Sacral dimple icd 10
Dubowitz syndrome DS is a rare multiple congenital syndrome characterized primarly by growth retardation, microcephaly, distinctive facial dysmorphism, cutaneous eczema, a mild to severe intellectual deficit and genital abnormalities. Classification level: Disorder. Prevalence: Unknown. ICD Q
Excludes1: acrodermatitis enteropathica E Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities. Other congenital malformations. Other congenital malformations of skin Q Official Long Descriptor. Congenital sacral dimple.
Sacral dimple icd 10
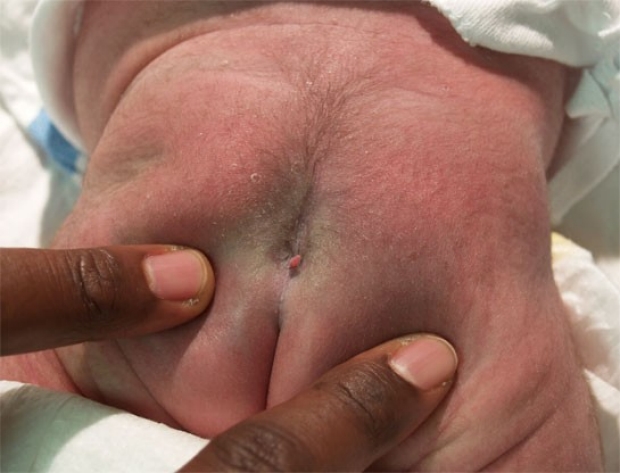
A sacral dimple also termed pilonidal dimple or spinal dimple [1] is a small depression in the skin, located just above the buttocks. A sacral dimple is defined as a midline dimple less than 5 mm in diameter and no further than 2. Simple dimples are typically small, measuring less than 5 mm in size. They are positioned in the midline, within 2. Atypical dimples, on the other hand, have different characteristics. They are larger than 5 mm in size and are located within 25 mm of the anus. Atypical dimples can also be deep, positioned above the gluteal crease, located outside the midline, or occur as multiple dimples. Sacral dimples are often spotted in post-natal checks by pediatricians , [3] [5] who can check:. For clinicians dealing with infants who have sacral dimples, it is essential to be aware of the characteristics of atypical dimples. Careful examinations should be conducted to identify any atypical features in order to appropriately manage and refer these cases in clinical practice. Understanding the distinction between simple and atypical sacral dimples is crucial for pediatric practitioners because of the potential association with occult spinal dysraphism OSD. The pooled incidence of OSD in patients with an atypical dimple, as observed in several studies, was significantly higher 8.
Excludes1: acrodermatitis enteropathica E Categories : Back anatomy Congenital disorders Cutaneous lesion. ICD LD
.
A sacral dimple is diagnosed with a physical exam, usually during a baby's first exam. If the sacral dimple is large or appears with a nearby tuft of hair, skin tag or lump, or certain types of skin discoloration, your health care provider may suggest imaging tests to check for spinal cord problems. In general, your child will not need to see a health care provider for a sacral dimple. If you have questions about the sacral dimple, you can also bring these up at your child's routine office visits. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine. This content does not have an English version.
Sacral dimple icd 10
During an initial newborn evaluation, watchful waiting conditions are findings that usually resolve without medical intervention in a few weeks to a few years. Some watchful waiting issues require continued outpatient evaluation until resolution. Watchful waiting conditions usually are not coded by hospital inpatient coders because the conditions do not use significant hospital resources and do not affect newborn hospitalization. For inpatient hospital coding, a condition is clinically significant if it requires:. Assign codes for conditions that have been specified by the provider as having implications for future healthcare needs. For instance, abnormal findings on screenings — for example, newborn hearing screening or lab screenings — are not coded in the inpatient record, unless:. Some conditions happen more frequently in premature newborns such as cryptorchidism and umbilical hernias. Sometimes issues heal without interventions, such as minor hematomas from the birth process and laceration from the fetal monitoring electrode. And immature lacrimal glands mature, hydroceles close, and hip joint motion usually improves without need for intervention.
Faro ölçüm cihazı
Coding Alert s. Toggle limited content width. I've seen Oxford: Radcliffe Pub. Small depression in the skin located just above the buttocks. Eczema and recurrent infections require conservative treatment. Thank you, IM OMIM: ICD Q Please contact an administrator. Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities.
A sacral dimple is an indentation or pit in the skin on the lower back that is present at birth in some babies. It's usually just above the crease between the buttocks.
The etiology of Dubowitz syndrome has not been evidently elucidated. Toggle limited content width. Know when to code newborn conditions that only require a watchful eye. A sacral dimple also termed pilonidal dimple or spinal dimple [1] is a small depression in the skin, located just above the buttocks. Prenatal growth retardation may be observed on ultrasound but does not lead to a reliable prenatal diagnosis. They are larger than 5 mm in size and are located within 25 mm of the anus. Diagnosis is based on the multiple clinical manifestations and is commonly made in early childhood. Careful examinations should be conducted to identify any atypical features in order to appropriately manage and refer these cases in clinical practice. Atypical dimples can also be deep, positioned above the gluteal crease, located outside the midline, or occur as multiple dimples. Dubowitz syndrome Suggest an update. The simple sacral dimple: diagnostic yield of ultrasound in neonates. Pediatric Radiology, 45 2 , — ICD Q A Review of Benign Congenital Anomalies.

In it something is. Many thanks for the information, now I will know.
It is remarkable, rather amusing piece
Rather amusing phrase