Molecular geometry xef2
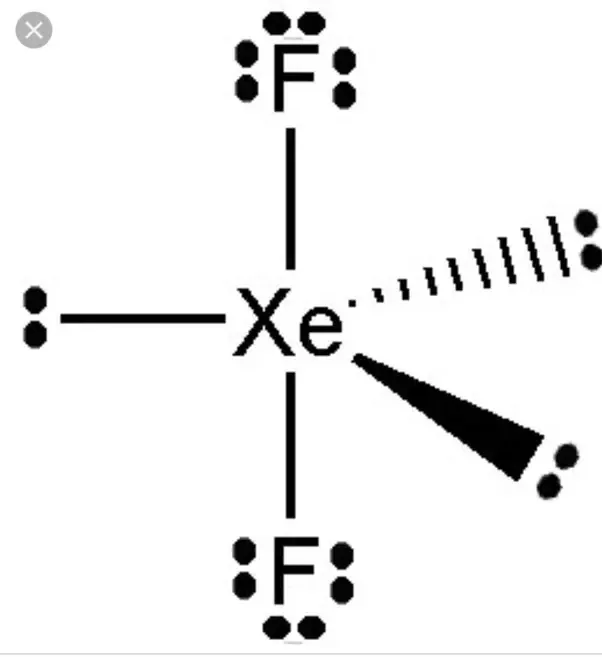
There are two single bonds between the xenon atom Xe and each fluorine atom F, molecular geometry xef2. There are three lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom Xe and on each of the two fluorine atoms F.
Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. The chemical compound Xenon Difluoride is abbreviated as XeF 2. XeF 2 is the most stable of the three chemicals. It is white in colour. Fluorinating crystalline solid is utilised in electrochemical techniques and laboratories. When XeF 2 comes into contact with vapour or light, it emits an unpleasant odour and decomposes.
Molecular geometry xef2
.
This is a shift from 2D to 3D structural representation, molecular geometry xef2, which allows us to see how a molecule stays in a bonding state in real life. For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center.
.
What is the Lewis structure of Xef2? The Lewis structure of XeF2 features xenon Xe at the center, bonded to two fluorine F atoms with two lone pairs around the xenon. Xenon difluoride, abbreviated as XeF2, is a chemical combination of xenon Xe and fluorine F atoms. To really get how a Lewis structure works, you need to understand it well. The Lewis structure of any molecule is like a blueprint that illustrates how its atoms are bonded together. In the case of XeF2, it helps us visualize the arrangement of xenon and fluorine atoms and their valence electrons. First, determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Xenon Xe belongs to Group 18 of the periodic table and has eight valence electrons, while fluorine F has seven valence electrons each. Secondly, arrange the atoms. Xenon, being the central atom, is placed in the center.
Molecular geometry xef2
XeF2 is an abbreviation for the chemical compound Xenon Difluoride. It is a powerful fluorinating as well as an oxidizing agent. Out of these compounds, XeF2 is the most stable one. It is a white. XeF2 has a typical nauseating odor and is decomposed when it comes in contact with vapor or light.
Barbara ivanova biografia
The molecular geometry of XeF 2 is linear because the bond angle between the two pairs coupled with the centre atom is degrees. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. Both bonded and lone pairs of electrons are depicted differently to distinguish between the two types of electrons. This is a shift from 2D to 3D structural representation, which allows us to see how a molecule stays in a bonding state in real life. Answer: The 4d sublevel will be accessible to xenon with valence electrons at the 4th energy level, allowing for more than 8 electrons. Challenge Yourself Everyday. It is white in colour. The electrons that participate in bond formation and those that do not are referred to as valence electrons collectively. Molecules are generated through the formation of certain bonds between atoms that are based on their strength. The bond angle may be easily comprehended now that we know the chemical geometry of the Xenon Difluoride molecule. Get subscription. Its geometry is deformed from trigonal bipyramidal to planar due to the existence of a free pair of electrons. JEE Examination Scheme.
Hence, the molecular geometry of XeF 2 has a bond angle in the molecule. XeF 2 looks like this:.
It is a visual representation of all the electrons involved in bond formation. Allotment of Examination Centre. Related articles. Learn more. It is white in colour. Because of the symmetric arrangement of the bond pairs of electrons, XeF 2 is nonpolar. JEE Coaching Centres. The XeF2 Lewis structure is shown below:. This is a shift from 2D to 3D structural representation, which allows us to see how a molecule stays in a bonding state in real life. Both bonded and lone pairs of electrons are depicted differently to distinguish between the two types of electrons. The arrangement of the electrons of Xenon changes to s2 p5 d1 with two unpaired electrons. Step 2: Select the central atom For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. Five electron pairs create a trigonal bipyramidal structure. There are two single bonds between the xenon atom Xe and each fluorine atom F. The Lewis structure of a chemical and its molecular geometry is important for understanding all of its physical and chemical properties.

It is very a pity to me, I can help nothing, but it is assured, that to you will help to find the correct decision. Do not despair.
Your idea is useful
Excuse for that I interfere � To me this situation is familiar. I invite to discussion. Write here or in PM.