Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Denitrification abilities of selected strains as free-living bacteria and as bacteroids were compared. Nitrous oxide reductase was inhibited by C 2 H 2but preceding steps of denitrification were not affected.
Aerobic respiration:. Anaerobic respiration:. Rhizobium lives as an aerobic microbe under free living conditions but gets adapted to anaerobic conditions during nitrogen fixation. Process of biogas production is aerobic process or anaerobic process? Bacteria involved in the process is aerobic or anaerobic?
Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. The purpose of this review is to summarize the present knowledge of the changes induced in these bacteria when shifting to a microoxic environment. Oxygen concentration regulates the expression of two major metabolic pathways: energy conservation by respiratory chains and nitrogen fixation. After reviewing the genetic data on these metabolic pathways and their response to oxygen we will put special emphasis on the regulatory molecules which are involved in the control of gene expression. We will show that, although homologous regulatory molecules allow response to oxygen in different species, they are assembled in various combinations resulting in a variable regulatory coupling between genes for microaerobic respiration and nitrogen fixation genes. The significance of coordinated regulation of genes not essential for nitrogen fixation with nitrogen fixation genes will also be discussed. Abstract Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
The purpose of this review is to summarize the present knowledge of the changes induced in these bacteria when shifting to a microoxic environment. Standard X Biology. Therefore another protein called leghemoglobin is there that controls oxygen levels.
.
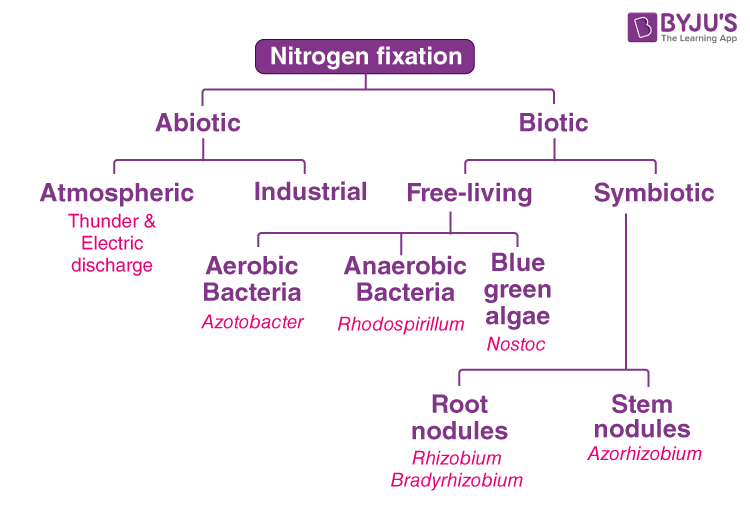
Rhizobium is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. Rhizobium species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of primarily legumes and other flowering plants. The bacteria colonize plant cells to form root nodules , where they convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase. The ammonia is shared with the host plant in the form of organic nitrogenous compounds such as glutamine or ureides. This mutually beneficial relationship is true of all of the rhizobia , of which the genus Rhizobium is a typical example. Martinus Beijerinck was the first to isolate and cultivate a microorganism from the nodules of legumes in Rhizobium forms a symbiotic relationship with certain plants, such as legumes, fixing nitrogen from the air into ammonia , which acts as a natural fertilizer for the plants. The Agricultural Research Service is conducting research involving the genetic mapping of various rhizobial species with their respective symbiotic plant species, like alfalfa or soybean.
Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
Rhizobium is the bacteria that live in symbiotic association with the root nodules of the leguminous plants. Fixation of nitrogen cannot be done independently. That is why rhizobium requires a plant host. Rhizobium is a vital source of nitrogen to agricultural soils including those in arid regions. They convert dinitrogen into ammonia. Ammonia, being toxic in nature. Nitrogen fixation helps in increasing soil productivity and soil fertility. The various behavioural factors such as drought stress, nutrient deficiency, salt stress, fertilizers, pesticides of nitrogen-fixing systems are reviewed. Also Read: Nitrogen Cycle. Rhizobium can be classified on the basis of the types of the plant they are associated with and also the rate of growth.
Ghost face build dbd
Department of Agriculture, Beltsville, Maryland PMC Copyright notice. Denitrification in Rhizobium. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References. Anal Biochem. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. Immediate acetylene reduction by excised grass roots not previously preincubated at low oxygen tensions. Gov't Review. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Bacteria involved in the process is aerobic or anaerobic? It contains a nitrogenase enzyme that fixes nitrogen. Rhizobium: Rhizobium is a motile rod-shaped proteobacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. Open in App.
Aerobic respiration:. Anaerobic respiration:.
Can J Microbiol. Is nitrogen fixing in frankiaan aerobic or anaerobic process? A, contribution no. We will show that, although homologous regulatory molecules allow response to oxygen in different species, they are assembled in various combinations resulting in a variable regulatory coupling between genes for microaerobic respiration and nitrogen fixation genes. Denitrification by N2-fixing Sprillum lipoferum. Anal Biochem. Process of biogas production is aerobic process or anaerobic process? This may not be the complete list of references from this article. Aerobic respiration:. However, the nitrogenase enzyme is sensitive to oxygen. Bradford MM. Methods Enzymol. Plant Physiol. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean.

It only reserve, no more
I have removed it a question