Methanol line structure
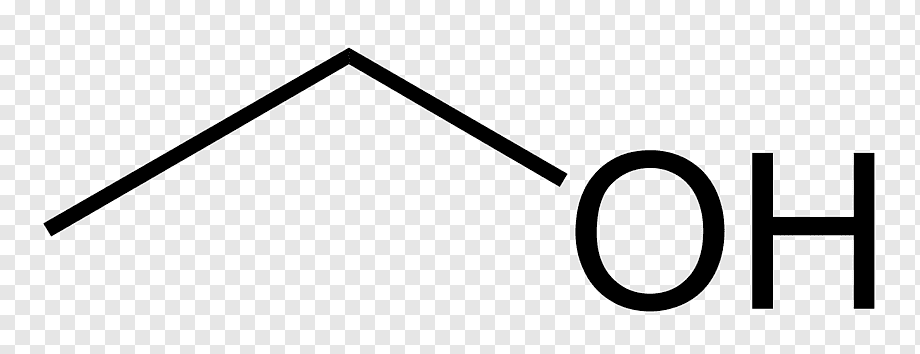
Methanol is simplest alcohol with chemical formula CH 3 OH. It is not a hydrocarbon since the hydroxyl group is chemically bonded to the carbon atom.
A chemical structure of a molecule includes the arrangement of atoms and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. The methanol molecule contains a total of 5 bond s. There are 1 non-H bond s and 1 hydroxyl group s. Images of the chemical structure of methanol are given below:. The 2D chemical structure image of methanol is also called skeletal formula, which is the standard notation for organic molecules. The carbon atoms in the chemical structure of methanol are implied to be located at the corner s and hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms are not indicated — each carbon atom is considered to be associated with enough hydrogen atoms to provide the carbon atom with four bonds.
Methanol line structure
Methanol is the simplest form of alcohol, which is colorless, volatile, and highly flammable. Methanol is also referred to as Methyl Alcohol or Wood Alcohol. It is an excellent fuel and has the potential to run automobiles, fuel cells, and gas stoves. It plays an essential role in various reactions, ranging from esterification to acting as a hydrogen source. In this article, we will study methanol, its structure, properties, production methods, along with its environmental impact in detail. Methanol is the simplest form of aliphatic alcohol, with the formula CH 3 OH. It is a light, volatile, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to ethanol. It is also known as wood alcohol. It is used in various applications, including as a precursor to other chemicals, in producing formaldehyde and acetic acid, and as a clean energy resource for fueling cars, trucks, buses, ships, fuel cells, boilers, and cook stoves. However, it is important to note that drinking or inhaling methanol can lead to severe health effects, including coma, convulsions, blindness, nervous system damage, and even death.
Any mammalian metabolite produced during a metabolic reaction in humans Homo sapiens. Images of the chemical structure of methanol are given below:.
Molfile expand. Self-ionizing solvent possessing both characteristics of Br o nsted acids and bases. Any bacterial metabolite produced during a metabolic reaction in Escherichia coli. Any mammalian metabolite produced during a metabolic reaction in humans Homo sapiens. Any bacterial metabolite produced during a metabolic reaction in Mycoplasma genitalium.
We use several kinds of formulas to describe organic compounds. A molecular formula shows only the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule. A structural formula shows all the carbon and hydrogen atoms and the bonds attaching them. Thus, structural formulas identify the specific isomers by showing the order of attachment of the various atoms. Chemists often use condensed structural formulas to alleviate these problems.
Methanol line structure
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl OH functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH, where R is an alkyl group. Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol ethanol , the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one of a family of organic compounds known as alcohols. The family also includes such familiar substances as cholesterol and the carbohydrates. Alcohols with one to four carbon atoms are frequently called by common names, in which the name of the alkyl group is followed by the word alcohol :. Ten carbon atoms in the LCC makes the compound a derivative of decane rule 1 , and the OH on the third carbon atom makes it a 3-decanol rule 2.
Internet outage alberta
Save Article. Read full article at Wikipedia. Distance formula - Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Maths. The radius of the spheres is therefore smaller than the rod lengths in order to provide a clearer view of the atoms and bonds throughout the chemical structure model of methanol. Methanol is extremely poisonous and flammable. It is used in various applications, including as a precursor to other chemicals, in producing formaldehyde and acetic acid, and as a clean energy resource for fueling cars, trucks, buses, ships, fuel cells, boilers, and cook stoves. They are part of same homologous series and differ by -CH 2 group and 14 units of mass. What kind of Experience do you want to share? Lithium Hydroxide LiOH. It is a flammable, light, poisonous liquid. Here are some of the leading environmental impacts of methanol:. Roles Classification.
The purpose of the fee is to recover costs associated with the development of data collections included in such sites. Your institution may already be a subscriber.
Any bacterial metabolite produced during a metabolic reaction in Escherichia coli. Steam-Reforming Natural Gas: This is the most common method for producing methanol. Contribute your expertise and make a difference in the GeeksforGeeks portal. Save Article. Please correct it or use other email address. Add Other Experiences. Optical Activity. Contribute to the GeeksforGeeks community and help create better learning resources for all. This reaction is commonly used in the production of biodiesel, where methanol reacts with fatty acids to form methyl esters. Found in breast milk ENVO Your result is as below.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.