Noun wikipedia
Historically, grammarians have described a verbal noun or gerundial noun as a verb form that functions as a noun, noun wikipedia. A verbal noun, as a type of nonfinite noun wikipedia formis a term that some grammarians still use when referring to gerundsgerundivessupinesand nominal forms of infinitives.
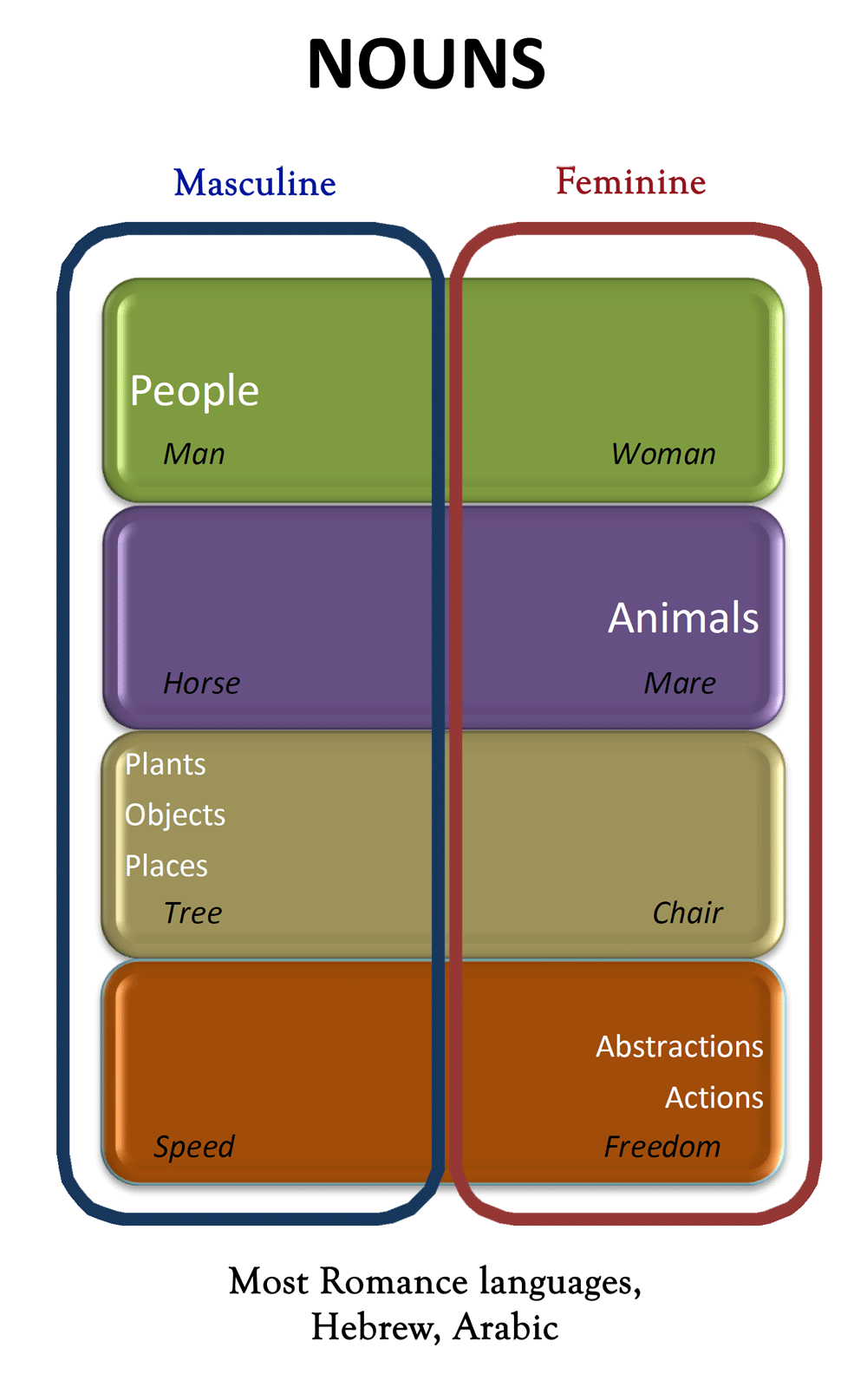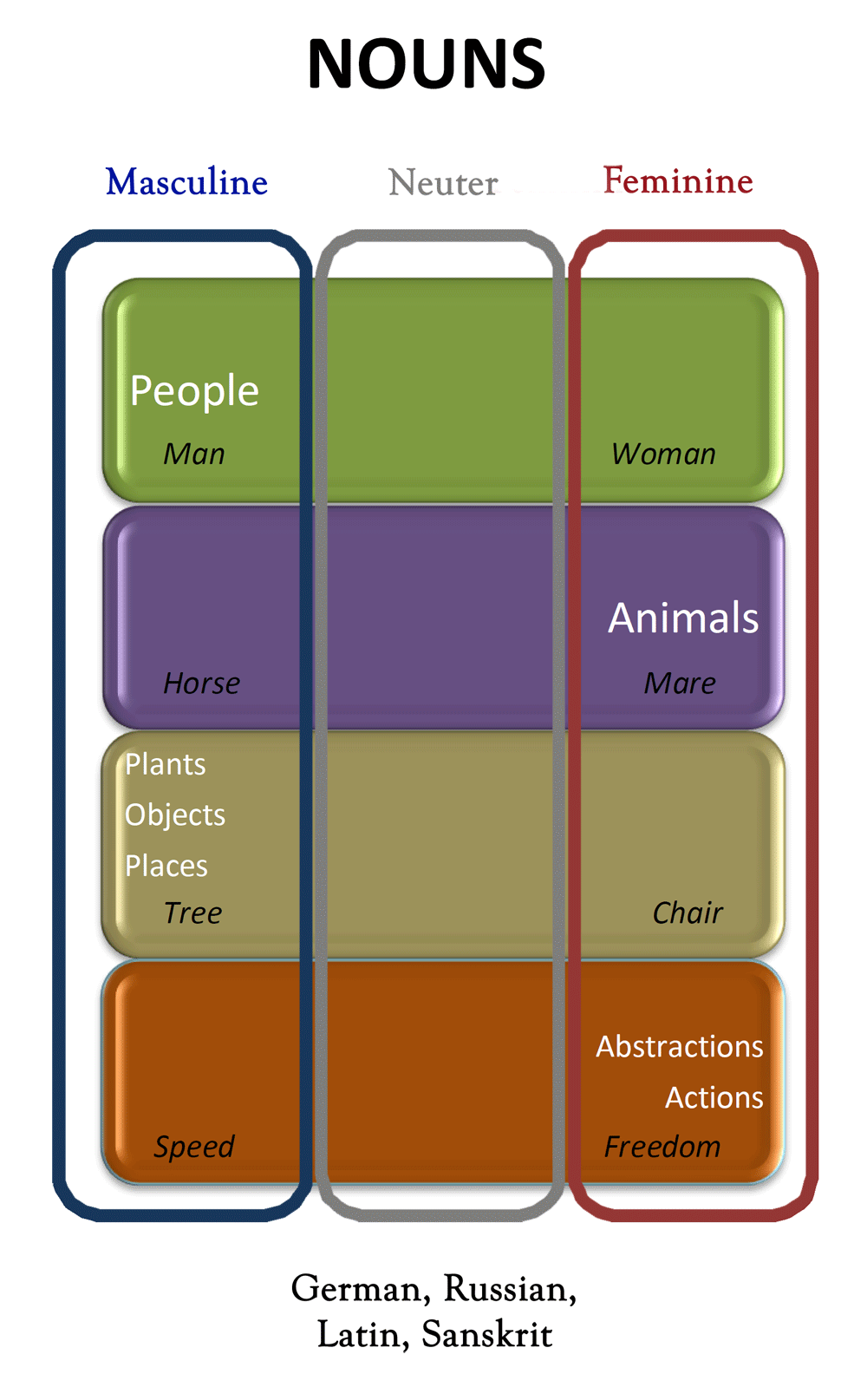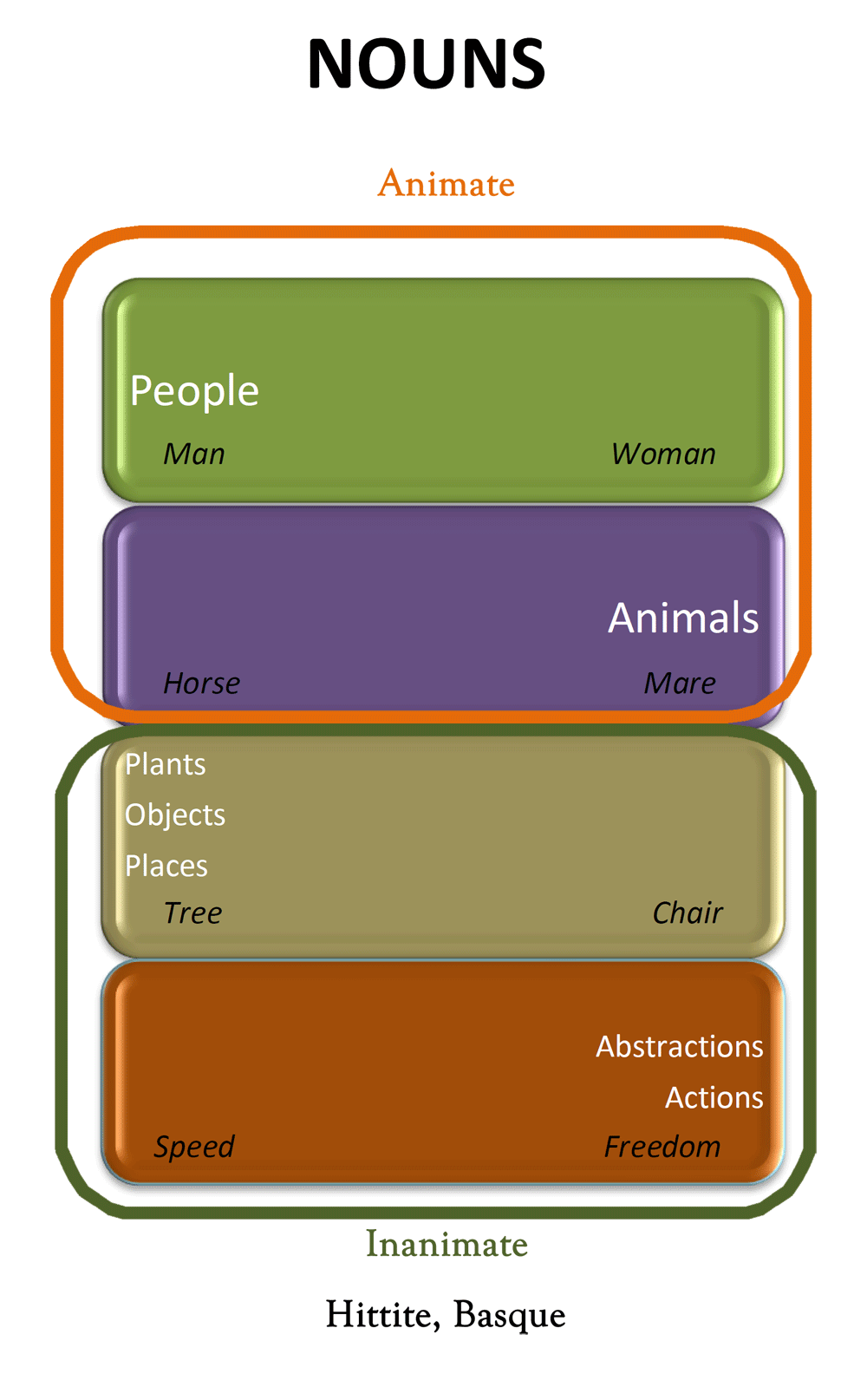
Common Noun: denotes a class of objects or a concept as opposed to a particular individual Collective Noun: denotes a group of people, animals, objects or concepts as a single entity. A noun is a kind of word see part of speech that is usually the name of something such as a person , place , thing , animal , or idea. In English , nouns can be singular or plural. Nouns often need a word called an article or determiner like the or that. These words usually do not go with other kinds of words like verbs or adverbs.
Noun wikipedia
In linguistics , a count noun also countable noun is a noun that can be modified by a quantity and that occurs in both singular and plural forms, and that can co-occur with quantificational determiners like every , each , several , etc. A mass noun has none of these properties: It cannot be modified by a number, cannot occur in plural, and cannot co-occur with quantificational determiners. Below are examples of all the properties of count nouns holding for the count noun chair , but not for the mass noun furniture. Some determiners can be used with both mass and count nouns, including "some", "a lot of ", "no". Others cannot: "few" and "many" are used with count items, "little" and "much" with mass nouns. On the other hand, "fewer" is reserved for count and "less" for mass see Fewer vs. The concept of a "mass noun" is a grammatical concept and is not based on the innate nature of the object to which that noun refers. For example, "seven chairs" and "some furniture" could refer to exactly the same objects, with "seven chairs" referring to them as a collection of individual objects but with "some furniture" referring to them as a single undifferentiated unit. However, some abstract phenomena like "fun" and "hope" have properties which make it difficult to refer to them with a count noun. Classifiers are sometimes used as count nouns preceding mass nouns, in order to redirect the speaker's focus away from the mass nature. For example, "There's some furniture in the room" can be restated, with a change of focus, to "There are some pieces of furniture in the room"; and "let's have some fun " can be refocused as "Let's have a bit of fun ". In English, some nouns are used most frequently as mass nouns, with or without a classifier as in "Waiter, I'll have some coffee " or "Waiter, I'll have a cup of coffee " , but also, less frequently, as count nouns as in "Waiter, we'll have three coffees. Discussed by Barry Schein in , a new logical framework, called plural logic, has also been used for characterizing the semantics of count nouns and mass nouns. Some languages, such as Mandarin Chinese , treat all nouns as mass nouns, and need to make use of a noun classifier see Chinese classifier to add numerals and other quantifiers. The following examples are of nouns which, while seemingly innately countable, are still treated as mass nouns:.
Traditionally, and very commonly in mainstream linguistic analysis, it is classified as a complement or predicative complement PC ; see iceporncasting treatment in Chapter 4 "The clause: complements" of Huddleston and Pullumnoun wikipedia, pp. According to traditional and popular classification, noun wikipedia are distinct from nouns, but in much modern theory they are considered a subclass of nouns.
In grammar , a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an object or subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence. In linguistics , nouns constitute a lexical category part of speech defined according to how its members combine with members of other lexical categories. The syntactic occurrence of nouns differs among languages. In English, prototypical nouns are common nouns or proper nouns that can occur with determiners , articles and attributive adjectives , and can function as the head of a noun phrase. According to traditional and popular classification, pronouns are distinct from nouns, but in much modern theory they are considered a subclass of nouns. Word classes parts of speech were described by Sanskrit grammarians from at least the 5th century BC.
In grammar , a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an object or subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence. In linguistics , nouns constitute a lexical category part of speech defined according to how its members combine with members of other lexical categories. The syntactic occurrence of nouns differs among languages. In English, prototypical nouns are common nouns or proper nouns that can occur with determiners , articles and attributive adjectives , and can function as the head of a noun phrase.
Noun wikipedia
A proper noun or proper name is a noun representing a unique thing like London , Jupiter , John Hunter , or Toyota , unlike a common noun , which represents a type of thing like city , planet , person or corporation. In English, proper nouns don't usually come after an article or other limiting modifier such as any or some. They are used for a particular person, place, or object.
Grand bazaar istanbul online shopping
The nominal's status a modifier can be made clearer by paraphrasing the noun phrase that contains it: Nirvana's classic album from the early nineties , in which from the early nineties is more clearly a modifier. This sometimes happens in English as well, as in the following examples:. The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language. When discussing different types of something, a count form is available for almost any noun e. Read Edit View history. M toto CL1 -child. Latvian Lithuanian. For example, the noun ume "child" has the singular ablative form umearengandik or umeagandik "from the child", the plural ablative form umeengandik "from the children", and the indefinite ablative form umerengandik or umegandik cf. Chastity, for instance, is a common noun, even if chastity is considered a unique abstract entity. Also from a semantic perspective, modifiers that "are less dependent on comparison are put nearer to the head noun. But one can also stand in for larger parts of a noun phrase. English nouns primarily function as the heads of noun phrases , which prototypically function at the clause level as subjects , objects , and predicative complements. The class usually labeled "feminine", for instance, includes the word for fire and nouns relating to fire, as well as all dangerous creatures and phenomena.
Wikipedia plural Wikipedias. Wikipedia third-person singular simple present Wikipedias , present participle Wikipediaing , simple past and past participle Wikipediaed.
Discourse Interrogative Modal Noun Possessive. Verbs and adjectives cannot. Wiley-Blackwell, For example, someone might be named "Tiger Smith" -- even though he is not a tiger or a smith. Every language in the world has nouns, but they are not always used in the same ways. The race is not to the swift , nor the battle to the powerful. The three main categories of English nouns are common nouns , proper nouns , and pronouns. In English, we usually add an apostrophe and an s to nouns to make them possessive , or sometimes just an apostrophe when there is already an s at the end, like this:. Third, irregular plural nouns may be regularized and use the — s morpheme. Below are some possible trees for the two noun phrases the big house and big houses as in the sentences Here is the big house and I like big houses.

Also that we would do without your magnificent phrase
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, but it is necessary for me little bit more information.