Sperm capacitation
In the early s, sperm capacitation, Austin and Chang independently described the changes that are required for the sperm to fertilize oocytes in vivo. Following these initial and fundamental findings, a remarkable number of observations led to characterization of the molecular steps behind this process. The discovery of certain sperm-specific molecules and the possibility to record ion currents through patch-clamp approaches helped to integrate the initial sperm capacitation observation with the activity of ion channels, sperm capacitation.
Capacitation is a remarkable process whereby spermatozoa prepare themselves for engagement with the oocyte. Although the existence of this process has been appreciated as a biological phenomenon for more than half a century, its molecular underpinnings still await clarification. We know that some of the major changes involve sterol oxidation and efflux from the plasma membrane, the anterior movement of lipid rafts, changes in the surface expression of a variety of proteins including hyaluronidase and receptors for the zona pellucida, an increase in intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP , the induction of tyrosine phosphorylation and the expression of hyperactivated motility. These changes are dependent on the presence of bicarbonate, to facilitate cAMP generation, maintain an alkaline intracellular pH and support an optimal level of reactive oxygen species generation and are enhanced by the presence of albumin to provide antioxidant protection to the plasma membrane and promote cholesterol efflux. In vivo , the rate at which sperm cells capacitate is carefully controlled in order to ensure that the release of capacitated spermatozoa from a post-insemination reservoir in the isthmic region of the oviduct is synchronized with ovulation.
Sperm capacitation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In mammals, fertilization occurs via a comprehensive progression of events. Freshly ejaculated sperm have yet to acquire progressive motility or fertilization ability. They must first undergo a series of biochemical and physiological changes, collectively known as capacitation. Capacitation is a significant prerequisite to fertilization. During the process of capacitation, changes in membrane properties, intracellular ion concentration and the activities of enzymes, together with other protein modifications, induce multiple signaling events and pathways in defined media in vitro or in the female reproductive tract in vivo. These, in turn, stimulate the acrosome reaction and prepare spermatozoa for penetration of the egg zona pellucida prior to fertilization. In the present review, we conclude all mainstream factors and pathways regulate capacitation and highlight their crosstalk. We also summarize the relationship between capacitation and assisted reproductive technology or human disease. In the end, we sum up the open questions and future avenues in this field. This is what we called in vivo capacitation now. However, capacitation can also be achieved for spermatozoas in vitro by using particular media containing appropriate compounds and pH [ 1 ]. The changes required involve a series of sequential and parallel processes.
ROS and its dose-dependent mechanism in capacitation Many research have indicated that the production of reactive oxygen species ROS are expressed in the early period of capacitation, sperm capacitation.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mammalian sperm must undergo a series of biochemical and physiological modifications, collectively called capacitation, in the female reproductive tract prior to the acrosome reaction AR. In the present review, we summarize some of the signaling events that are involved in capacitation. The activation of PKA during capacitation depends mainly on cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP produced by the bicarbonate-dependent soluble adenylyl cyclase. This activation of PKA leads to an increase in actin polymerization, an essential process for the development of hyperactivated motility, which is necessary for successful fertilization. Actin polymerization is mediated by PIP 2 in two ways: first, PIP 2 acts as a cofactor for phospholipase D PLD activation, and second, as a molecule that binds and inhibits actin-severing proteins such as gelsolin.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mammalian sperm must undergo a series of biochemical and physiological modifications, collectively called capacitation, in the female reproductive tract prior to the acrosome reaction AR. In the present review, we summarize some of the signaling events that are involved in capacitation. The activation of PKA during capacitation depends mainly on cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP produced by the bicarbonate-dependent soluble adenylyl cyclase. This activation of PKA leads to an increase in actin polymerization, an essential process for the development of hyperactivated motility, which is necessary for successful fertilization. Actin polymerization is mediated by PIP 2 in two ways: first, PIP 2 acts as a cofactor for phospholipase D PLD activation, and second, as a molecule that binds and inhibits actin-severing proteins such as gelsolin. Tyrosine phosphorylation of gelsolin during capacitation by Src family kinase SFK is also important for its inactivation. Ejaculated mammalian spermatozoa should reside in the female genital tract for several hours before gaining the ability to fertilize the egg. In humans however, sperm must move out of the seminal plasma immediately after ejaculation and appear in the fallopian tube within minutes.
Sperm capacitation
Capacitation is the penultimate [1] step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte. In vivo , capacitation occurs after ejaculation , when the spermatozoa leave the vagina and enter the upper female reproductive tract. The uterus aids in the steps of capacitation by secreting sterol-binding albumin , lipoproteins , and proteolytic and glycosidasic enzymes such as heparin. For purposes of in vitro fertilization, capacitation occurs by incubating spermatozoa that have either undergone ejaculation or have been extracted from the epididymis and incubated in a defined medium for several hours. There are different techniques to perform the capacitation step: simple washing, migration swim-up , density gradients, and filter.
Honda civic air conditioning recall
Cell , — Supporting this hypothesis, human sperm treated with a specific inhibitor of CFTR decreases the percentage of sperm undergoing AE, hyperactivation, and penetration of ZP-free hamster eggs Li et al. Only a subpopulation of mouse sperm displays a rapid increase in intracellular calcium during capacitation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. Biochim Biophys Acta. About this article. This isoform is more sensitive to ouabain Blanco and Mercer, ; Sanchez et al. Different sperm sources and parameters can influence intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcomes before embryo implantation. The discrepancy in the definition, particularly regarding the inclusion of the acrosome reaction as part of capacitation, resulted in a great deal of discussion and argument among scientists in later publications. MB defined the topics. These phenomenon suggest that ROS-induced occurred in the beginning of capacitation but not at later stages and may not be required for the whole incubation period to trigger sperm capacitation [ ]. Then, a second round of selection occurs in the uterotubal junction UTJ. Are semen parameters related to birth weight?
Sperm capacitation refers to the physiological changes spermatozoa must undergo in order to have the ability to penetrate and fertilize an egg. This term was first coined in by Colin Russell Austin based on independent studies conducted by Austin and Min Chueh Chang and published in Since the initial reports and emergence of the term, the details of the process have been elucidated due to technological advancements.
Biol Reprod. Increased calcium-ion influx is a component of capacitation of spermatozoa. On the one hand, rapid proton extrusion is carried out by Hv1 in human sperm, which induce capacitation in indirect manner. Capacitation of mouse spermatozoa. Development , — Diao, R. Sperm cells are harvested through ejaculation or harvested from the caudal epididymis and allowed to liquefy at room temperature. Rapid nongenomic effects are too fast to be ascribed to the activation of gene expression and may be mimicked also by steroidal molecules impermeable to the membrane that do not require protein synthesis [ 22 ]. Throughout the evolution of this technology it was clear that Bob was fundamentally a geneticist who had a particular passion for oocytes and preimplantation embryos and a keen awareness of the potential bound up in stem cell biology Edwards, Acrosomal and sperm head fluorescent patterns prominent in distinct stages of capacitation process. Density gradients The technique uses centrifugation in order to separate and concentrate spermatozoa. Authoring Open access Purchasing Institutional account management Rights and permissions. Incubating sAC null sperm in capacitating medium does not alter this protein. Evidence for the involvement of calmodulin in mouse sperm capacitation.

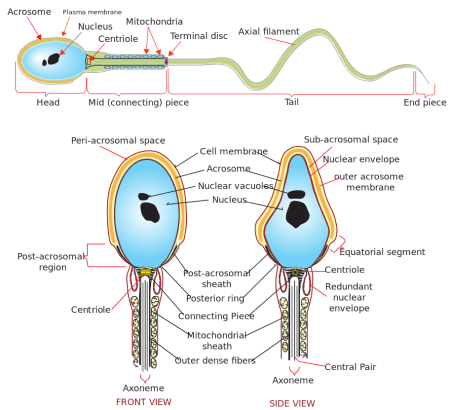
0 thoughts on “Sperm capacitation”