What is pulmonary surfactant
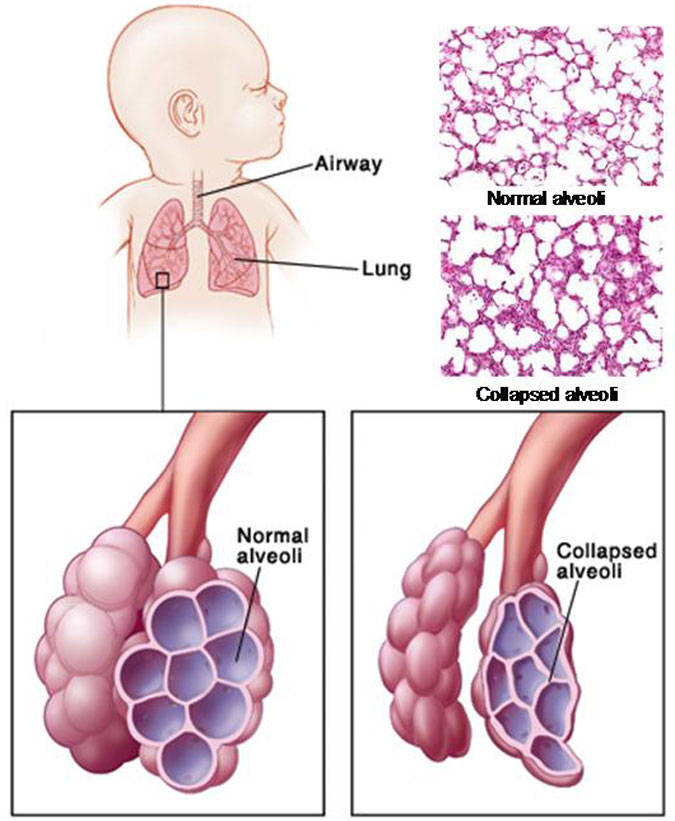
Pulmonary surfactant is a complex and highly surface active material composed of lipids and proteins which is found in the fluid lining the alveolar surface of the lungs. Surfactant prevents alveolar collapse at low lung volume, and preserves bronchiolar patency during normal and forced respiration biophysical functions. In addition, it is involved in the protection of the lungs from injuries and infections what is pulmonary surfactant by inhaled particles and micro-organisms immunological, non-biophysical functions.
Surfactant is an agent that decreases the surface tension between two media. The surface tension between gaseous-aqueous interphase in the lungs is decreased by the presence of a thin layer of fluid known as pulmonary surfactant. It is essential for efficient exchange of gases and for maintaining the structural integrity of alveoli. Surfactant is a secretory product, composed of lipids and proteins. The lipid and protein components are synthesized separately and are packaged into the lamellar bodies in the AT-II cells.
What is pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. By adsorbing to the air-water interface of alveoli , with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine DPPC , reduces surface tension. As a medication, pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines , the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Alveoli can be compared to gas in water, as the alveoli are wet and surround a central air space. The surface tension acts at the air-water interface and tends to make the bubble smaller by decreasing the surface area of the interface. Compliance is the ability of lungs and thorax to expand. Lung compliance is defined as the volume change per unit of pressure change across the lung. This difference in inflation and deflation volumes at a given pressure is called hysteresis and is due to the air-water surface tension that occurs at the beginning of inflation. However, surfactant decreases the alveolar surface tension , as seen in cases of premature infants with infant respiratory distress syndrome. Pulmonary surfactant thus greatly reduces surface tension , increasing compliance allowing the lung to inflate much more easily, thereby reducing the work of breathing. It reduces the pressure difference needed to allow the lung to inflate. The lung's compliance, and ventilation decrease when lung tissue becomes diseased and fibrotic. As the alveoli increase in size, the surfactant becomes more spread out over the surface of the liquid. This increases surface tension effectively slowing the rate of expansion of the alveoli.
Changes in the surfactant mixture composition alter the pressure and temperature conditions for phase changes and the phospholipids' crystal shape as well. As a medication, pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicinesthe most important medications needed in a what is pulmonary surfactant health system. However the significance of his discovery was not understood by the scientific and medical community at that time.
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hina Khawar ; Komal Marwaha. Authors Hina Khawar ; Komal Marwaha 1.
What is pulmonary surfactant
Lung surfactant is a complex with a unique phospholipid and protein composition. Its specific function is to reduce surface tension at the pulmonary air-liquid interface. The underlying Young-Laplace equation, applying to the surface of any geometrical structure, is the more important the smaller its radii are. It therefore applies to the alveoli and bronchioli of mature lungs, as well as to the tubules and saccules of immature lungs. Maturation of the surfactant system is not essentially due to increased synthesis but to decreased turnover of specific components. As there is no need for a surface-associated surfactant reservoir, SP-C is absent in birds as well. Airflow is lowest and particle sedimentation highest in the extrapulmonary air-sacs, rather than in the gas-exchange area. Consequently, SP-A and -D for particle opsonization are absent in bird surfactant. In essence, comparative analysis is consistent with the concept that surfactant is adapted to the physiologic needs of a given vertebrate species at a given developmental stage. Keywords: Airways surfactant; Bird surfactant; Mammalian surfactant; Phospholipid molecular species; Surfactant variability; Young—Laplace-equation.
Costco 14 pro max
Lung compliance is defined as the volume change per unit of pressure change across the lung. Nevertheless, without the other substances of the pulmonary surfactant mixture, the DPPC's adsorption kinetics is very slow. The surface tension acts at the air-water interface and tends to make the bubble smaller by decreasing the surface area of the interface. Toggle limited content width. The fast adsorption velocity is necessary to maintain the integrity of the gas exchange region of the lungs. Experimental Lung Research. Ex-situ measurements of surface tension and interfacial rheology can help to understand the functionality of pulmonary surfactants. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Contents move to sidebar hide. There are a number of types of pulmonary surfactants available. Tools Tools. Thus, the surfactant density at the air water interface remains high and is relatively preserved throughout expiration, decreasing the surface tension even further.
Pulmonary surfactant is a complex and highly surface active material composed of lipids and proteins which is found in the fluid lining the alveolar surface of the lungs. Surfactant prevents alveolar collapse at low lung volume, and preserves bronchiolar patency during normal and forced respiration biophysical functions. In addition, it is involved in the protection of the lungs from injuries and infections caused by inhaled particles and micro-organisms immunological, non-biophysical functions.
In late s von Neergaard [22] identified the function of the pulmonary surfactant in increasing the compliance of the lungs by reducing surface tension. Acta Biomaterialia. Compliance is the ability of lungs and thorax to expand. They undergo much post-translational modification, ending up in the lamellar bodies. This difference in inflation and deflation volumes at a given pressure is called hysteresis and is due to the air-water surface tension that occurs at the beginning of inflation. Pulmonary surfactant thus greatly reduces surface tension , increasing compliance allowing the lung to inflate much more easily, thereby reducing the work of breathing. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Therefore, during ventilation, surface tension is usually lower than at equilibrium. Pure and Applied Chemistry. Hidden categories: All articles lacking reliable references Articles lacking reliable references from May Wikipedia articles needing page number citations from May CS1 Vietnamese-language sources vi CS1 maint: location missing publisher CS1 German-language sources de Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from May Alveolar surfactant has a half-life of 5 to 10 hours once secreted. Read Edit View history. Nevertheless, without the other substances of the pulmonary surfactant mixture, the DPPC's adsorption kinetics is very slow. Annual Review of Physiology. Wikimedia Commons.

0 thoughts on “What is pulmonary surfactant”