Sf6 dot and cross diagram
Q: On your paper, draw a correct Lewis structure for the following molecule, where element E is in…. It is….
Substances with high melting points have strong forces of attraction between their atoms or ions. Substances with low melting points have weak forces of attraction between their molecules. Giant structures with ionic or covalent bonds are solids with high melting points: It takes a lot of energy to break the many strong forces between the particles. Molecular solids have low melting points: The forces within the molecules are strong. But the forces between the molecules are fairly weak so it does not take much energy to overcome these. Liquids have low melting points. The forces within the molecules are strong.
Sf6 dot and cross diagram
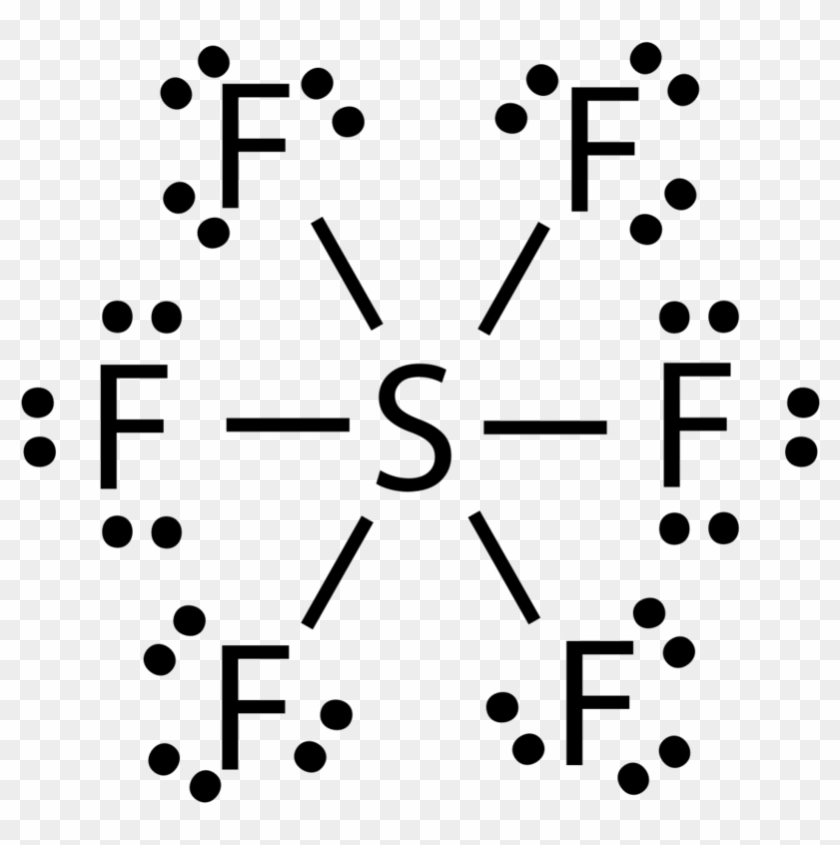
Covalent and dative sometimes called co-ordinate bonds occur between two or more non-metals, e. But what actually are they? A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. They are found in molecular elements or compounds such as chlorine or sulfur, but also in macromolecular elements and compounds like SiO2 and graphite. Single covalent bonds have just one shared pair of electrons. Regularly, each atom provides one unpaired electron the amount of unpaired electrons is usually equal to the number of covalent bonds which can be made in the bond. Dot and cross diagrams represent the arrangement of electrons in covalently bonded molecules. A shared pair of electrons is represented by a dot and a cross to show that the electrons come from different atoms. Unpaired electrons are used to form covalent bonds as previously mentioned. The unpaired electrons in orbitals of one atom can be shared with another unpaired electron in an orbital but sometimes atoms can promote electrons into unoccupied orbitals in the same energy level to form more bonds. This does not always occur, however, meaning different compounds can be formed - PCl3 and PCl4 are examples of this. An example where promotion is used is in sulfur hexafluoride SF6. The regular configuration of sulfur atoms is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. It promotes, as shown in the diagram see excited state , two electrons: one from the 3s electrons to the 3d orbital and one from the 3p to the 3d.
Step by step Solved in 2 steps with 1 images.
They repel each other equally. It is a linear molecule. Carbon dioxide has two double bonds. There are two groups of two bonding pairs of electrons around the central carbon atom. The groups of electrons repel each other equally, so carbon dioxide is also a linear molecule.
Lewis used dots to represent the valence electrons in his teaching of chemical bonding. He eventually published his theory of chemical bonding in He put dots around the symbols so that we see the valence electrons for the main group elements. Formation of chemical bonds to complete the requirement of eight electrons for the atom becomes a natural tendency. Lewis dot symbols of the first two periods are given here to illustrate this point.
Sf6 dot and cross diagram
SF6 or sulfur hexafluoride is an inorganic and one of the most stable gases that are known in chemistry. This gas has more density than air. There is also no taste of the gas as such. SF6 is noncombustible and nonflammable in nature.
Gls alcalá de guadaira
Part 1 from diatomic molecules to polyatomic molecules. Close suggestions Search Search. By breaking the molecule into 4 parts each part looks at 1 of the 4 Carbons , we determine how many electron groups there are and find out the shapes. These often are not given a particular shape name, but never-the-less, an appreciation of the 3D spatial arrangement is expected e. Phil Knight. Each fluorine atom give one electron to make a bond with sulfur atom. Another nice pattern in a changing bond angle trend but do pre-university exam boards realise this?. There are three rules to this part: 1. The forces between the molecules are the weak van der Waals forces. The molecule is then non-polar see Figure 2. ELectronegativity and intermoLecuLar forces Learning outcomes Electronegativity On completion of this section, you should be able to: Electronegativity is the ability of a particular atom involved in covalent bond formation to attract the bonding pair of electrons to itself. Three groups of bond pairs. NH3 b. In an ionic compound the number of positive and negative charges must balance, e.
SF 6 is an inorganic colorless greenhouse non-flammable gas with an octahedral geometry in which one sulfur atom is attached with six fluorine atoms. It has an orthorhombic crystalline structure and hypervalent in nature. In SF 6 , the S-F single bond length is
Bonding and Structure Document 72 pages. The H means that the actual structure is a single composite form which lies between these two structures. Jason King. Sigma bonds a bonds Sigma bonds a bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along a line drawn between the two nuclei. Apart from graphite they are hard: the three-dimensional network of strong bonds in different directions is too difficult to break. Methane is a molecule with a tetrahedral shape. Q: What determines which atoms are the central atoms? Conduct electricity only when molten or dissolved in water: the ions can only move when molten or dissolved in water. The structure only shows the atoms and how they are…. Well, we want to optimize the bond angle of each central atom attached to each other. Refer back to the Lewis dot diagram of CO 2. Part 1 from diatomic molecules to polyatomic molecules. As there are two pyramids, the shape of the molecule is a trigonal bipyramid. Since sulfur now has more than 8 electrons, we say that it "expands octet". The elements are said to have "expanded their octet".

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.