Pkc kinase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Protein kinase C PKC isoforms comprise a family of lipid-activated enzymes that have been implicated in a wide range of cellular functions. PKCs are modular enzymes comprised of a regulatory domain that pkc kinase the membrane-targeting motifs that respond to lipid cofactors, pkc kinase, and in the case of some PKCs calcium and a relatively conserved catalytic domain that binds ATP and substrates.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Phosphorylation by PKC is important in regulating a variety of cellular events such as cell proliferation and the regulation of gene expression. In the immune system, PKC s are involved in regulating signal transduction pathways important for both innate and adaptive immunity, ultimately resulting in the expression of key immune genes. PKC s act as mediators during immune cell signalling through the immunological synapse.
Pkc kinase
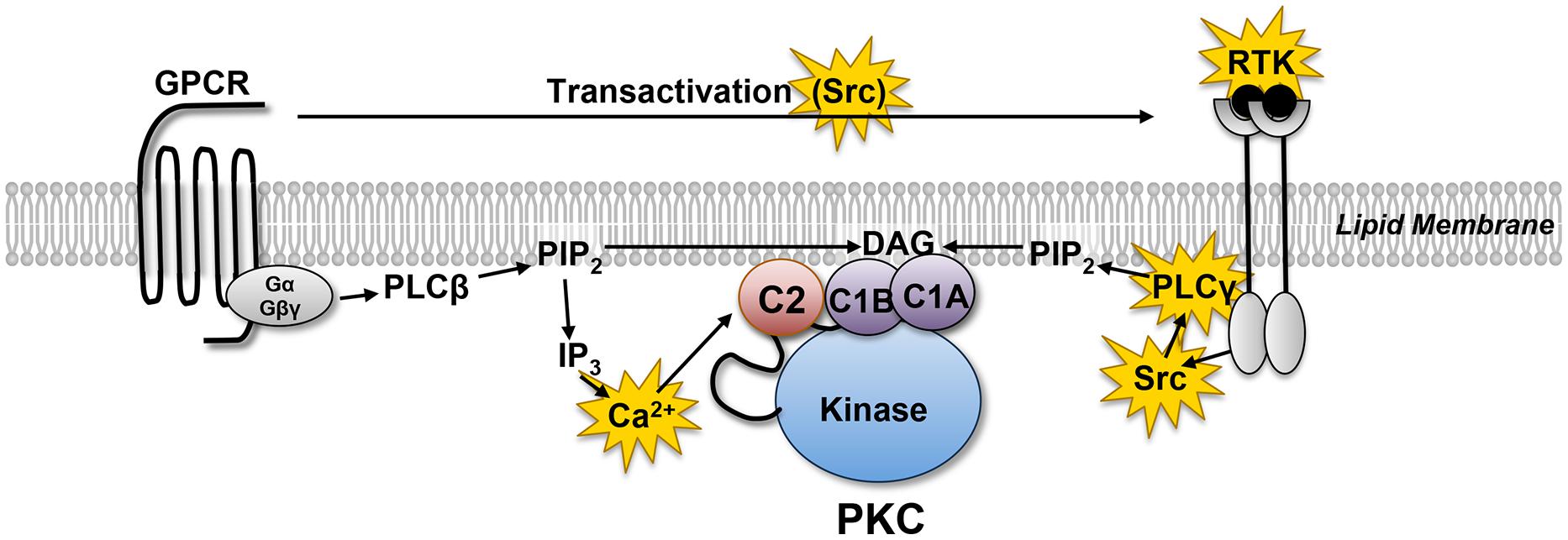
Protein kinase C PKC family members regulate numerous cellular responses including gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and the inflammatory response. The basic protein structure includes an N-terminal regulatory region connected to a C-terminal kinase domain by a hinge region. PKC enzymes contain an auto-inhibitory pseudosubstrate domain that binds a catalytic domain sequence to inhibit kinase activity. Differences among PKC regulatory regions allow for variable second messenger binding and are the basis for the division of the PKC family into 3 broad groups. Distantly related protein kinase D proteins are often associated with novel PKC enzymes as they respond to DAG but not calcium stimulation. Control of PKC activity is regulated through three distinct phosphorylation events. Phosphorylation occurs in vivo at Thr in the activation loop, at Thr through autophosphorylation, and at the C-terminal hydrophobic site Ser Request Permission for Pathway. View PDF. Would you like to visit your country specific website? YES NO. Save This Selection. All Rights Reserved. Pathway Description Legend Protein kinase C PKC family members regulate numerous cellular responses including gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and the inflammatory response.
Corresponding author. J Biol Chem ; —6.
It was first identified in in bovine cerebellum by Nishizuka and co-workers as a protein kinase that phosphorylated histone and protamine. Since then, its involvement in many biological processes has been demonstrated, including development, memory, differentiation, proliferation and carcinogenesis. Once thought to be a single protein, PKC is now known to comprise a large family of enzymes that differ in structure, cofactor requirements and function. Ten isoforms of PKC have been identified, varying in tissue expression and cellular compartmentalization, allowing for specific interactions with substrates. These are not closely related to the PKC family due to very different regulatory domains; however, they can be considered to be part of the PKC superfamily.
Protein kinase C PKC family members regulate numerous cellular responses including gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and the inflammatory response. The basic protein structure includes an N-terminal regulatory region connected to a C-terminal kinase domain by a hinge region. PKC enzymes contain an auto-inhibitory pseudosubstrate domain that binds a catalytic domain sequence to inhibit kinase activity. Differences among PKC regulatory regions allow for variable second messenger binding and are the basis for the division of the PKC family into 3 broad groups. Distantly related protein kinase D proteins are often associated with novel PKC enzymes as they respond to DAG but not calcium stimulation. Control of PKC activity is regulated through three distinct phosphorylation events. Phosphorylation occurs in vivo at Thr in the activation loop, at Thr through autophosphorylation, and at the C-terminal hydrophobic site Ser
Pkc kinase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Phosphorylation by PKC is important in regulating a variety of cellular events such as cell proliferation and the regulation of gene expression.
Myislandhealth
Gopalakrishna R, Jaken S. While there are a number of PKC regulators in clinical trials for various diseases, the main research of autoimmune PKC activity and drug targeting is in T cells due to the pivotal role that T cells play in the immune response. Borrowing from computer science terminology at the time, he coined the term transducer for the molecule that affects this type of information processing, setting the stage for the identification of G proteins and his Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine. J Mol Biol. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Malviya AN, Block C. Biochim Biophys Acta ; — Immunocytochemical localization of eight protein kinase C isozymes over-expressed in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Some, if not all, PKC isoforms can be proteolytically cleaved at the hinge between the regulatory and catalytic domains by proteases such as the calcium-activated calpain, generating a free, cofactor-independent, catalytic subunit known as protein kinase M PKM. PKC isoforms are broadly subdivided into three subfamilies based on differences in their NH 2 -terminal regulatory domain structure. Would you like to visit your country specific website? In and out of the bull's eye: protein kinase Cs in the immunological synapse. Calcium released in the cytoplasm causes cytoplasmic PKC to translocate to the plasma membrane while calcium that is released within the nucleus translocates nuclear PKC to the nuclear envelope. The regulatory domain or the amino-terminus of the PKCs contains several shared subregions.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Other structural determinants of C1 domain function are as indicated on the figure. J Cell Sci ; Pt 13 — Cell Death Differ. Nuclear protein kinase C. J Biol Chem ; —7. Current concepts of the controls of PKC phosphorylation are based largely on studies of heterologously overexpressed enzymes. Both the ATP-binding protein ATP - and the substrate- binding sites are located in the cleft formed by these two terminal lobes. CxS phosphorylation is implicated as a mechanisms that decreases gap junction permeability and intercellular communication Blood ; —6. The C1 domain , present in all of the isoforms of PKC has a binding site for DAG as well as non-hydrolysable, non-physiological analogues called phorbol esters. J Exp Biol. Immunity ; 23 — PKC isoform variable regions are shown in gray. Rodbell viewed signal transduction as a process in which discriminators or receptors on the cell surface receive information from outside the cell and transmit this information to an amplifier or effector such as adenylyl cyclase via some form of go-between. Bornancin F, Parker PJ.

0 thoughts on “Pkc kinase”