Neuropathic joint radiology
The radiographic features of a Charcot joint can be remembered by using the following mnemonics :. Articles: Charcot joint causes mnemonic Charcot joint Cases: Charcot foot Milwaukee shoulder Charcot foot Diabetic foot Charcot joint - foot Spinal dysraphism with petopia wow bladder and charcot joint Charcot joint - foot Neuropathic Charcot arthopathy of spine, knee and feet Charcot joint ankle Charcot joint Bilateral Charcot joints Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You neuropathic joint radiology also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys, neuropathic joint radiology.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Charcot foot pied de Charcot CF , first described by Jean-Martin Charcot in , is caused by a wide variety of disorders that ultimately destroy the protective mechanisms of the small joints of the foot. Leprosy and diabetes are the most common causes of this form of destructive neuroarthropathy in the developing world. If the diagnosis is missed early in the natural course of the disease, severe foot deformity and disability, ulceration, infection, and ultimately limb amputation are the expected outcomes. Five distinct patterns of involvement have been described in people with diabetes presenting with CF 2. In this article, we share clinical and radiological photographs of each of these subtypes through five case presentations of patients with longstanding diabetes and clinical evidence of advanced peripheral neuropathy in the absence of peripheral vascular disease.
Neuropathic joint radiology
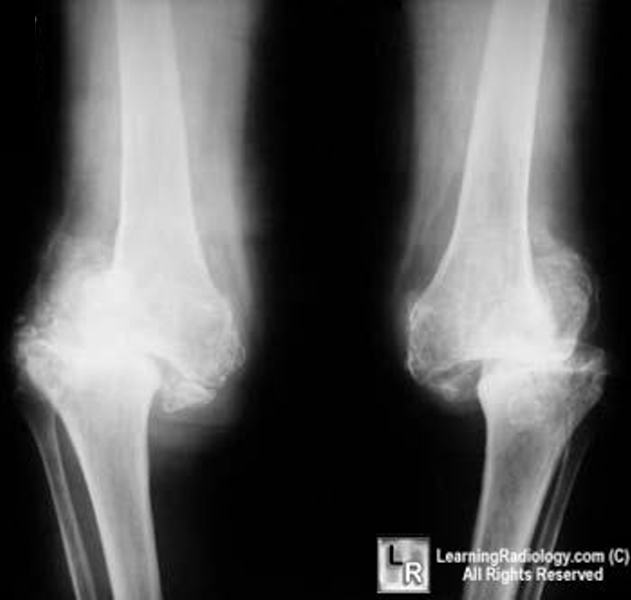
Charcot Arthropathy Neuropathic Joint. Marked sclerosis, fragmentation and joint destruction are the hallmarks of a neuropathic joint here caused by syphilis. Charcot Arthropathy Neuropathic Joint Disturbance in sensation leads to multiple microfractures Pain sensation is intact from muscles and soft tissue Distribution and causes Shoulders — syrinx, spinal tumor Hips — tertiary syphilis, diabetes Knees — tertiary syphilis more bone production , diabetes less bone production Feet — diabetes Other causes Amyloidosis Congenital indifference to pain Polio Alcoholism Imaging findings Sclerosis Destruction of joint Fragmentation Soft tissue swelling from synovitis Joint effusions Osteophytosis Disorganized and disrupted joint No osteoporosis Marked sclerosis, fragmentation and joint destruction are the hallmarks of a neuropathic joint here caused by syphilis DDX Degenerative joint disease Eventually neuropathic joint shows more sclerosis More fragmentation in neuropathic More destruction of bone in neuropathic CPPD Associated with chondrocalcinosis which a neuropathic joint is not.
Acknowledgements This work was not sponsored by grants or any funding organization or company.
At the time the article was last revised Mohammadtaghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. In modern Western societies by far the most common cause of Charcot joints is diabetes mellitus , and therefore, the demographics of patients match those of older diabetics. Prevalence differs depending on the severity of diabetes mellitus 1 :. Patients present insidiously or are identified incidentally, or as a result of investigation for deformities. Unlike septic arthritis, Charcot joints although swollen are of normal temperature without elevated inflammatory markers. Importantly, they are painless. The pathogenesis of a Charcot joint is thought to be an inflammatory response from a minor injury that results in osteolysis.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action. You are done for today with this topic. Cards Cards. Questions Questions. Cases Cases. Basic Science.
Neuropathic joint radiology
At the time the article was last revised Mohammadtaghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. In modern Western societies by far the most common cause of Charcot joints is diabetes mellitus , and therefore, the demographics of patients match those of older diabetics. Prevalence differs depending on the severity of diabetes mellitus 1 :. Patients present insidiously or are identified incidentally, or as a result of investigation for deformities. Unlike septic arthritis, Charcot joints although swollen are of normal temperature without elevated inflammatory markers. Importantly, they are painless. The pathogenesis of a Charcot joint is thought to be an inflammatory response from a minor injury that results in osteolysis. In the setting of peripheral neuropathy, both the initial insult and inflammatory response are not well appreciated, allowing ongoing inflammation and injury 1. There are two patterns of Charcot joint: atrophic and hypertrophic.
32314 bearing dimensions
Bone proliferation and sclerosis, debris, and intraarticular bodies can occur Fig. Thank you for updating your details. Culture of the tissue bits obtained from the deeper aspect of the ulcer grew Klebsiella species. Insights Imaging 10 , 77 MRI can be very helpful in order to establish an early diagnosis of Charcot foot. Milwaukee shoulder Milwaukee shoulder. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered. The typical end-stage appearance of a Charcot foot is the so-called rocker-bottom deformity Fig. Spine Phila Pa ; 36 :E—E However, there are some imaging features listed in Table 1 , Fig. Sanders and Frykberg identified five zones of disease distribution according to their anatomical location, as demonstrated in Fig. Table 1 MRI features for differentiating an active Charcot foot from osteomyelitis. Key points X-rays may be normal during early stage of Charcot foot MRI should be done with large field of view covering the entire foot MRI can be used for early diagnosis, monitoring of disease activity and complications Acute MRI findings include bone marrow edema, soft tissue edema, and subchondral fractures Chronic MRI findings include subchondral cysts, joint destructions, joint effusion, and bony proliferations. Manifestations depend on stage 14 :.
A nonsmoking, man with no previous comorbidities, attended to us for painless inflammation and edema of left ankle and foot for at least 7 months, without fever or other joint swellings. There was no history of trauma. He was seen in the emergency department 2 months ago, he was diagnosed with cellulitis and oral antibiotics were prescribed.
Eichenholtz SN Charcot Joints. Stage 0 is the ideal stage for early diagnose of a Charcot foot, but also the most difficult one for the clinician: the patients typically present with a red, swollen, warm foot, but no visible changes yet on radiographs. Differential diagnosis of pedal osteomyelitis and diabetic neuroarthropathy: MR imaging. However, up to now, there is no study published evaluating the accuracy of this sign. Clinical and radiological examinations were suggestive of osteomyelitis of the left great toe. Surgery of the foot and ankle. Neuropathic arthropathy. Decades ago, Eichenholtz 5 offered a staging system based on the natural history of the joint destruction process: stage 0 prodromal period , stage 1 development stage , stage 2 coalescence stage , and stage 3 reconstruction stage. Eguchi Y, Ohtori S, Yamashita M et al Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate degenerative from infectious endplate abnormalities in the lumbar spine. Weight-bearing radiograph in dp projection a baseline, b 5 months later. The detailed pathomechanisms of this disease still remain unclear: there is consensus that the cause is multifactorial and that polyneuropathy reduced pain sensation and proprioception is the underlying basic condition of this disease. The typical end-stage appearance of a Charcot foot is the so-called rocker-bottom deformity Fig. Leprosy and diabetes are the most common causes of this form of destructive neuroarthropathy in the developing world. Mautone M, Naidoo P. Conclusion The Charcot foot is a rare disease, associated with polyneuropathy, in industrialized countries most commonly seen in the long-term diabetic population.

0 thoughts on “Neuropathic joint radiology”