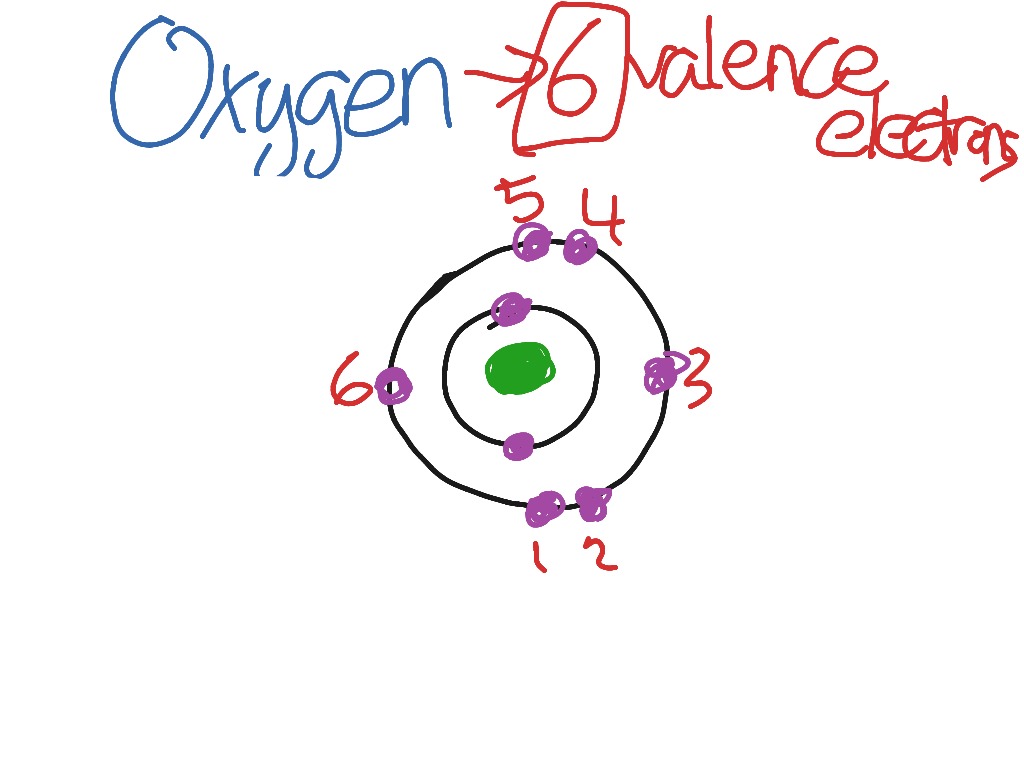
Valence electrons of oxygen
However, valence electrons feel an effective charge from the nucleus, or a charge brought about after the positive charge of the nucleus is subtracted by the number of core electrons.
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. A way to remember this is to note that it is in column 16 of the periodic table. For the representative elements columns 1, 2, , the digit in the units place of the column number is the same as the number of valence electrons. Elements in column 1 have one valence electrons, elements in column 13 have 3 valence electrons, etc. How many valence electrons does oxygen have? Chemistry Electron Configuration Valence Electrons.
Valence electrons of oxygen
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Atomic structure and electron configuration. About About this video Transcript. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2 s subshell and four in the 2 p subshell. Created by Sal Khan. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted. Posted 8 months ago. At
Specifically, atoms after helium have nuclei that exhibit an effective charge on electrons outside of the core.
If there are 8 protons in the oxygen nucleus, the atom must also contain 8 negative charges, i. Two of these electrons are inner core, and are not conceived to participate in bonding. The remaining 6 are valence electrons , which participate in bonding and influence structure. Generally, 2 of these electrons combine with the electrons of donor atoms cf hydrogens to form covalent bonds. The remaining 4 valence electrons reside in stereochemically active lone pairs, which influence structure. What is the number of valence electrons in oxygen?
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. A way to remember this is to note that it is in column 16 of the periodic table. For the representative elements columns 1, 2, , the digit in the units place of the column number is the same as the number of valence electrons. Elements in column 1 have one valence electrons, elements in column 13 have 3 valence electrons, etc. How many valence electrons does oxygen have? Chemistry Electron Configuration Valence Electrons. Apr 15, Related questions Why are valence electrons important?
Valence electrons of oxygen
The following procedure can be used to construct Lewis electron structures for more complex molecules and ions:. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. Arrange the atoms to show specific connections. Place a bonding pair of electrons between each pair of adjacent atoms to give a single bond.
Ff9 characters
Why is it that Oxygen has 6 Valence electrons and not 8? This column out here has three valence electrons, four valence electrons, five valence electrons, six valence electrons, and seven valence electrons. See all questions in Valence Electrons. In other words, it will react in such a way to gain a new electron and fulfill its valence shell. So how many valence electrons does calcium have? Image by John Wiley and Sons, Inc. How does any atom? Khan says a full oute Angelica Chen. What about the d, f etc orbitals for atoms with more shells? But, I wanted to leave you with a question.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. Aug 25, See all questions in Valence Electrons. Related questions Why are valence electrons important? This pattern begins to break down for elements in the third period like sulfur and chlorine who can still have an octet and achieve stability, but still have an unfilled d subshell. Sort by: Top Voted. How many valence electrons are in an atom of phosphorus? Therefore, the electrons closer to the nucleus feel more and more of its attractive force, while the ones farther away feel less; it's not a perfect cancellation. So being stable when talking about valence electrons means that the valence shell has been filled completely or half filled. Once you reach the fourth period and the transition metals they follow an 18 electron rule of stability, but it's the same idea as before in that they are attempting to fill their valence electron shells in order to become stable.

I can look for the reference to a site with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.
It agree, the useful message
Thanks for an explanation, I too consider, that the easier, the better �