Valence and arousal
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To valence and arousal the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The built environment represents the stage surrounding our everyday life activities.
Valence and arousal
The main prediction of the Uncanny Valley Hypothesis UVH is that observation of humanlike characters that are difficult to distinguish from the human counterpart will evoke a state of negative affect. LPP and EMG provided direct psychophysiological indices of affective state during passive observation and the SAM provided self-reported indices of affective state during explicit cognitive evaluation of static facial stimuli. The results provide no support for the notion that category ambiguity along the DHL is specifically associated with enhanced experience of negative affect. On the contrary, the LPP and SAM-based measures of arousal and valence indicated a general increase in negative affective state i. In conclusion, this multi-method approach using well-validated psychophysiological and self-rating indices of arousal and valence rejects — for passive observation and for explicit affective evaluation of static faces — the main prediction of the UVH. The longstanding Uncanny Valley Hypothesis UVH predicts that difficulty distinguishing a realistic humanlike character or object e. Mori suggests that this state is characterized by a sense of strangeness and personal disquiet and, when experienced more intensely, by revulsion and disgust. Attention to the originally untested UVH has been spurred by recent progress in robotics and computer graphics technologies in the realistic simulation of aspects of human appearance and behavior and, therefore, by interest in understanding the impact of enhanced anthropomorphic realism on affective experience e. But empirical support for the predicted uncanny effect has been inconsistent e. This has led to the query as to how research should now best proceed Zlotowski et al. To move beyond this seeming impasse, some of the reasons for inconsistency in findings and new avenues of approach can be considered. Illustration of the Uncanny Valley Hypothesis.
Indeed, previous research found that moving the user's view from one point to another can provide a compelling sense of self-motion 44valence and arousal, 45 Specific brain networks during explicit and implicit decoding of emotional prosody. Visual search for a socially defined feature: what causes the search asymmetry favoring cross-race faces?
Information about the affective meanings of words is used by researchers working on emotions and moods, word recognition and memory, and text-based sentiment analysis. Three components of emotions are traditionally distinguished: valence the pleasantness of a stimulus , arousal the intensity of emotion provoked by a stimulus , and dominance the degree of control exerted by a stimulus. We extended that database to nearly 14, English lemmas, providing researchers with a much richer source of information, including gender, age, and educational differences in emotion norms. As an example of the new possibilities, we included stimuli from nearly all of the category norms e. Hinojosa, N. Graham G. Scott, Anne Keitel, … Sara C.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The circumplex model of affect proposes that all affective states arise from cognitive interpretations of core neural sensations that are the product of two independent neurophysiological systems. This model stands in contrast to theories of basic emotions, which posit that a discrete and independent neural system subserves every emotion. We propose that basic emotion theories no longer explain adequately the vast number of empirical observations from studies in affective neuroscience, and we suggest that a conceptual shift is needed in the empirical approaches taken to the study of emotion and affective psychopathologies. The circumplex model of affect is more consistent with many recent findings from behavioral, cognitive neuroscience, neuroimaging, and developmental studies of affect. Moreover, the model offers new theoretical and empirical approaches to studying the development of affective disorders as well as the genetic and cognitive underpinnings of affective processing within the central nervous system. The reigning experimental paradigm in affective neuroscience research posits that emotions can be divided into discrete and independent categories and that specific neural structures and pathways subserve each of these emotional categories.
Valence and arousal
According to several researchers, core affect lies at the foundation of our affective lives and may be characterized as a consciously accessible state combining arousal activated-deactivated and valence pleasure-displeasure. The interaction between these two dimensions is still a matter of debate. All things being equal, the higher the arousal, the more a given stimulus would be experienced as pleasant or unpleasant. While marshaling some preliminary evidence in favor of this hypothesis, we also show how it might be relevant in reframing our conception of depressive disorders i.
Nat king cole youtube
Coburn, A. For example, startle reflex amplitudes are greatest for negatively valenced photos but decrease with positive emotional content in photos Anders et al. Normal walking speed: A descriptive meta-analysis. Soares, A. Blue and red lines represent cold and warm architectural designs, respectively. Room preference as a function of architectural features and user activities. Incidental effects of emotional valence in single word processing: An fMRI study. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Brain Res. Leather, P. Neurophysiological correlates of the recognition of facial expressions of emotion as revealed by magnetoencephalography. Post-hoc collection of behavioural data from an independent sample The most important result of our study, namely the interaction between valence and arousal dimensions in insular cortex, was supported by a similar interactive pattern in the accuracy rates, but not in the reaction times. Table 5 Correlations of present ratings with similar studies across languages Full size table.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
ACM Comput. Written word neighbourhood size N -size and frequency N -frequency values were taken from the ELP database Balota et al. References Adank P. Lewis and J. Berlin sample: emotionality As in the Sussex sample, RT results revealed a main effect of emotionality, this time consistent across participant and item analyses F 1 1. Normal walking speed: A descriptive meta-analysis. The use of a different task design that allows clear interpretation of RT data of the SAM-based measures of valence and arousal might be used to examine this. Energy Build. An ecological valence theory of human color preference. Relationships between the three dimensions and age of acquisition, word frequency, imageability, and sensory experience ratings, presented as scatterplot smoother lowess trend lines. Psychological Review , 69 , — Considered in terms of the UVH, the human endpoints in these studies are in effect exemplars of the non-human category. Kollias, D. Finally, the statistical difference in the observed frequency distribution was assessed by chi-squared tests. Cheetham, M.

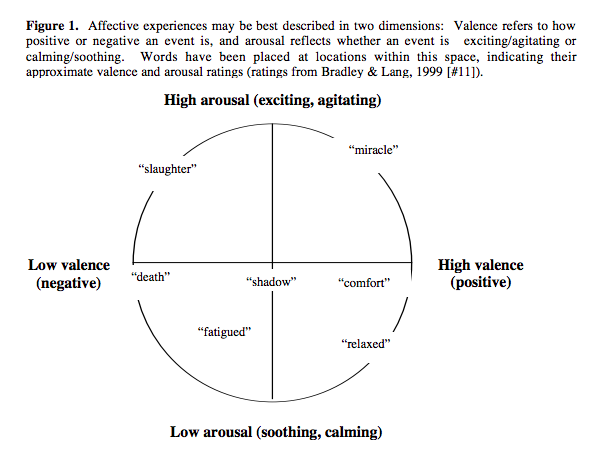
It � is impossible.