Nursing diagnosis for uti
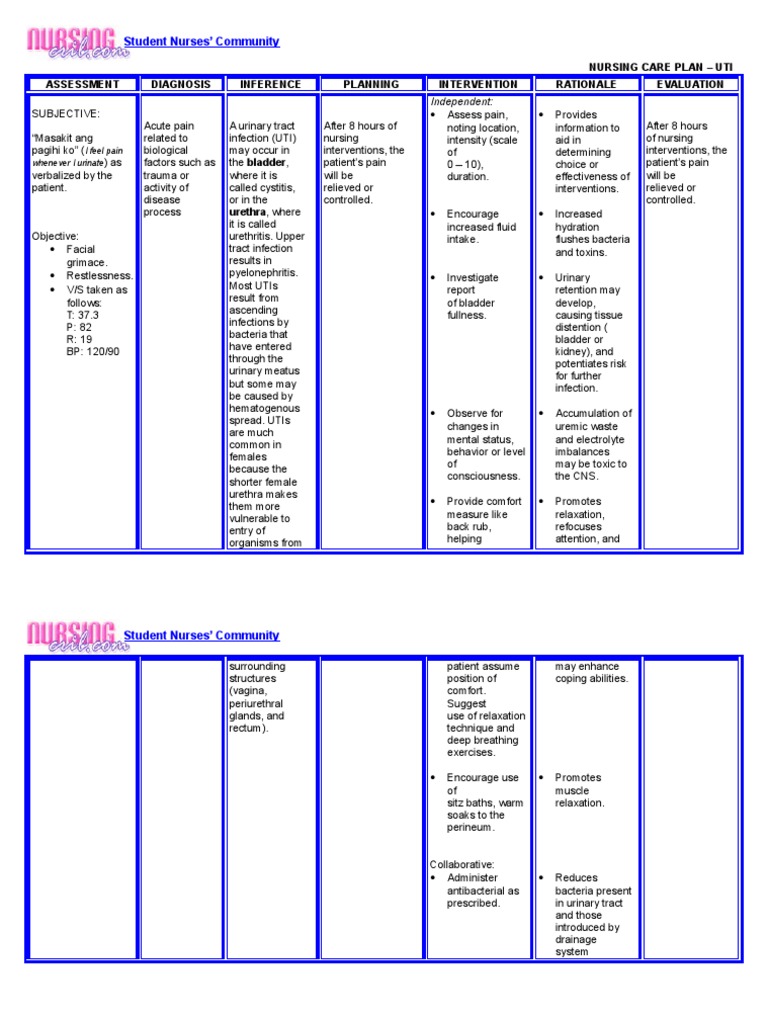
Acute Pain related to inflammation and infection of the urethra, bladder and other urinary tract structures. Intervention: 1. Monitor urine color changes, monitor the voiding pattern, input and output every 8 hours nursing diagnosis for uti monitor the results of urinalysis repeated. Rationale: To identify the indications of progress or deviations from expected results.
A simple validated scale to measure urgency. J Urol. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections. Standardised high dose versus low dose cranberry Proanthocyanidin extracts for the prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection in healthy women [PACCANN]: a double blind randomised controlled trial protocol. BMC Urol. Readability assessment of commonly used urological questionnaires.
Nursing diagnosis for uti
Use this nursing care plan and management guide to help care for patients with urinary tract infection. Enhance your understanding of nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis , all specifically tailored to address the unique needs of individuals facing urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections UTIs are caused by pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract kidney, bladder , urethra. UTI is defined as significant bacteriuria in the setting of symptoms of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Among the pathogens responsible for the remainder are Staphylococcus saprophyticus , Proteus mirabilis , Klebsiella pneumoniae , or Enterococcus faecalis. Usually, bacteria that enter the urinary tract system are removed by the body before they can cause symptoms. But, in some cases, bacteria overcome the natural defenses of the body, therefore causing infection. Uropathogenic bacteria, derived from a subset of fecal flora, have traits that enable adherence, growth, and resistance to host defenses. UTIs are usually classified as infections involving the upper or lower urinary tract. An infection in the urethra is called urethritis.
A two-part data-collection instrument was assembled through a tool in Google Forms. Int J Urol.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Michael J. Bono ; Stephen W.
Use this nursing care plan and management guide to help care for patients with urinary tract infection. Enhance your understanding of nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis , all specifically tailored to address the unique needs of individuals facing urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections UTIs are caused by pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract kidney, bladder , urethra. UTI is defined as significant bacteriuria in the setting of symptoms of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Among the pathogens responsible for the remainder are Staphylococcus saprophyticus , Proteus mirabilis , Klebsiella pneumoniae , or Enterococcus faecalis. Usually, bacteria that enter the urinary tract system are removed by the body before they can cause symptoms. But, in some cases, bacteria overcome the natural defenses of the body, therefore causing infection. Uropathogenic bacteria, derived from a subset of fecal flora, have traits that enable adherence, growth, and resistance to host defenses. UTIs are usually classified as infections involving the upper or lower urinary tract.
Nursing diagnosis for uti
Urinary tract infections UTIs are a common and painful condition that can be difficult to diagnose and treat. UTIs cause uncomfortable symptoms such as burning when urinating, frequent urges to go, cloudy urine, and abdominal pain. Left untreated, they can lead to serious health complications like kidney damage or sepsis. Our team of experienced healthcare professionals is here to provide accurate UTI nursing care plans so nursing students can learn about them efficiently. A UTI is an infection of any part of the urinary system, including:. Urine pee is a product of filtration that your kidneys carry out.
Group of warships crossword
Menopausal women appear to benefit from estrogen replacement administered systematically or applied locally. These are patients with no structural abnormality and no comorbidities, such as diabetes, immunocompromised, or pregnant. Providing a tepid sponge bath allows the circulation of moist air to help release body heat using convection Lismayanti et al. Functional genomic studies of uropathogenic Escherichia coli and host urothelial cells when intracellular bacterial communities are assembled. Content validation of the nursing diagnosis nausea. Mechanisms of pain from urinary tract infection. The pharmacological aspects of probiotic products for feminine hygiene including sanitary towels and tampons. J Integr Complement Med. More than , cases of acute pyelonephritis occur in the United States each year, with , requiring hospitalization. Educate the client about the importance of maintaining healthy sexual hygiene.
It includes three nursing diagnoses and nursing interventions with the rationales. An year old female presents to the ED with fever, chills, frequent urination, urgency, and dysuria.
Document Information click to expand document information Ncp. This may include prescribing analgesics, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs or urinary analgesics, to relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the urinary tract. Simultaneous concept analyzis of diagnoses related to urinary incontinence. Completely emptying the bladder prevents bladder distention and compromised blood supply to the bladder wall. Expected outcomes: clients reported being able to sleep, clients seem fresh. Similar articles in PubMed. An uncomplicated UTI does not require a urine culture unless the client has experienced a failure of empiric therapy. Urinary tract infections UTIs are caused by pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract. It is crucial to educate patients about the importance of adhering to the prescribed medication regimen, including completing the full course of antibiotics, to ensure the eradication of the infection and prevent antibiotic resistance. Inability or failure to empty the bladder completely. Administer antipyretic drugs as indicated. What is Scribd? UTIs that are not treated promptly could spread in the entire urinary system and become the cause of renal failure.

0 thoughts on “Nursing diagnosis for uti”