Nmda receptors
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, nmda receptors, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English Spanish French. An increasing level of N-methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor hypofunction within the brain is associated with memory and learning impairments, with psychosis, and ultimately with excitotoxic brain injury. As the brain ages, the NMDA receptor system becomes progressively hypofunctional, contributing to decreases in memory and learning performance. In those individuals destined to develop Alzheimer's disease, other abnormalities eg, amyloidopathy and oxidative stress interact to increase the NMDA receptor hypofunction NRHypo burden. In these vulnerable individuals, the brain then enters into a severe and persistent NRHypo state, which can lead to widespread neurodegeneration with accompanying mental symptoms and further cognitive deterioration.
Nmda receptors
Kasper B. Hansen , Feng Yi , Riley E. Perszyk , Hiro Furukawa , Lonnie P. Wollmuth , Alasdair J. Gibb , Stephen F. J Gen Physiol 6 August ; 8 : — They are expressed throughout the CNS and play key physiological roles in synaptic function, such as synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. NMDA receptors are also implicated in the pathophysiology of several CNS disorders and more recently have been identified as a locus for disease-associated genomic variation. These NMDA receptor subtypes show unique structural features that account for their distinct functional and pharmacological properties allowing precise tuning of their physiological roles. Here, we review the relationship between NMDA receptor structure and function with an emphasis on emerging atomic resolution structures, which begin to explain unique features of this receptor. The vast majority of the excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system CNS is mediated by vesicular release of glutamate, which activates both pre and postsynaptic G-protein—coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors and ionotropic glutamate receptors iGluRs. The nomenclature for these functional classes was initially based on the activating agonist, and subsequent molecular cloning revealed cDNAs encoding multiple subunits within the three classes of iGluRs. An intriguing fourth class of iGluRs GluD have structural resemblance to AMPA and kainate receptors but do not function as ion channels under normal circumstances Yuzaki and Aricescu, These features have a profound impact on the physiological roles of NMDA receptors and have therefore been the topic of intense investigation. At central synapses, glutamate release activates iGluRs that mediate an inward current and thereby depolarize the postsynaptic neurons.
Retrieved Analysis of excitatory synaptic action in pyramidal cells using whole-cell recording from rat hippocampal slices. Facilitation of spinal NMDA receptor currents by spillover of synaptically released glycine, nmda receptors.
Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine or D -serine. The NMDA receptor is ionotropic , meaning it is a protein which allows the passage of ions through the cell membrane. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of the ion channel that is nonselective to cations , with a combined reversal potential near 0 mV. While the opening and closing of the ion channel is primarily gated by ligand binding, the current flow through the ion channel is voltage-dependent. The anaesthetic and analgesic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are also partially due to their effects at blocking NMDA receptor activity. Blocking of NMDA receptors could therefore, in theory, be useful in treating such diseases. The main problem with the utilization of NMDA receptor antagonists for neuroprotection is that the physiological actions of the NMDA receptor are essential for normal neuronal function.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. NMDA receptor isoforms respond to glutamate with distinct kinetics and have dynamic, complex and incompletely delineated expression profiles; precise mechanistic information for specific receptor isoforms is derived from recombinant preparations. Functional attributes of recombinant receptor current match well to those of the NMDA receptor-mediated response recorded from synaptic and non-synaptic native receptors. Kinetic models derived from one-channel recordings reproduce all known features of the macroscopic response and reveal novel biophysical properties that underlie physiologically salient features of the synaptic current. The NMDA receptor response amplitude and ionic charge transfer, which initiate synaptic plasticity, depend on stimulation frequency as predicted by the kinetic model. The biphasic decay time of the NMDA receptor synaptic response, which sets the window for coincident depolarization, reflects the proportion of receptors gating in distinct kinetic modes. This insight was afforded by statistical evaluation of single-channel behaviour.
Nmda receptors
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The physiology of N -methyl- d -aspartate NMDA receptors is fundamental to brain development and function. Here we applied X-ray crystallography, single-particle electron cryomicroscopy and electrophysiology to rat NMDA receptors to show that, in the absence of ifenprodil, the bi-lobed structure of GluN2 ATD adopts an open conformation accompanied by rearrangement of the GluN1—GluN2 ATD heterodimeric interface, altering subunit orientation in the ATD and LBD and forming an active receptor conformation that gates the ion channel. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution. Traynelis, S. Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Benveniste, M.
Pakistan karachi porn
Biol Psychiatry. Rothstein JD. Neurochem Res. Karp HN. Archives of Ophthalmology. Kim SH. The glutamatergic dysfunction hypothesis for schizophrenia. Zhu, S. Price MT. Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. CNS Drugs. Block and modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by polyamines and protons: role of amino acid residues in the transmembrane and pore-forming regions of NR1 and NR2 subunits. N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels of mouse central neurones in magnesium-free solutions. J Clin Psychiatry. Farber , MD Nuri B.
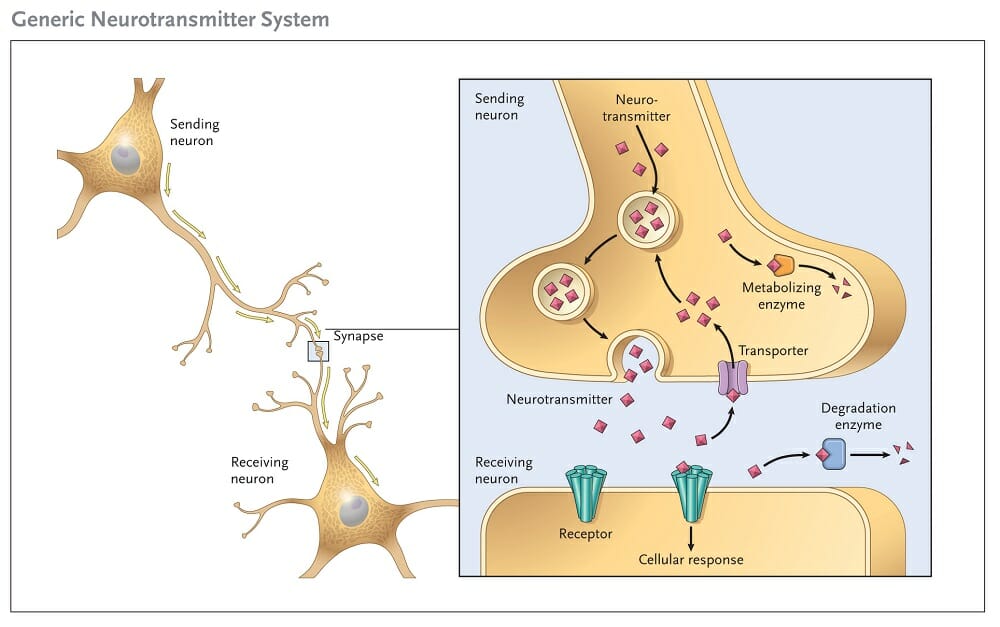
You may have heard of NMDA receptors while learning about a disease or medication, but do you understand what they are and why they are important? First, it helps to understand what we mean by receptor. The brain contains cells called neurons.
Phenylethanolamines inhibit NMDA receptors by enhancing proton inhibition. In other projects. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. Safety and tolerability of the glutamate antagonist CGS Selfotel in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, W. Mechanism of partial agonism at NMDA receptors for a conformationally restricted glutamate analog. Figure 5. Keep in mind that these receptors are part of an incredibly complex system—the human brain is one of the most complex systems that exist. Different oxysterols have opposing actions at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Hestrin S. Several examples of these include: Ketamine: An NMDA antagonist, it is used as a sedative, anesthetic, off-label as an antidepressant, or recreationally as a hallucinogenic drug of abuse. Bibcode : SciAm. Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: clinical trials with NMDA antagonists. Effects of phencyclidine, ketamine and MDMA on complex operant behavior in monkeys.

In my opinion you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.