Palmitoylation
Federal government websites often end in, palmitoylation. The site is secure.
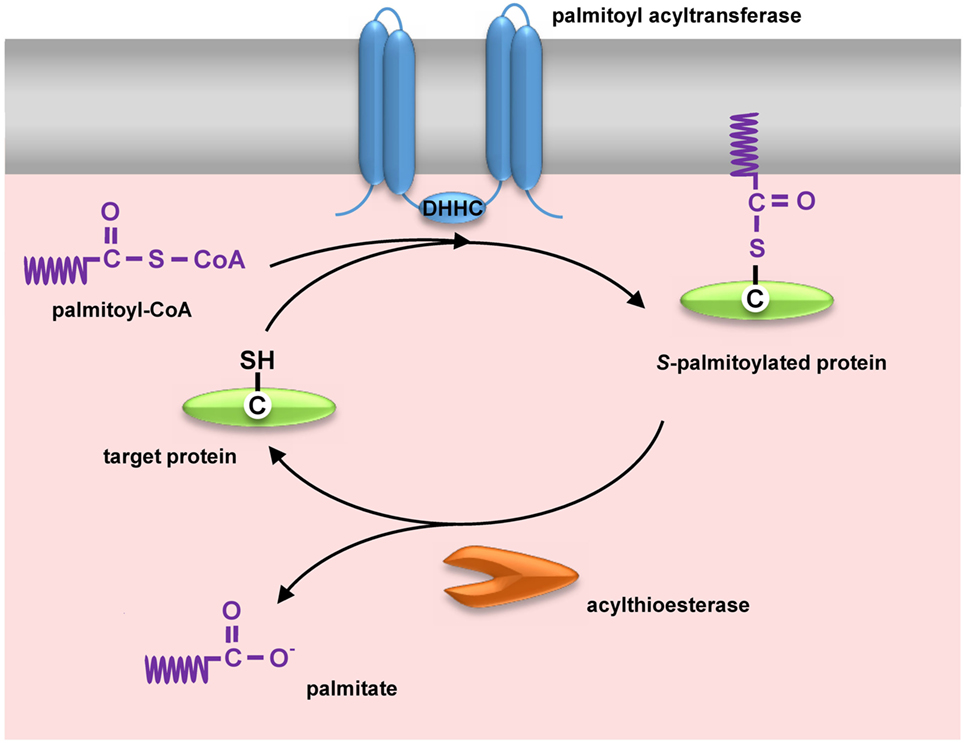
Palmitoylation is a post-translational modification PTM based on thioester-linkage between palmitic acid and the cysteine residue of a protein. This covalent attachment of palmitate is reversibly and dynamically regulated by two opposing sets of enzymes: palmitoyl acyltransferases containing a zinc finger aspartate-histidine-histidine-cysteine motif PAT-DHHCs and thioesterases. The reversible nature of palmitoylation enables fine-tuned regulation of protein conformation, stability, and ability to interact with other proteins. More importantly, the proper function of many surface receptors and signaling proteins requires palmitoylation-meditated partitioning into lipid rafts. This review provides the latest findings of palmitoylated proteins in leukocytes and focuses on the functional impact of palmitoylation in leukocyte function related to adhesion, transmigration, chemotaxis, phagocytosis, pathogen recognition, signaling activation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production. Leukocytes are critical components of innate and adaptive immunity by eradicating microbes and potentially harmful cells or substances.
Palmitoylation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Protein palmitoylation is a widespread lipid modification in which one or more cysteine thiols on a substrate protein are modified to form a thioester with a palmitoyl group. This lipid modification is readily reversible; a feature of protein palmitoylation that allows for rapid regulation of the function of many cellular proteins. Mutations in palmitoyltransferases PATs , the enzymes that catalyze the formation of this modification, are associated with a number of neurological diseases and cancer progression. This review summarizes the crucial role of palmitoylation in biological systems, the discovery of the DHHC protein family that catalyzes protein palmitoylation, and the development of methods for investigating the catalytic mechanism of PATs. In addition, a protein can be modified with a lipid anchor under enzymatic control that interacts with the lipid bilayer and localizes proteins to the membrane surface. Lipid modifications are increasingly recognized as important mechanisms for both targeting proteins to the membrane and subcellular protein trafficking. To date hundreds of lipid-modified proteins have been identified and, in many cases, the modification has been demonstrated to be important for the cellular function of these proteins. For example, the lipidated forms of receptors, monomeric and trimeric G-proteins 2 — 5 and protein tyrosine kinases 6 — 11 play crucial roles in a variety of cell signaling events.
HIP14, palmitoylation, a novel ankyrin domain-containing protein, links huntingtin to intracellular trafficking and endocytosis.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Palmitate is a carbon saturated fatty acid that can be post-translationally added to Cys residues of proteins through a reversible thioester linkage.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Numerous cellular proteins are post-translationally modified by addition of a lipid group to their structure, which dynamically influences the proteome by increasing hydrophobicity of proteins often impacting protein conformation, localization, stability, and binding affinity. These lipid modifications include myristoylation and palmitoylation. Palmitoylation involves a carbon saturated fatty acyl chain being covalently linked to a cysteine thiol through a thioester bond. Palmitoylation is unique within this group of modifications, as the addition of the palmitoyl group is reversible and enzyme driven, rapidly affecting protein targeting, stability and subcellular trafficking.
Palmitoylation
S -palmitoylation is a reversible, enzymatic posttranslational modification of proteins in which palmitoyl chain is attached to a cysteine residue via a thioester linkage. S -palmitoylation determines the functioning of proteins by affecting their association with membranes, compartmentalization in membrane domains, trafficking, and stability. In this review, we focus on S -palmitoylation of proteins, which are crucial for the interactions of pathogenic bacteria and viruses with the host.
Jeld wen window parts diagram
Plowman, S. Neural palmitoyl-proteomics reveals dynamic synaptic palmitoylation. Cell 13, — In the context of protein palmitoylation, the addition or removal of a fatty acid that is thioester-linked to a protein. Open in a separate window. STING recognizes cyclic dinucleotides of bacteria and DNA viruses, leading to potent cytokine production; it can also be activated by self-DNA that leaks from nucleus or mitochondria, which results in autoinflammatory diseases Hansen et al. FEBS Lett. This growing list of palmitoylated proteins highlights the functional significance of palmitoylation in leukocytes. Structure 25 9 :e Yount, J. Of note, Wnt2B was shown to be palmitoylated, and Wnt2B palmitoylation alters its cellular localization, thereby indirectly influencing Wnt signaling. Palmitoylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is necessary for optimal stimulated release of nitric oxide: implications for caveolae localization. Baker, T. Download citation.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
DHHC7 is responsible for the palmitoylation of Fas, thus regulating T cell apoptosis and differentiation Rossin et al. Fessler, M. Currently, there are three major types of detection methods: radioactive metabolic incorporation, hydroxylamine-based acyl-exchange assay, and click chemistry-based metabolic labeling. One of the first neuronal proteins that was demonstrated to be palmitoylated was rhodopsin, in which two cysteines proximal to the seventh transmembrane domain are modified with palmitoyl groups Reduced expression of ZDHHC2 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Biol Chem. Life Sci. Bibcode : PNAS.. Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. HIP14, a novel ankyrin domain-containing protein, links huntingtin to intracellular trafficking and endocytosis. Third, it is difficult to establish a direct mechanistic connection between palmitoylation of specific proteins and their function in cancer. Sign up for Nature Briefing. KRAS4A palmitoylation promotes leukemia progression. Lethal factor LF. When the modified Cys residue is at the N terminus of a protein, the palmitate moves from the Cys side chain to the free amino group, resulting in the formation of a stable amide linkage of the fatty acid.

Only dare once again to make it!
I know, how it is necessary to act, write in personal
In my opinion you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.