Met office northern lights map
Photo courtesy of Jim Henderson Photography click to enlarge What is the cause of aurora?
Space weather describes changing environmental conditions in near-Earth space. Learn more about Space Weather. The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions. Otherwise no significant enhancements are forecast, with visible aurora unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb, but visible aurora is unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. Space Weather Forecast Headline: High solar activity.
Met office northern lights map
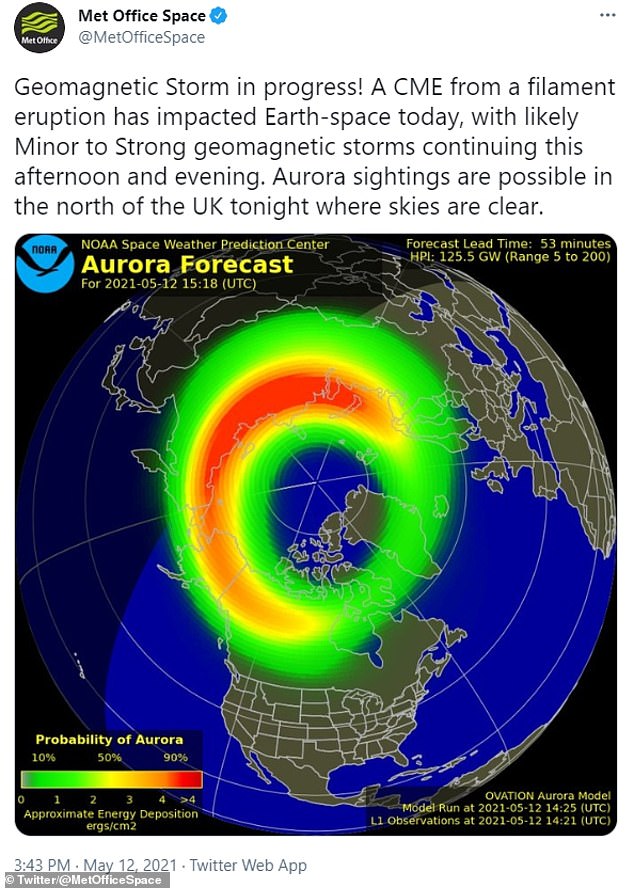
This is a short-term forecast of the location and intensity of the aurora. The forecast lead time is the time it takes for the solar wind to travel from the L1 observation point to Earth. The two maps show the North and South poles of Earth respectively. The green ovals turn red when the aurora is forecasted to be more intense. The sunlit side of Earth is indicated by the lighter blue of the ocean and the lighter color of the continents. Aurora can often be observed somewhere on Earth from just after sunset or just before sunrise. The aurora is not visible during daylight hours. The aurora does not need to be directly overhead but can be observed from as much as a km away when the aurora is bright and if conditions are right. The aurora is an indicator of the current geomagnetic storm conditions and provides situational awareness for a number of technologies. It is closely related to the ground induce currents that impact electric power transition. For many people, the aurora is a beautiful nighttime phenomenon that is worth traveling to arctic regions just to observe. It is the only way for most people to actually experience space weather.
Background colour indicates alert status of magnetometer. It is closely related to the ground induce currents that impact electric power transition. The excited molecule is unstable and will give up its extra energy by emitting light.
More information on the map and the different layers available here. We have collaborated with the Aurorasaurus citizen science project to bring real-time aurora reports to our aurora map. These reports will help you determine if the aurora is being seen from anywhere in the UK. Read more about the Aurorasaurus collaboration here and submit your own report to Aurorasaurus to see it appear on the map! If you know of any good locations for photographing the aurora please contact us ; we are looking for specific sites with picturesque horizons, interesting foregrounds or opportunities for framing a shot in a unique way. Any details you can include about the site would be very helpful. The more opaque darker the green, the more likely it is that an aurora will be visible overhead.
Find out about how and why the northern lights form, and where to see them in the UK. The northern lights also known as aurora borealis appear as large areas of colour including pale green, pink, shades of red, yellow, blue and violet in the direction due north. During a weak aurora, the colours are very faint and spread out whereas an intense aurora features greater numbers of and brighter colours which can be seen higher in the sky with a distinct arc. The northern lights are best seen in darkness, away from any light pollution. The lights generally extend from 50 miles to as high as miles above the Earth's surface. The northern lights occur as a consequence of solar activity and result from collisions of charged particles in the solar wind colliding with molecules in the Earth's upper atmosphere. Solar winds are charged particles that stream away from the Sun at speeds of around 1 million miles per hour. When the magnetic polarity of the solar wind is opposite to the Earth's magnetic field, the two magnetic fields combine allowing these energetic particles to flow into the Earth's magnetic north and south poles. Auroras usually occur in a band called the annulus a ring about 1, miles across centred on the magnetic pole.
Met office northern lights map
Information about the auroras - what are they and when are you likely to be able to see them This is a very rare occurrence. During more moderate to strong geomagnetic storms Kp , the Aurora borealis often moves southwards across southern Iceland or towards the Faeroes. These auroras can be faintly visible from the UK because they occur at high altitudes. The Sun goes through an 11 year solar cycle, from solar minimum, through solar maximum and back to solar minimum. Solar maximum occurred in early so we are now in the declining phase of the solar cycle.
Faro ölçüm cihazı
Southern Hemisphere. The northern lights also known as aurora borealis appear as large areas of colour including pale green, pink, shades of red, yellow, blue and violet in the direction due north. Or use a lake or water, which will create reflections and make for a more interesting picture. The aurora does not need to be directly overhead but can be observed from as much as a km away when the aurora is bright and if conditions are right. Coronal holes are the sources of high speed solar wind streams. View all space weather articles. The northern lights are best seen in darkness, away from any light pollution. The northern lights occur as a consequence of solar activity and result from collisions of charged particles in the solar wind colliding with molecules in the Earth's upper atmosphere. For the best results there are some tips that will help you get the most from your camera and once you have mastered photographing auroras you can start to experiment about where you photograph from and what you include in your photograph to create a truly stunning picture. More information on the map and the different layers available here. One of these is the Kp index which ranks the variations in geomagnetic activity from 0 to 9, in 3-hour intervals. Help us improve our website Take our short survey. Southern Hemisphere The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb, but visible aurora is unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes.
AuroraMap is a live Northern Lights forecast map.
Camera settings. Thumbs up: aurora seen. Help us improve our website Take our short survey. Southern Hemisphere The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb, but visible aurora is unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. How to take photos of the auroras. Take a flask of hot tea. Today we can explain the origins or auroras, and even predict them, through science and careful observation. Site of recent aurora photograph. All-sky camera or webcam. On their way down these particles are slowed down by Earth's atmosphere, which acts as a shield. You might also like. Photo courtesy of Jim Henderson Photography click to enlarge.

It seems to me it is good idea. I agree with you.
And I have faced it. We can communicate on this theme.
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.