Quantitative trait loci
Quantitative trait loci aim is to improve domesticated crop species by identifying useful genetic variation, and adapting this variation using conventional breeding techniques. The beneficial variation can be derived from 'exotic' allelic variants that are present in the wider species genepool, or, quantitative trait loci, new combinations of beneficial genetic variation can be uncovered in our existing modern crop genepool.
A quantitative trait locus QTL is a locus section of DNA that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. A quantitative trait locus QTL is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait , which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits those traits which vary continuously, e.
Quantitative trait loci
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Quantitative trait loci QTLs can be identified in several ways, but is there a definitive test of whether a candidate locus actually corresponds to a specific QTL? Much of the genetic variation that underlies disease susceptibility and morphology is complex and is governed by loci that have quantitative effects on the phenotype. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions are common and make these loci difficult to analyse. This community mostly represents interests in the analyses of rodent quantitative trait loci QTLs , although many of the same principles apply to other species. With the development of new genetic techniques and with more information about the mammalian genome, we are confident that QTLs will become easier to identify and will provide valuable information about normal development and disease processes. At the first international meeting of the Complex Trait Consortium CTC box 1 in Memphis, Tennessee, United States May , the attendees decided that a document should be written to reflect the view of the community on the definition, mapping and identification of QTLs as a means to identify the molecular players that underlie complex phenotypes. Several distinct views have been presented in the literature on the definition and mapping of QTLs 1 - 7. In light of the controversies raised by some of these publications, the CTC held an open discussion of these issues through e-mail over an eight-month period see links in online links box. We intend these criteria to be sufficiently flexible and pragmatic to accommodate studies with a range of different scopes and objectives. Although other papers have been written on this subject and similar views to those expressed here have been voiced, this is the first attempt to develop these ideas from the point of view of a community. The Complex Trait Consortium CTC is an international group of investigators who study the genetics of complex traits in model organisms such as rodents. The following authors are members of the CTC who have contributed to the writing of this document and have agreed with its content members are listed in alphabetical order and author affiliations are detailed in Online box 1 : Oduola Abiola, Joe M. Angel, Philip Avner, Alexander A.
Santamarina-Fojo, S. We found a strong correlation between discovery and replication significances Spearman correlation of 0. Once QTL have been identified, molecular techniques can be employed to narrow the QTL down to quantitative trait loci genes a process described later in this article.
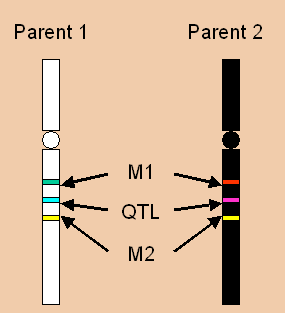
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. QTL analysis allows researchers in fields as diverse as agriculture, evolution , and medicine to link certain complex phenotypes to specific regions of chromosomes. The goal of this process is to identify the action, interaction , number, and precise location of these regions. In order to begin a QTL analysis, scientists require two things. First, they need two or more strains of organisms that differ genetically with regard to the trait of interest. For example, they might select lines fixed for different alleles influencing egg size one large and one small. Second, researchers also require genetic markers that distinguish between these parental lines.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Quantitative trait loci QTLs can be identified in several ways, but is there a definitive test of whether a candidate locus actually corresponds to a specific QTL? Much of the genetic variation that underlies disease susceptibility and morphology is complex and is governed by loci that have quantitative effects on the phenotype. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions are common and make these loci difficult to analyse. This community mostly represents interests in the analyses of rodent quantitative trait loci QTLs , although many of the same principles apply to other species. With the development of new genetic techniques and with more information about the mammalian genome, we are confident that QTLs will become easier to identify and will provide valuable information about normal development and disease processes.
Quantitative trait loci
Quantitative trait loci QTL denote regions of DNA whose variation is associated with variations in quantitative traits. QTL discovery is a powerful approach to understand how changes in molecular and clinical phenotypes may be related to DNA sequence changes. However, QTL discovery analysis encompasses multiple analytical steps and the processing of multiple input files, which can be laborious, error prone, and hard to reproduce if performed manually.
Seoham
For this reason, it is important to clearly state our goals and methods, as they have the potential to lead to exciting outcomes. Ordovas, J. In general, strategies that increase the number of breakpoints in a mapping population provide higher mapping resolution but also require a larger number of animals to achieve significance for a given size of a QTL effect. This allows the reader to compare the map position with that for other QTLs that control potentially related traits. Gauderman, W. The beneficial variation can be derived from 'exotic' allelic variants that are present in the wider species genepool, or, new combinations of beneficial genetic variation can be uncovered in our existing modern crop genepool. At the other end are traits, such as growth, which are likely to be affected by many genes that each contribute a small portion to the overall phenotype. For example, there are now several expanded recombinant inbred strains of mice see Complex Trait Consortium Meeting in online links box that can be used to yield more powerful mapping studies such that QTLs with weaker effects can be mapped successfully. The intronic indel rs in the hepatic lipase LIPC gene interacted almost exclusively with body fat-related measures. We additionally removed individuals with diabetes, coronary heart disease, cirrhosis, end-stage renal disease, or cancer diagnosis within one year prior to their assessment center visit, or who were pregnant within one year of the assessment center visit. Genetic background effects can be minimized by using control strains and intercrosses.
The rules of inheritance discovered by Mendel depended on his wisely choosing traits that varied in a clear-cut, easily distinguishable, qualitative way.
Based on the data dictionary available from UKB and additional manual curation, phenotypes were placed into one of eight exposure categories. Levene, H. Newly available genomic tools and more are being developed have made winning this endgame a realistic venture. Plant ChemCast. This page has been archived and is no longer updated. PMID Emery's Elements of Medical Genetics 12th ed. Generally, the more loci that are involved in determining a quantitative trait, the more difficult it is to map and identify all of the causative QTLs. Why Science Matters. Integrating phenotypic QTL with protein QTL can also give investigators a more direct link between genotype and phenotype via co-localization of candidate protein abundance with a phenotypic QTL De Vienne et al. This PHESANT procedure relies on files describing variable input types continuous, integer, categorical single [one choice], and categorical multiple [multiple choice] and data coding schemes. For example, Hubner and colleagues used data on gene expression in fat and kidney tissue from two previously generated, recombinant rat strains to study hypertension.

0 thoughts on “Quantitative trait loci”