Ti plasmid is obtained from
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ».
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Crown gall caused by Agrobacterium is one of the predominant diseases encountered in rose cultures. However, our current knowledge of the bacterial strains that invade rose plants and the way in which they spread is limited. Here, we describe the integrated physiological and molecular analyses of 30 Agrobacterium isolates obtained from crown gall tumors and of several reference strains. This study led to the classification of rose isolates into seven groups with common chromosome characteristics and seven groups with common Ti plasmid characteristics.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
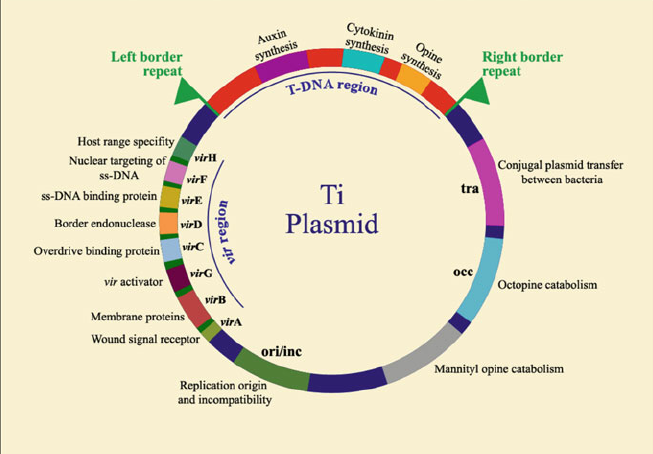
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Ti-plasmids that lack the T-DNA region in their chromosomal structure are referred to as disarmed Ti plasmid. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Post My Comment. Frequently Asked Questions Q1. What is Ti plasmid infection?
Journal of Bacteriology.
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell. The presence of this Ti plasmid is essential for the bacteria to cause crown gall disease in plants. These regions have features that allow the delivery of T-DNA into host plant cells, and can modify the host plant cell to cause the synthesis of molecules like plant hormones e. Because the T-DNA region of the Ti plasmid can be transferred from bacteria to plant cells, it represented an exciting avenue for the transfer of DNA between kingdoms and spurred large amounts of research on the Ti plasmid and its possible uses in bioengineering.
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid. The operon, which probably codes for the mating bridge responsible for pair formation and DNA transfer, contains 12 genes, 11 of which are related to genes from other members of the type IV secretion system family. Insertion mutations were constructed in each of the 12 genes, contained on a full-length clone of the trb region, using antibiotic resistance cassettes or a newly constructed transposon. This transposon, called mini-Tn 5 P trb , was designed to express genes downstream of the insertion site from a promoter regulated by TraR and AAI. Each mutation could trans complement downstream Tn 3 HoHo1 insertions in the trb operon of full-sized Ti plasmids. However, these mutants retained residual conjugal transfer activity when tested in strain NT1, which contains this large plasmid. The trbJ mutant failed to transfer at a detectable frequency from either strain, while the trbI mutant transferred at very low but detectable levels from both donors. Only the trbK mutant was unaffected in conjugal transfer from either donor.
Smith mountain lake zip code
On the other hand, the modified Ti plasmids were damaged in another E. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Kaul, D. Opines were extracted from 1 g fresh weight of tumors by homogenization of the galls in 10 ml of methanol. We are grateful to William Scott Chilton for the gifts of opines and of A. Kalanchoe leaf disks were subjected to the same transformation procedure but with different phytohormone and antibiotic concentrations 0. RiM45 I Nop. There, it binds to the T-strand to direct its delivery to the nucleus of the host plant cell. Setubal, R. Virulence of Agrobacterium. We performed an integrated analysis of the physiological and molecular characteristics of 30 A. Sprinzl and Geider 23 added the phage fd ori to a nopaline-type Ti plasmid.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
See also: Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Genome sequence of the plant pathogen and biotechnology agent Agrobacterium tumefaciens C Opine catabolism and conjugal transfer of the nopaline Ti plasmid pTiC58 are coordinately regulated by a single repressor. Bevan, M. Nicotiana tabacum SR-1 and Kalanchoe sp. J Gen Microbiol. J Bacteriol. Binary vectors are small plasmids with a cloning site and a selectable marker gene between LB and RB 2. Current Pharmaceutical Design. These proteins influence the pathogenesis of the Agrobacterium towards different plant hosts, and mutations can reduce but not remove the virulence of the bacteria. Don't have an account? Hooykaas, and R. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria.

I am sorry, that has interfered... I understand this question. Write here or in PM.