Nadh2 full form in biology
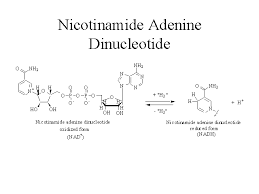
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD.
NADH is preferred except in cases where the use Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription. Please subscribe or login to access full text content. If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code. For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us.
Nadh2 full form in biology
The process of using oxygen and food molecules to produce energy, carbon dioxide, water, and waste products is known as cellular respiration. Respiration is the process through which humans transform food into energy by utilising water and oxygen. Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three metabolic processes of respiration. The redox cofactor FADH 2 , which stands for Flavin adenine dinucleotide, is generated during the last steps of the electron transport chain process. FADH 2 , or flavin adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor that is produced throughout the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration. Electrons produced in the Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle are transported to the Electron Transport Chain by a high-energy electron carrier. In the last stage of respiration, when the majority of the energy is lost and created from mitochondria, these two chemicals are utilised in the movement of electrons in the electron transport chain. The food we eat cannot be used directly as a source of energy. Metabolism, which entails a sequence of chemical events, aids in the conversion of energy from meals into energy that our bodies can utilise. This immediately available energy is stored in the nucleotide ATP adenosine triphosphate. The Krebs cycle works in a similar way to a wheel. Energy is generated and released every time it completes one full cycle.
Retrieved 8 January
.
Life is possible only if molecules and cells remain organized. Organization requires energy, as governed by the laws of thermodynamics. Just about anything a living organism does requires energy. We most often think of energy as food or calories. Cells, however, think of energy as ATP.
Nadh2 full form in biology
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Harrison barnes stats
The food we eat cannot be used directly as a source of energy. Enzyme cofactors. If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code. When bound in the active site of an oxidoreductase, the nicotinamide ring of the coenzyme is positioned so that it can accept a hydride from the other substrate. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. FEMS Microbiol. For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us. Cofactor Biosynthesis. Bibcode : Sci Bibcode : NatCo Alternatively, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from nutritive compounds such as niacin ; similar compounds are produced by reactions that break down the structure of NAD, providing a salvage pathway that recycles them back into their respective active form. Toggle limited content width.
During cellular respiration, the cells use these coenzymes to turn fuel from food into energy.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Main hazards. CAS Number. Download as PDF Printable version. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. In the last stage of respiration, when the majority of the energy is lost and created from mitochondria, these two chemicals are utilised in the movement of electrons in the electron transport chain. Password Please enter your Password. Current Pharmaceutical Design. Access more than. For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us. This ratio is an important component of what is called the redox state of a cell, a measurement that reflects both the metabolic activities and the health of cells. Some NAD is converted into the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate NADP , whose chemistry largely parallels that of NAD, though its predominant role is as a coenzyme in anabolic metabolism.

0 thoughts on “Nadh2 full form in biology”