What is kranz anatomy class 11
We saw a vast variety of plants around us and each plant species has its own adaptations to survive in their habitat. Can you tell me what are the physiological adaptations, which plants gained during evolution?
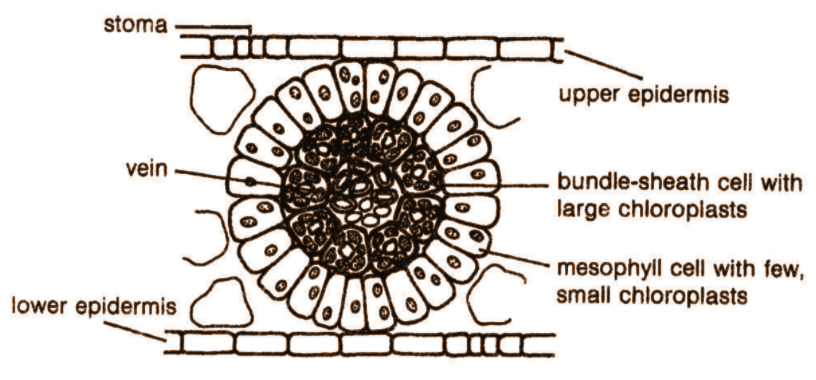
In this article, we have discussed the kranz anatomy. We have also discussed the examples and the diagram of Kranz anatomy. The mainly large cells surrounding the vascular bundles of the C4 plants are termed bundle sheath cells and the leaves which have such structure are said to have Kranz anatomy. Kranz means wreath and shows the preparation of cells. The bundle sheath cells may create several sheets around the vascular bundles that are categorized by numerous chloroplasts, impenetrable walls for gaseous exchange, and no intercellular spaces.
What is kranz anatomy class 11
Question 41 In what kind of plants do you come across 'Kranz anatomy'? To which conditions are those plants better adapted? How are these plants better adapted than the plants, which lack this anatomy? Use app Login. What is Kranz anatomy? Write a note on photosynthesis of those plants in which this anatomy is found. Open in App. Verified by Toppr. C 4 plants have Kranz anatomy which is the special structure of leaves where the tissue equivalent to the spongy mesophyll cells is clustered in a ring around the leaf veins, outside the bundle-sheath cells. The bundle-sheath cells contain large chloroplasts whereas the spongy mesophyll cells have a few chloroplasts. C 4 carbon fixation or the Hatch-Slack pathway is a photosynthetic process in C 4 plants. It is the first step in extracting carbon from carbon dioxide to be able to use it in sugar and other biomolecules. It is one of three known processes for carbon fixation. C 4 refers to the four-carbon molecule that is the first product of this type of carbon fixation.
The chloroplasts are divided into two according to the presence and absence of grana in them.
Kranz anatomy is a specialized structure in C 4 Plants where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle-sheath cells in a ring-like fashion. The number of chloroplasts in the bundle-sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cells. This is found in C 4 grasses such as maize and a few dicots. The Kranz anatomy is developed in three different steps:. Also read: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. The light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle are separated in the C 4 plants.
Kranz Anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the C4 plants that are specialized in nature. This is where the spongy mesophyll cells are found bundled up. They are seen in a ring-like shape that surrounds the veins of a leaf. Kranz anatomy is a unique structure observed in C4 plants. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. This entire structure is densely packed and plays a major role in C4 photosynthesis. We have established with the help of the above definitions that Kranz Anatomy is a significant part of C4 plants. Thus, this has several advantages to the respective plants. Some of those advantages can be found below:. It helps in preventing photorespiration.
What is kranz anatomy class 11
Kranz anatomy is a unique feature of C 4 plants where the mesophyll cells form a circular pattern around the bundle-sheath cells. This structure is named after the German word 'Kranz' which translates to 'wreath' or 'ring'. It's commonly observed in C 4 grasses like maize and some dicotyledonous plants. The development of Kranz anatomy takes place in three main stages:. Further reading: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. In C 4 plants, the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle are spatially separated. The Calvin cycle takes place in the bundle-sheath cells while the light-dependent reactions occur in the mesophyll cells. Firstly, the atmospheric oxygen is converted into a 4-carbon compound, oxaloacetate, in the mesophyll cells, a process catalyzed by PEP carboxylase.
Enobaria
Neet Result Toppers list rank cut off. This ring of vascular tissue is called the Kranz Anatomy. In the majority of plants, carbon dioxide is fixed into a 3 carbon compound by the action of Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase Rubisco. Rice B. The examples of C4 plants are maize, sugarcane, pearl millet, Sorghum , crabgrass, Amaranthus , Euphorbia etc. Skip to main navigation. Banyan C. But one of their drawbacks is the loss of photorespiration which is a wasteful process. C4 practices the Hatch-Slack Pathway for the dark reaction of photosynthesis. The plants that practice fixation of the carbon dioxide by Rubisco are known as C3 plants. The product found in the C4 cycle is a compound composed of 4 carbon atoms— oxaloacetic acid. Verified by Toppr.
Kranz Anatomy is a distinctive arrangement found in C4 plants, characterized by mesophyll cells forming a ring around the bundle-sheath cells. Kranz Anatomy is found in angiosperms like sugarcane and grasses which undergo C4 photosynthesis.
The plants that practice fixation of the carbon dioxide by Rubisco are known as C3 plants. C 4 overcomes photorespiration where the enzyme RuBisCO wastefully fixes oxygen rather than carbon dioxide. Photorespiration is absent in C4 plants. As a result, the plant is able to produce more sugar and oxygen for utilisation by the plant. Based on Season: C3 plants are plants of the cold season, commonly found in cool and wet areas. It is specialised to perform light reactions. One is that these plants are able to produce more biomass than plants with alternative leaf structures. Login To View Results. During development, these variations have happened more than fifty times in an extensive range of blooming plants, representing that, even with being critical, it is a comparatively easy trail to progress. The main differences between the C3 and C4 plants are that the bundle sheath cells of C3 plants do not contain chloroplast whereas the bundle sheath cells of C4 plants do. The C4 biochemical pathway depends on a particular set of functional leaf characteristics known as Kranz anatomy. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. No starch grains present.

0 thoughts on “What is kranz anatomy class 11”