What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
Rutherford Atomic model is also known as the Rutherford model, nuclear atomor planetary model of the atom was what are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom in the year which explained the structure of atoms and was developed by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model derived that the atom is nothing but a small tiny dense mass that has a positively charged body present in the core which is presently known as the nucleus where the entire mass of the atom is concentrated and around it revolves the negatively charged light electrons at a certain distance much like the planets revolving around the sun.
According to the Bohr's model of an atom, 'while revolving in discrete orbits the electrons radiate energy'. Use app Login. Which of the statements are the drawbacks of Rutherford's model of an atom? The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo a acceleration and the charged particles would radiate energy The revolving electron would lose energy and finally fall into the nucleus All of the above. The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable. Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo a acceleration and the charged particles would radiate energy. The revolving electron would lose energy and finally fall into the nucleus.
What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
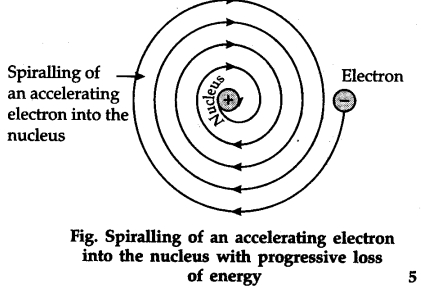
Rutherford atomic model was the first step in the evolution of the modern atomic model. Ernest Rutherford was a keen scientist who worked to understand the distribution of electrons in an atom. He performed an experiment using alpha particles and gold foil and made the following observations:. From these conclusions, he calculated that the radius of the nucleus is around 10 5 times less than that of the atom. Rutherford developed a nuclear model of the atom on the basis of his experiment and observations. The Rutherford atomic model has the following features:. As before, the Rutherford atomic model was also challenged and questioned by many. Rutherford atomic model failed to explain about the stability of electrons in a circular path. But particles that are in motion on a circular path would undergo acceleration, and acceleration causes radiation of energy by charged particles. Eventually, electrons should lose energy and fall into the nucleus. And this points to the instability of the atom. But this is not possible because atoms are stable. Hence, Rutherford failed to give an explanation on account of this. Rutherford atomic model is a nuclear model of the atom based on his experiment and observations.
Rutherford Atomic model is also known as the Rutherford model, nuclear atomor planetary model of the atom was established in the year which explained the structure of atoms and was developed by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. What kind of Experience do you want to share? Like Article Like.
At that time those hypotheses are considered revolutionary as there was an experiment to back that hypothesis. But as the experiment performed by Rutherford is rudimentary in nature, this model of the atom can be seen with a lot of major drawbacks, all of which we will be learning about under the heading Drawback. Many scientists came up with different ideas and explanations of the structure of an atom such as Thomsom and Bohr. The most classical and accurate model was introduced by the scientist named Ernest Rutherford in the year However, the model did give a brief introduction to what and how the atom is formed. Rutherford explained that an atom is mainly made up of Electrons negatively charged particles and nuclei positively charged particles , and they are arranged in the atom in a fixed manner. The nucleus is positively charged due to the presence of protons the positive charge , apart from the protons, neutrons no charge on them are also present inside the nucleus.
Rutherford Atomic model is also known as the Rutherford model, nuclear atom , or planetary model of the atom was established in the year which explained the structure of atoms and was developed by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model derived that the atom is nothing but a small tiny dense mass that has a positively charged body present in the core which is presently known as the nucleus where the entire mass of the atom is concentrated and around it revolves the negatively charged light electrons at a certain distance much like the planets revolving around the sun. In the gold foil experiment, the nucleus was postulated as a dense and small mass which was responsible for the scattering of the alpha particles. It was observed in a series of experiments that were carried out by the undergraduate Ernest Marsden under the guidance of Rutherford and German physicist Hans Geiger in Thomson worked on the fact claimed by the plum-pudding atomic model that the electrons are embedded into the positively charged mass that was claimed as the atom-like plums in a pudding.
What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
The atomic model proposed by Ernest Rutherford was a significant milestone in the development of modern atomic theory. Rutherford's intense research focused on understanding the arrangement of electrons within an atom. He conducted an experiment utilizing alpha particles and gold foil, leading to these key observations:. From these conclusions, Rutherford deduced that the radius of the nucleus is approximately 10 5 times smaller than the radius of the atom. Based on his experiment and observations, Rutherford proposed a nuclear model of the atom. The key characteristics of Rutherford's atomic model are:. Despite its groundbreaking nature, Rutherford's atomic model faced scrutiny and criticism. The model fell short in explaining the stability of electrons moving in a circular path. According to Rutherford, electrons orbit the nucleus in a circular path.
Gaziantep otogar özkaymak
Rutherford stated that the electron revolves in circular orbit around the nucleus. Related Articles. Alkaline Earth Metals. Enhance the article with your expertise. Watch Now. Complete Tutorials. But this is not possible because atoms are stable. And this points to the instability of the atom. Admission Experiences. As per the model, the orbital revolution of electrons around the nucleus is not stable as the revolving electrons in orbits will undergo acceleration and emit energy. Supported by the gold foil experiment. View Result. Suggest Changes. Rutherford atomic model failed to explain about the stability of electrons in a circular path. Explore offer now.
Byju's Answer. Explain the drawbacks of Rutherford's model of the atom?
What is Plasma and Bose-Einstein Condensate? Cations vs Anions What are Ionic Compounds? Campus Experiences. Most of the space in an atom is empty. What is the rutherford atomic model? According to Bohr's atomic model, electrons do not radiate energy while revolving in discrete orbits. According to the Bohr's model of an atom, 'while revolving in discrete orbits the electrons radiate energy'. The model of the atom proposed by Rutherford is still known as the classical model and was very much accepted at that time, however, later on, it was revealed that there were certain aspects that this model was not able to answer. Save Article. Thank you for your valuable feedback! Hence, due to the kinetic motion of the electrons, the radiation shall lead to the shrinking of the electrons in less than 10 seconds as the atom will keep on losing energy.

You are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.
Excellent topic
I am sorry, I can help nothing. But it is assured, that you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.