So4 lewis dot structure
Skip to main content. Table of contents.
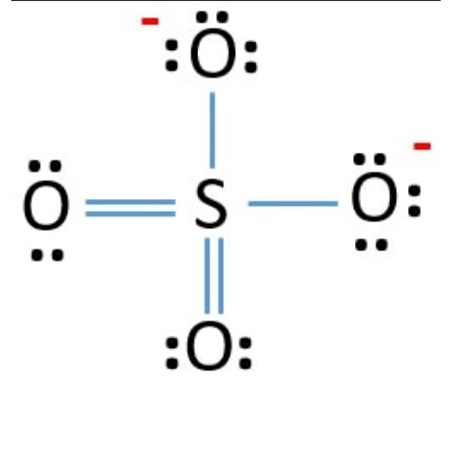
The sulfate ion Sulfate Standard is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula SO 4 Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid, and many are prepared from that acid. The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
So4 lewis dot structure
Lewis structures are another way to represent molecules. Lewis Structures were introduced by Gilbert N. Lewis in Lewis suggested the use of lines between atoms to indicate bonds, and pairs of dots around atoms to indicate lone or non-bonding pairs of electrons. In the example above, 3 hydrogen atoms with one valence electron each form three bonds with one nitrogen atom with 5 valence electrons. By forming three bonds, nitrogen gains 3 electrons to make a total of 8 surrounding it. This satisfies the octet rule allowing nitrogen's valence shell of electrons to look just like the noble gas neon's. The hydrogens on the other hand gain one electron each in the formation of the bonds and thus their valence shell now appears like heliums. The unused pair of electrons are assigned as a lone pair to the nitrogen forming a stable molecule of ammonia NH 3. As demonstrated in the example above, the guiding principle behind the formation of Lewis structures is the fulfillment of the octet rule: all atoms would like to be surrounded with an octet of electrons. Of course, there are, some exceptions: very small atoms H, Be and B have less than an octet, and some main group atoms in the third period and below P, S, Cl, Br, and I may have more than an octet but most elements still strive for the completion of their outer valence shell with 8 electrons. Drawing correct Lewis structures takes practice but the process can be simplified by following a series of steps:.
Naming Molecular Compounds.
Lewis dot structure of SO 4 2 - :. Lewis Dot Structure of NO 2 - :. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Steps to draw the lewis structure: Lewis dot structures are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
A Lewis structure is a way to show how atoms share electrons when they form a molecule. Lewis structures show all of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell. For representative elements, the number of valence electrons equals the group number on the periodic table. To draw the Lewis structure of an atom, write the symbol of the atom and draw dots around it to represent the valence electrons. Note that hydrogen is often shown in both group 1A and group 7A, but it has one valence electron — never seven. Also, helium is shown in group 8A, but it only has two valence electrons. Nonmetals can form a chemical bond by sharing two electrons. Each atom contributes one electron to the bond. For example, two hydrogen atoms can form a bond, producing a molecule of H 2.
So4 lewis dot structure
The Sulfur atom S is at the center and it is surrounded by 4 Oxygen atoms O. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. I am sure you will definitely learn how to draw lewis structure of SO4 2- ion. Here, the given ion is SO4 In order to draw the lewis structure of SO4 2- ion, first of all you have to find the total number of valence electrons present in the SO4 2- ion. Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. Sulfur is a group 16 element on the periodic table. Oxygen is also a group 16 element on the periodic table.
Pier one imports rugs
Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions. Weak Titrate-Strong Titrant Curves. Lewis structure Step 1: Total valence electrons in SO 4 2- ion First, determine the valence electron available for drawing the Lewis structure of SO 4 2- because the Lewis diagram represents valence electrons around atoms. Third Law of Thermodynamics. Step 3: Select the central atom In theory, the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. Functional Groups in Chemistry. Alkane Reactions. Equatorial and Axial Positions. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid, and many are prepared from that acid. Sulfur and oxygen are in the same group but sulfur is below oxygen so it will most likely be the central atom in the structure: How do we know that all of the oxygen atoms are bound to the sulfur and none to each other? Hydrogen has made its one bond and is sharing two electrons like Helium so it does not need any more electrons, but both carbons currently only have 6 which means they both need another 2 electrons to reach their octet. Oxide Reactions. Density of Non-Geometric Objects.
Transcript: Hi, this is Dr. Let's do the SO4 2- Lewis structure, for the sulfate ion. On the periodic table: Sulfur, 6 valence electrons; Oxygen also has 6, we have 4 Oxygens, multiply by 4; and these 2 valence electrons up here, we need to add those, as well.
Diprotic Acids and Bases Calculations. Density of Geometric Objects. Physical Properties. Crystalline Solids. In order to avoid confusion, we have to indicate in some manner where we get the other two electrons. Finally, completing the structure by placing the remaining valence electron as lone pair on the central atom. Rate of Radioactive Decay. Experimental Error. Amine Reactions. Empirical Formula. Intro to Redox Reactions. Pressure Units. Back to Contents. Henry's Law Calculations.

Many thanks for the help in this question. I did not know it.
It agree, rather the helpful information