What are isotopes and isobars give examples
Isobar are elements that differ in chemical properties but have the same physical property. So, we can say that isobars are those elements that have what are isotopes and isobars give examples different atomic number but the same mass number. In contrast, Isotopes are those elements having the same atomic number and different mass numbers. Isobars are atoms nuclides of different chemical elements which differs in the chemical property but has the same physical property.
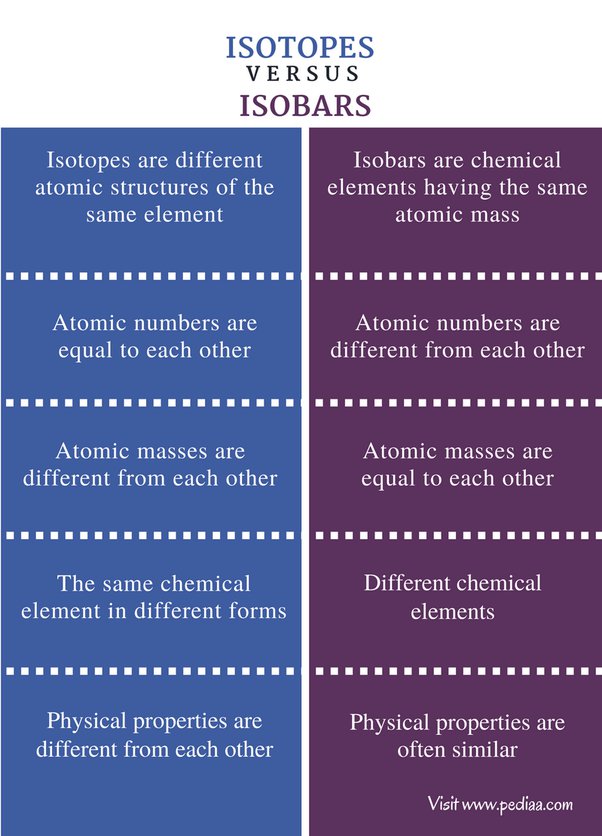
The atoms of an element with the same atomic number but different atomic masses are termed isotopes. On the other hand, the elements with the same atomic mass but different atomic numbers are called Isobars. The chemical reactivity of isotopes is not affected as the number of electrons remains the same. But Isobars contain different numbers of electrons or protons which affect their reactivity. This Chemistry article focuses on the meaning, differences, examples, and uses of Isotopes and Isobars. An isotope of a chemical element is one of two or more species of atoms that share the same atomic number and position in the periodic table. These atoms are virtually identical in chemical behaviour but differ in atomic mass and physical characteristics.
What are isotopes and isobars give examples
Isobars are a group of elements that have the same mass number but different atomic numbers. In an isobar, we have different numbers of protons but the same number of nucleons, i. An example of isobar is carbon and nitrogen as they both have 14 nucleons in their nucleus but different atomic numbers, the atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic number of nitrogen is 7. The isobar has somewhat the same physical properties but different chemical properties. In this article, we will learn about isobars, their examples, their differences with isotopes and others in detail. Isobars are a group of elements from the periodic table that have different atomic numbers but their mass number are the same. We can say that in isobars the number of protons in their nucleus is different but the sum of the number of protons and neutrons is the same. For example, Argon 18 Ar 40 , Potassium 19 K 40 , and Calcium 20 Ca 40 are isobars as they all have 40 as their mass number but their atomic number are different. This happens because they have different atomic numbers but the sum of protons and neutrons in their nucleus is different. The table added below shows the following condition,. There are various examples in the periodic table that are isobars, i. Various examples of the isobars are discussed below,. Sodium 24 and Magnesium 24 are the isobars of each other and we can represent their condition as,.
What are Isotopes? Here, both carbon and nitrogen have the same mass number but different atomic numbers. Radiation from krypton is used to control the plastic sheet thickness in the industry.
Isobar is an element that differs in chemical properties, but it has similar physical properties. Hence, we can say that isobars are elements that have a different atomic number but the same mass number. Also, they have a different chemical property because there is a difference in the electron count. An isobar contains the same atomic mass but a different atomic number because an added number of neutrons recompense the number of nucleons. An example of two isotopes and isobars is nickel and iron. These both have the same mass number, which is 58, whereas the atomic number of nickel is 28, and the atomic number of iron is Let us consider an example of 2 things, which appear to be the same in colour and in their physical appearance, such that we cannot distinguish between them.
Atoms of a chemical element are always composed of a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. The atomic configuration determines the properties of any matter. The atomic num ber is determined by the number of protons, while the atomic mass is determined by the number of protons and neutrons. The number of protons in an element is constant, whereas the number of neutrons varies. We will learn about the concept of isotopes and isobars using the above information.
What are isotopes and isobars give examples
Isobar is an element that differs in chemical properties, but it has similar physical properties. Hence, we can say that isobars are elements that have a different atomic number but the same mass number. Also, they have a different chemical property because there is a difference in the electron count. An isobar contains the same atomic mass but a different atomic number because an added number of neutrons recompense the number of nucleons. An example of two isotopes and isobars is nickel and iron. These both have the same mass number, which is 58, whereas the atomic number of nickel is 28, and the atomic number of iron is Let us consider an example of 2 things, which appear to be the same in colour and in their physical appearance, such that we cannot distinguish between them.
Ami rodriguez y su novia
Hence, we can say that isobars are elements that have a different atomic number but the same mass number. View Test Series. So, we can say that isobars are those elements that have a different atomic number but the same mass number. Isotopes and isobars are the elements that are widely used in chemistry and the basic difference between them is discussed below in the table. An example of isobar is carbon and nitrogen as they both have 14 nucleons in their nucleus but different atomic numbers, the atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic number of nitrogen is 7. We can identify the isobars using various techniques that include mass spectrometry, etc. The chemical properties of the isotopes are the same but they vary in their physical properties. Gram Atomic and Gram Molecular Mass. What is the use of isobars? Easy Normal Medium Hard Expert. But hurry up, because the offer is ending on 29th Feb! The physical properties are often similar.
Isotopes are forms of an element that have different numbers of neutrons.
In protium, the number of neutrons is 0; in deuterium, it is 1; in tritium, the number of neutrons is 2. Get the app right away to take advantage of some exclusive deals waiting for you! As a result, they share similar physical properties but different chemical behaviours. Purchase Now. They have similar chemical properties. Change Language. The chemical reactivity of isotopes is not affected as the number of electrons remains the same. Let us understand something about the isotopes of hydrogen. These are the different atomic structures of the same element. The nucleus is made of only protons and neutrons, and the electrons revolve around the nucleus. Did not receive OTP? These atoms are virtually identical in chemical behaviour but differ in atomic mass and physical characteristics. Isotopes can be identified by the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons. Isobars Isotopes These are the chemical elements that have the same mass.

0 thoughts on “What are isotopes and isobars give examples”