Splunk stdev
Splunk Inc. Summary Performance Analysis Advice.
One of the most powerful uses of Splunk rests in its ability to take large amounts of data and pick out outliers in the data. For some events this can be done simply, where the highest values can be picked out via commands like rare and top. However, more subtle anomalies or anomalies occurring over a span of time require a more advanced approach. By the end of this article you should have a better familiarity with these statistical concepts and gain some intuition on the appropriate uses of such techniques. There are several commands and subcommands that this technique uses.
Splunk stdev
Detecting anomalies is a popular use case for Splunk. In this tutorial we will consider different methods for anomaly detection, including standard deviation and MLTK. I will also walk you through the use of streamstats to detect anomalies by calculating how far a numerical value is from its neighbors. Using standard deviation to find outliers is generally recommended for data that is normally distributed. In security contexts, user behavior is most often an exponential distribution, low values being commonly seen with high values being more rare. Standard deviation can be used to find outliers but a certain percentage of data will always be seen as outlier. This means more data equals more outliers equals more alerts. One example would be if we were looking for users logging in from an anomalous number of sources in an hour. The distribution of source count is an exponential distribution:. However, what if we were to have separate upper bounds for each user? Much of the activity was buried under a high upper bound from users or accounts that regularly log in from many sources. Requiring more than 15 data points, there are 14, results. One of the included algorithms for anomaly detection is called DensityFunction. This algorithm is meant to detect outliers in this kind of data.
Labels 3.
Aggregate functions summarize the values from each event to create a single, meaningful value. Most aggregate functions are used with numeric fields. However, there are some functions that you can use with either alphabetic string fields or numeric fields. The function descriptions indicate which functions you can use with alphabetic strings. For an overview, see Overview of SPL2 stats functions.
Now how can we calculate the average for the access time for past 7 days of each user? I know we can calculate the average for the single field value by using the avg command. But this scenario is different where the field values of accessTimerange are 2 hourly fields. Is there any possibility of calculating the averages for them in Splunk? View solution in original post. I am trying to calculate the average for the past 7 days for each user.
Splunk stdev
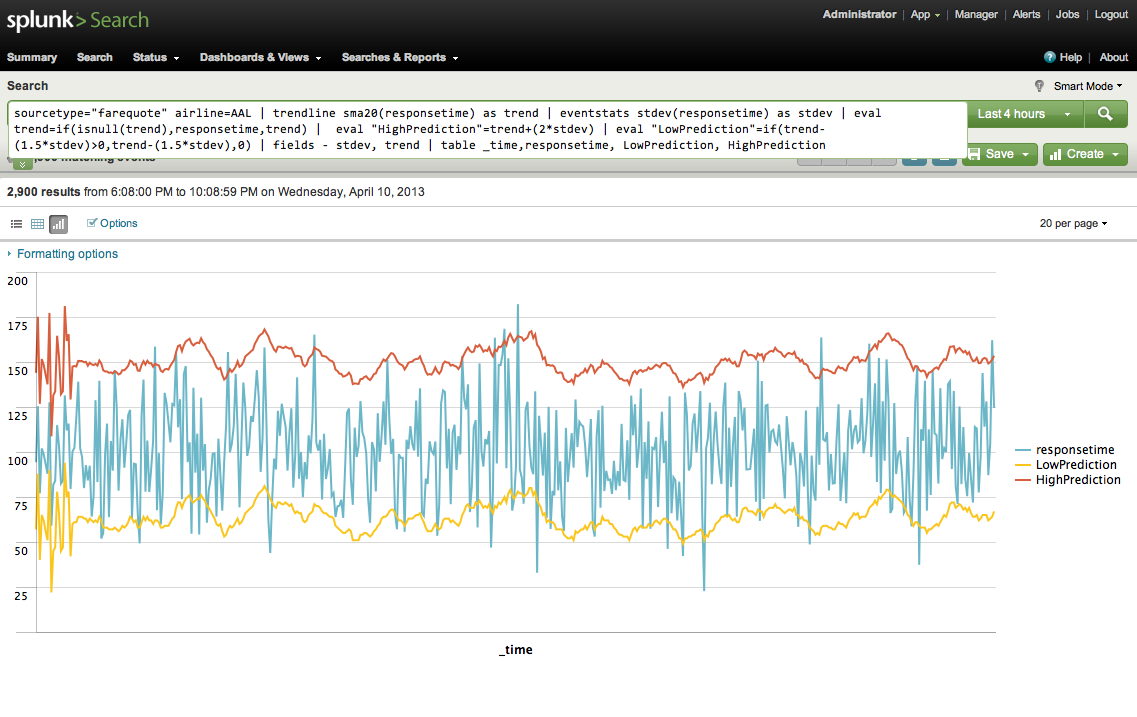
I'm working on a chart which will map a baseline of existing data. The search I am currently using is as follows. That works great for getting the average charting. I now also want to take the Standard Deviation of the timechart of the count, and map that as well. Anyone have any idea how to do that? I've tried a second eventstats, which throws me back some very weird standard deviations on the data itself. Of course this is going to sound like a shameless plug, but honestly, the easiest way to do this is with the Prelert Anomaly Detective app. By the way, don't get caught up in trying to use standard deviation as your approach to express anomalousness. Standard deviation assumes that the data samples in this case, "counts of events" conforms to a nice, symmetrical Gaussian Bell curve.
Bible exodus 20
Jump to solution. What about MLTK? For example:. However, hope you are looking for the following:. Custom eval functions Custom command functions Custom data types Documenting custom functions. Price Transform. Are you ready for an adventure in learning? Running this search over 30 days returns 10 results, and even accessing a few new sources can trigger an anomaly. Feedback submitted, thanks! If the values in the field are non-numeric, the maximum value is found using lexicographical ordering. This is a more general rule stating that for a wide class of probability distributions, we only expect values to be a certain distance measured in standard deviation from the mean. Same as ascending we need to use sort 0. Index This How many sides does a circle have? Financial Services. Turn on suggestions.
Aggregate functions summarize the values from each event to create a single, meaningful value. Most aggregate functions are used with numeric fields.
The cluster numbers are essentially random. Symbols are not standard. So do you want to plot a flat line across the whole bar chart to show the standard deviation? The following example calculates the population standard deviation of the field lag. Open main menu. Splunk Administration. Learn More. One example would be if we were looking for users logging in from an anomalous number of sources in an hour. Good to know, but did not help. In this tutorial we will consider different methods for anomaly detection, including standard deviation and MLTK. Feedback submitted, thanks! There are three percentile functions: exactperc , perc , and upperperc.

Yes, really. All above told the truth.
In it something is. I will know, many thanks for an explanation.
You have hit the mark. I like this thought, I completely with you agree.