, and they break down large molecules into small molecules. For example, large proteins into amino acids, or large carbohydrates into simple sugars, or large lipids into single fatty acids. And when they do that, they provide for the rest of the cell the nutrients that it needs to So, for example, if you can't do that, it can't break down large molecules into small molecules. You'll have storage of those large molecules, and this is a disease.
Follow NCBI. Feng D.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Lysosomes are the main proteolytic compartments of mammalian cells comprising of a battery of hydrolases. Lysosomes dispose and recycle extracellular or intracellular macromolecules by fusing with endosomes or autophagosomes through specific waste clearance processes such as chaperone-mediated autophagy or microautophagy. The proteolytic end product is transported out of lysosomes via transporters or vesicular membrane trafficking.
Lysosomes are small cell organelles in nucleus-bearing or eukaryotic cells. They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. They have a simple structure made up of an outer lysosomal membrane surrounding an acidic interior fluid. The main function of lysosomes is to help with cell metabolism by ingesting and dissolving unwanted parts of the cell, cell debris or foreign substances that have entered the cell. The digestive enzymes of their acidic interior break down large structures and molecules into simple components, and they then return the products to the cell for further use or disposal.
Which of the following describes a lysosome
Lysosomes were organelles, first discovered by a scientist named Christian de Duve in the year Its structure was first studied by a scientist named Novikoff in the year by performing electron microscopy. These are found abundantly in the cells or tissues that actively participate in the enzymatic digestion like liver, kidney, pancreas, macrophages etc. An animal cell contains many lysosomes, whereas a plant cell contains a single large lysosome or vacuole.
Fear the walking dead season 5 download free
Packets within the cell cytoplasm that contain powerful enzymes D. In contrast, haploinsufficient Beclin-1 heterozygous-null mice do not display atherosclerotic phenotype, suggesting that the basal level of autophagy is crucial for atheroprotection [ ]. Scotto Rosato A. Using a staining method for acid phosphatase, de Duve and Novikoff confirmed the location of the hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes using light and electron microscopic studies. However, it is still not clear whether rhLAL therapy is suitable to treat patients with atherosclerosis unrelated to LAL deficiency. Altered lysosomal acidification [ , ], misfolded protein aggregate formation [ ] and cellular nutrient status [ ] perturb lysosome positioning and motility. These diseases result in an accumulation of specific substrates , due to the inability to break them down. Autophagy: A lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Sign Up for Free. A single-membrane vesicle with powerful digestive enzymes E. A cation counterflux supports lysosomal acidification. Cheng X. Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase.
Some references are strict in their definition of an organelle. An organelle is a structure surrounded by two lipid bilayers. In this regard, nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast plastid are regarded as organelles because their membrane consists of two lipid bilayers whereas ribosomes and nucleosomes are not.
Lysosome Biogenesis Lysosomes are 0. Why is ATP known as energy currency of cell? McEwan D. Describe the functions of lysosomes. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in cell processes of secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis , cell signaling , and energy metabolism. Lysosome diagram showcasing enzyme complexes within the single-walled membrane. Cuajungco M. Qureshi O. Why are Lysosomes known as Suicidal Bags? Churchill G. Animal cell diagram. Reduction of atherosclerotic plaques by lysosomal acid lipase supplementation. Importantly, fibroblasts, isolated from skin biopsies of CMT4J patients and CMT4J mice, display enlarged vacuoles that stain positive for LAMP-2 with concomitant impairments in the late endosome-lysosome pathway [ , ]. Johnson D.

The authoritative answer
You commit an error. Let's discuss it.