Pancreatic acini
Michelle M. Cooley 1Elaina K. Jones 1Fred S.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Acinar cell carcinoma ACC is a rare pancreatic malignancy with distinctive clinical, molecular, and morphological features. The long-term survival of ACC patients is substantially superior to that of pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. As there are no significant patient series about ACCs, our understanding of this illness is mainly based on case reports and limited patient series. Surgical resection is the treatment of choice for patients with the disease restricted to one organ; however, with recent breakthroughs in precision medicine, medicines targeting the one-of-a-kind molecular profile of ACC are on the horizon. There are no standard treatment protocols available for people in which a total surgical resection to cure the condition is not possible.
Pancreatic acini
The pancreatic acinar cell is the functional unit of the exocrine pancreas. It synthesizes, stores, and secretes digestive enzymes. Under normal physiological conditions, digestive enzymes are activated only once they have reached the duodenum. Premature activation of these enzymes within pancreatic acinar cells leads to the onset of acute pancreatitis; it is the major clinical disorder associated with pancreatic acinar cells. Although there have been major advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of this disease in recent years, available treatment options are still limited to traditional nonspecific and palliative interventions. Novel therapeutic strategies have been suggested based on ongoing research in the physiology and pathophysiology of the disease; these include the administration of systemic antibiotics, antioxidants, cytokine antagonists, and more recently, inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system. Notwithstanding this promising development, most of these potential therapies are still in an experimental stage or clinical trial. Further investigation is needed to prove the efficacy of these novel treatment modalities. Abstract The pancreatic acinar cell is the functional unit of the exocrine pancreas. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
Marlowe et al.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Human pancreatic exocrine cells were cultured in 3D suspension and formed pancreatospheres composed of acinar-derived and duct-like cells. We investigated, up to 6 days, the fate of human pancreatic acinar cells using fluorescein-conjugated Ulex Europaeus Agglutinin 1 lectin, a previously published acinar-specific non-genetic lineage tracing strategy. These findings with human cells underscore the remarkable plasticity of pancreatic exocrine acinar cells, previously described in rodents, and could find applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
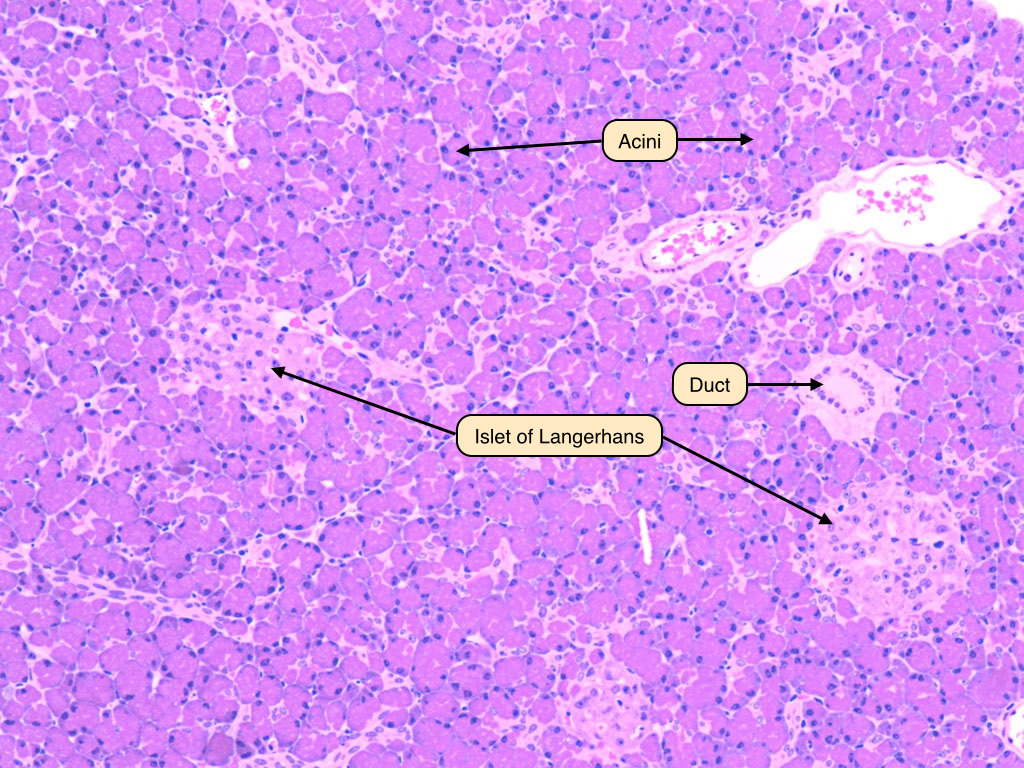
Pancreatic islets, also called the islets of Langerhans, are regions of the pancreas that contain its hormone-producing endocrine cells. The pancreas serves two functions, endocrine and exocrine. The exocrine function of the pancreas is involved in digestion, and these associated structures are known as the pancreatic acini. The pancreatic acini are clusters of cells that produce digestive enzymes and secretions and make up the bulk of the pancreas. The endocrine function of the pancreas helps maintain blood glucose levels, and the structures involved are known as the pancreatic islets, or the islets of Langerhans. Pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans : The islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine hormone-producing cells. The pancreatic islets are small islands of cells that produce hormones that regulate blood glucose levels.
Pancreatic acini
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. The acinar cell of the exocrine pancreas has the greatest rate of protein synthesis of any mammalian organ.
Standing wave gif
Holen et al [ 8 ] found that median survival for surgically resected cases was 36 mo, compared to 14 mo for those without surgical resection[ 8 ]. Figure 2. Later higher resolution studies by Jameson and Palade in pancreatic slices from guinea pig stimulated with secretagogue revealed the presence of label in the Golgi stacks 81 ; although in his Nobel acceptance speech Palade still depicted the ER transitional compartment as a direct route to the condensing vacuoles CT and MRI features of pure acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas in adults. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. Human pancreatic exocrine cells were cultured in 3D suspension and formed pancreatospheres composed of acinar-derived and duct-like cells. Variable architectural patterns; uniform cells; oval or spherical nuclei; granular cytoplasm; undetected nucleoli; minimal stroma. The exocrine pancreas has two major physiologic functions: it supplies the proenzymes and enzymes needed for digesting dietary lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins; and secretes a bicarbonate-rich fluid that neutralizes acidic gastric secretions and thus provides the correct pH for intestinal digestion by pancreatic enzymes. Elevated lipase may be the first sign of ACC. Axial post-contrast computed tomography image in the arterial phase shows a solid lobulated mass measuring 6. The current view is that this acetylation identifies properly folded i. Live pancreatic acinar imaging of exocytosis using syncollin-pHluorin. Non-specific amplification was investigated through performance of a dissociation curve and length analysis of the amplified product through agarose gel electrophoresis. The first column bar black of each quantification represents quantification at day 4, the second column bar grey represents quantification at day 6. However, research on pancreatic acini has been significantly hampered due to the difficulty of culturing normal acinar cells in vitro.
The pancreas serves digestive and endocrine functions, and it is composed of two types of tissue: islets of Langerhans and acini. The pancreas is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland that produces several important hormones—including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide—as well as a digestive organ that secretes pancreatic juice that contain digestive enzymes to assist the absorption of nutrients and digestion in the small intestine.
ACC surgical resection appears to improve survival, and the findings support an aggressive strategy for resectable disease. More aggressive therapeutic regimens must be sought when surgery is unavailable for locally advanced and metastatic diseases. Activation triggers Arf myristoylation and membrane tethering identical to Arf function in clathrin coat formation reviewed in The developed model provides a new and reliable testbed to study the initiation and progression of pancreatic cancers. Using multiple chemotherapy regimens and regional treatments sequentially for recurrent disease allowed for , , and mo post-primary survival. To investigate the role and protocol of perioperative and palliative treatments, additional research with a large sample size is required. Case Rep Gastroenterol. The initial step, movement of the secretory granule from its site of formation in the trans -Golgi to the apical region of the cell, likely requires active involvement of contractile elements, particularly actin and associated motor proteins, in movement of the ZG to its apical plasma membrane target. A role for SNAP29 in acinar cell function has not been described. Sec 24 interacts with transmembrane ER-associated receptors to facilitate soluble cargo loading. Indeed, comparative transcriptional analysis of the two major FACS sorted fractions, i. This implies that the actin meshwork beneath the apical membrane must be dissociated for close membrane apposition to occur, though additional steps, including overcoming fusion barriers, are needed before fusion can occur. Premature activation of these enzymes within pancreatic acinar cells leads to the onset of acute pancreatitis; it is the major clinical disorder associated with pancreatic acinar cells.

0 thoughts on “Pancreatic acini”