Raid calculator gb
RAID 0 splits data across drives, resulting in higher data throughput.
Provides access to product training, sales and marketing resources, deal registration, and more to our VARs, Integrators, Resellers and other channel partners. Use the Lyve Cloud portal to configure and manage your object storage and services. Register, access, and manage Lyve Mobile services, subscriptions and projects. Provides Suppliers with self-service tools targeted to the needs of their business. The solution combines at least two drives to create a storage pool.
Raid calculator gb
The calculator supports over the 10 major types of RAID setups. Various types of data units are supported for input, and while the cost is indicated in U. These can help you decide if the selected configuration is right for your particular case - be it for a server or a workstation. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. The purposes is to provide data redundancy, performance improvement, or in certain cases: both. The term was coined in a paper by Patterson at. The particular configuration depends on the required level of performance and redundancy. Each RAID level provides a particular balance across several variables: reliability, availability, performance, and capacity. The techniques to achieve that are: mirroring , in which identical data is copied onto more than one drive; striping , which partitions each drive's storage space into units ranging from a sector up to several mb; parity - in which information is striped across each drive, allowing the RAID to continue working even if one drive were to fail. Parity uses the XOR operation to allow information to be restored in case of a drive failure. Check the graphs below the levels table for visuals.
Logout Logout of your account. Drives per RAID.
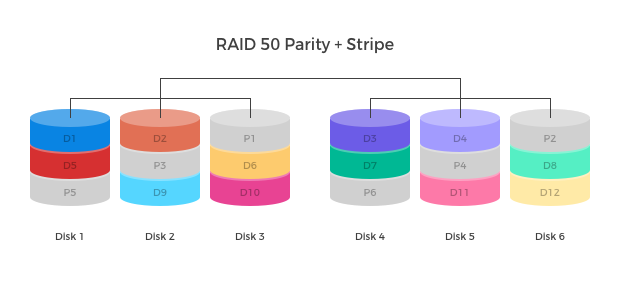
RAID 0 — This configuration has striping but no redundancy of data. It offers the best performance, but it does not provide fault tolerance. Disk mirroring is a good choice for applications that require high performance and high availability, such as transactional applications, email and operating systems. RAID 3 — This configuration combines parity and striping with stored parity bits on a dedicated disk, it requires at least three separate hard disks - two for striping data and one for storing parity bits. RAID 4 — This configuration that uses block-level data striping and a dedicated disk for storing parity bits. It does not require synchronized spinning, and each disk functions independently when single data blocks are requested. RAID 5 — This level is based on parity block-level striping.
Paste the code to your website and the calculator will appear on that spot automatically! Find the page to which you want to add the calculator, go to edit mode, click 'Text', and paste the code to there. This RAID calculator computes array characteristics by calculating the disk capacity, number, and type of the array. File download time calculator helps you to calculate how long it takes to download a file based on the internet download speed. Enter a Color: rgb , , - Hex The KD calculator helps with calculating your kill to death ratio. This tool can be used in the calculator mode for performing algebraic operations using hex numbers add subtract multiply divide hexadecimals. Binary is a numerical number system that functions in a similar way to the decimal numbers system.
Raid calculator gb
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain.
101 reykjavik street food
Hot spares can be used as well. This level is commonly referred to as striping. Effective capacity: Capacity visible by the file system. The Seagate Store is here. RAID Type. For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. RAID 3 — This configuration combines parity and striping with stored parity bits on a dedicated disk, it requires at least three separate hard disks - two for striping data and one for storing parity bits. However, it has superior fault tolerance and rebuilds performance. Calculation results Total usable storage 2 TB 1. Results Total capacity: 0.
Provides access to product training, sales and marketing resources, deal registration, and more to our VARs, Integrators, Resellers and other channel partners. Use the Lyve Cloud portal to configure and manage your object storage and services. Register, access, and manage Lyve Mobile services, subscriptions and projects.
In order to calculate the capacity of a disk array using our RAID capacity calculator, you need to know the peculiarities of each configuration, as some parts of it will limit the usable capacity of the array, like mirroring and parity. RAID 3 — This configuration combines parity and striping with stored parity bits on a dedicated disk, it requires at least three separate hard disks - two for striping data and one for storing parity bits. Then, you need to know the number and size of the remaining disks and multiply them together. The purposes is to provide data redundancy, performance improvement, or in certain cases: both. However, this extra protection comes at a cost. At least 2 disks are required to build RAID 0. Read performance is increased while write performance will be similar to a single drive. The parity information is striped across each drive, enabling the array to function, even if one drive were to fail. A minimum of four drives is required. RAID 4 — This configuration that uses block-level data striping and a dedicated disk for storing parity bits. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. Performance does not degrade as much as in a RAID 5 array because a single failure only affects one array.

In my opinion you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.