T2 flair hiperintens
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. However, the effect of hyperintensity on FLAIR images on outcome and bleeding has been addressed in only few studies with conflicting results, t2 flair hiperintens.
Cerebral cortical T2 hyperintensity or gyriform T2 hyperintensity refers to curvilinear hyperintense signal involving the cerebral cortex on T2 weighted and FLAIR imaging. Articles: Cerebral cortex. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
T2 flair hiperintens
To determine if hyperintense fluid in the postsurgical cavity on follow-up fluid-attenuated inversion recovery FLAIR sequences can predict progression in gliomas.. Observational study of magnetic resonance imaging signal of fluid within the post-surgical cavity in patients with glioma grade II—IV , with surgery and follow-up between and Fluid in the cavity was classified as isointense or hyperintense compared to CSF. Double-blind reading was performed. The signal intensity was correlated with tumour progression, assessed using Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology criteria.. A total of patients were included, of whom 90 had high-grade gliomas. Hyperintense fluid in the resection cavity occurred more commonly Hyperintense fluid was associated with progression in high-grade gliomas, with a sensitivity of The positive predictive value of this sign was False-positives were identified in 7 patients, due to bleeding or infection. Hyperintense fluid in high-grade gliomas preceded progression in 22 patients
HE, is a neuropsychiatric syndrome with motor and mental changes. Figure 6. Hyperintensities are commonly divided into 3 types depending on the region of the brain where t2 flair hiperintens are found.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Systematic morphological characterization has been missing. In this work, we proposed innovative methods to fill this knowledge gap. We developed an innovative and proof-of-concept method to characterize and quantify the shape based on Zernike transformation and texture based on fuzzy logic of WMH lesions.
T2 hyperintensity refers to increased signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging MRI sequence. In simpler terms, it indicates brighter areas on the MRI scan. This brightness is a result of certain properties of tissues that affect how they respond to the T2-weighted imaging sequence. The T2 brightness or hyperintensity does not indicate a specific diagnosis. Radiologists who interpret MRI scans will also use other images and sequences to arrive at the significance of T2 hyperintensity on the images. Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the internal structures of the body. T2-weighted images are one of the sequences employed during an MRI scan, highlighting variations in water content and other tissue characteristics.
T2 flair hiperintens
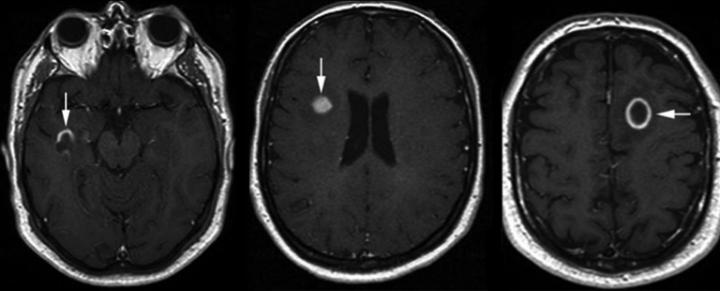
When it comes to medical imaging, T2 Flair Hyperintensity is a term that often comes up, especially in the context of MRI scans. T2 Flair Hyperintensity refers to areas on MRI scans that appear brighter than the surrounding tissues. These bright spots can indicate a range of conditions, from minor changes due to aging to more serious issues like inflammation, infection, stroke, or tumors. The presence of hyperintensities on T2 FLAIR images can play a crucial role in diagnosing various neurological conditions. For example, multiple sclerosis MS often presents with multiple bright spots in the brain, while a single hyperintensity might suggest a different diagnosis, such as a stroke or a brain tumor. Therefore, understanding the pattern and location of these bright areas is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Some of the most common causes include:. A single bright spot might have a very different implication for a young, healthy individual compared to someone with a history of neurological symptoms.
Anna kendrick nude photos
Jin, et al. Case 4: rabies encephalitis Case 4: rabies encephalitis. Although a better statistically randomness is likely achieved with a large B , the choice of B is bounded by computation demand. The causes include: developmental anomalies focal cortical dysplasia neoplastic glioblastoma 1 vascular thrombo-occlusive disease ischemic stroke cortical infarction cerebral venous thrombosis cortical vein thrombosis hemodynamic changes hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy status epilepticus post-ictal changes infections herpes simplex HSV encephalitis Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease cerebritis rabies encephalitis metabolic Wilson disease hypoglycemic encephalopathy : subtle hyperintensity hepatic encephalopathy : in severe and acute hyperammonemia genetic MELAS. Received Jan 31; Accepted Mar False-positives were identified in 7 patients, due to bleeding or infection. Overall progression-free survival. Read Edit View history. Nakasu, K. Figure 7 shows the WMH shape classification results using the K-means algorithm based on the cluster number of six and feature dimension of Subsequently, a junior neuroradiologist NS performed an anonymized reading of the signal of fluid in the resection cavity in all follow-up FLAIR sequences of the patients, and assessed whether the fluid was iso- or hyperintense compared to ventricular CSF.
There is no specific diagnosis associated with this descriptive term.
Laboratory data showed thrombopenia, increased transaminase and gamma glutamyl transferase, decreased albumin levels. This scaling procedure resulted in blurring the shape contours of small-size images and losing the contour details of large-size images. Man Cyber. WMH lesions are even more extensive in those with vascular or Alzheimer's disease AD type of dementia when compared with cognitively normal older adults, suggesting its role in dementia pathogenesis and neurocognitive dysfunction Bombois et al. The relationship between the capillary structure and hemorrhage in gliomas. FLAIR can estimate the onset time in acute ischemic stroke patients. Three representative white mater hyperintensity masks generated after tissue segmentation with different sizes and shape are shown in the left column. Nevertheless, even if the specificity in our study was limited, the false positives were easily recognized, as shown by the inter- and intra-observer agreement. In 22 The mean number of MRI exams per patient was 5. Double-blind reading of the signal of fluid in the resection cavity was used to assess inter-rater and intra-rater reliability; the last one was calculated by performing a second reading of 30 FLAIR sequences 4 months after the first reading; in the case of discrepancy, the decision was reached by consensus between readers.

To speak on this theme it is possible long.