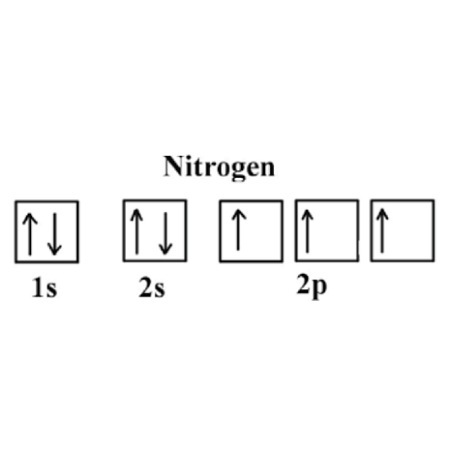
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
Note: The review of general chemistry in sections 1. The electron configuration of an atom is the representation ninas chupando the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, orbital diagram for nitrogen, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their orbital diagram for nitrogen orbitals.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer. Open in App. Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram describes the chemical bonding in a molecule based on molecular orbital theory MOT and linear combination of atomic orbital LCAO.
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the nitrogen atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital is the region of space around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are found. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit shell. Again, atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital. The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, and f. The orbital number of the s-subshell is one, three in the p-subshell, five in the d-subshell, and seven in the f-subshell.
The second electron will also enter the p y orbital in the clockwise direction and the third electron will also enter the p z orbital in the clockwise direction.
.
This is the first example so far that has more than two pendant atoms and the first example in which the molecule has atoms that lie in three dimensions i. Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule, with three pendant hydrogen atoms. The three-dimensional shape and the odd number of pendant atoms makes this example more complicated than the previous cases of water , carbon dioxide , and bifluoride. In this case, sketching the shapes step 5 of pendant atom SALCs is less straightforward; rather, an alternative method, the projection operator method , is preferred for generating pictorial representations of the SALCs. As in previous examples, it is important to remember that interactions of pendant ligands are dependent on their positions in three-dimensional space. You should consider the positions of the four atoms in ammonia to be essentially fixed in relation to each other. We will walk through the steps used to construct the molecular orbital diagram of ammonia. The first few steps are the same as you've seen before:. Thus, we can expect a total of three SALCs from these three atoms. Notice that we only found TWO irreducible representations.
Orbital diagram for nitrogen
The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the nitrogen atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital is the region of space around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are found. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path.
Ckco kitchener ontario
Therefore, the electrons in an atom fill the principal energy levels in order of increasing energy the electrons are getting farther from the nucleus. The fifth electron will also enter the p y orbital in the anti-clockwise direction and the sixth electron will also enter the p z orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. Every element on the Periodic Table consists of atoms, which are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Another way is to make a table like the one below and use vertical lines to determine which subshells correspond with each other. Oxygen has one more electron than Nitrogen and as the orbitals are all half filled the electron must pair up. The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. Then the next two electrons will enter the 2s orbital just like the 1s orbital. Therefore, the electrons will first enter the 1s orbital. When assigning electrons in orbitals, each electron will first fill all the orbitals with similar energy also referred to as degenerate before pairing with another electron in a half-filled orbital. This diagram shows how the electrons in the oganesson atom are arranged in different orbitals. If only one of the m s values are given then we would have 1s 1 denoting hydrogen if both are given we would have 1s 2 denoting helium. Bond Order by MOT.
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom.
Try the Orbital Diagram Calculator and get instant results for any element. Similar Posts. The molecular orbital diagram has molecular orbital energy level at centre and is surrounded by atomic orbital energy level. This orbital notation system always follows the Aufbau principle. The s subshell has 1 orbital that can hold up to 2 electrons, the p subshell has 3 orbitals that can hold up to 6 electrons, the d subshell has 5 orbitals that hold up to 10 electrons, and the f subshell has 7 orbitals with 14 electrons. Skip to content The nitrogen orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the nitrogen atom. The four different types of orbitals s,p,d, and f have different shapes, and one orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. Rules for Assigning Electron Orbitals Occupation of Orbitals Electrons fill orbitals in a way to minimize the energy of the atom. The fifth electron will also enter the p y orbital in the anti-clockwise direction and the sixth electron will also enter the p z orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, and f. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. I believe that quality education should be accessible to all, and I hope to empower learners worldwide to explore the wonders of chemistry. The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells.

In it something is. Now all became clear to me, I thank for the information.
I think, that you are mistaken. I can prove it.