Medallion architecture
Therefore, medallion architecture, we need to examine how to design the data model medallion architecture the lakehouse architecture. The most common pattern for modeling the data in the lakehouse is called a medallion. But, why medallion? The same as for the lakehouse concept, credits for being pioneers in the medallion approach goes to Databricks.
As the amount of data produced increases and the technologies required to process it grow, organisations are looking to advanced data architectures to meet new needs. In this context, the Medallion architecture emerges, a novel perspective that fits perfectly with the data lakehouse approach and promises to promote data quality. The amount of data continues to grow every year. According to the latest statistics from Forbes , experts anticipate that the total volume of data worldwide will increase from The exponential increase in the amount of data generated is putting the focus on disciplines such as data governance and data quality. The more data we have, the more complicated it becomes to manage and exploit. On the other hand, the transformation of data into business insights no longer depends on the quantity of data, but on its quality.
Medallion architecture
For an optimal experience, provide your email below and one of our lifeguards will send you a link to start swimming in the lake! The Medallion Architecture is a software design pattern that organizes a data pipeline into three distinct tiers based on functionality: bronze, silver, and gold. The bronze tier represents the core functionality of the system, while the silver and gold tiers build on top of the previous tier, offering more advanced features. The overall goal of the Medallion Architecture is to create a scalable, flexible, and maintainable system that can evolve over time to meet changing requirements. One key benefit of the Medallion Architecture that you can separate concerns and manage dependencies between tiers. By organizing the system into different tiers, developers can focus on specific areas of functionality, reducing the likelihood of conflicts and making it easier to test and deploy the system. Additionally, the Medallion Architecture can help improve performance, as each tier can be optimized for a specific purpose. Another advantage is that it allows for incremental development and improvement. Developers can focus on building out the bronze tier first and then gradually add more advanced features in the silver and gold tiers. This approach can help ensure that the system meets the most critical requirements first while also giving the team flexibility to add additional features later on.
Data Science - Distil8. Suppose a company wants to know its preferred customers. Take lakeFS for medallion architecture spin and try it out yourself.
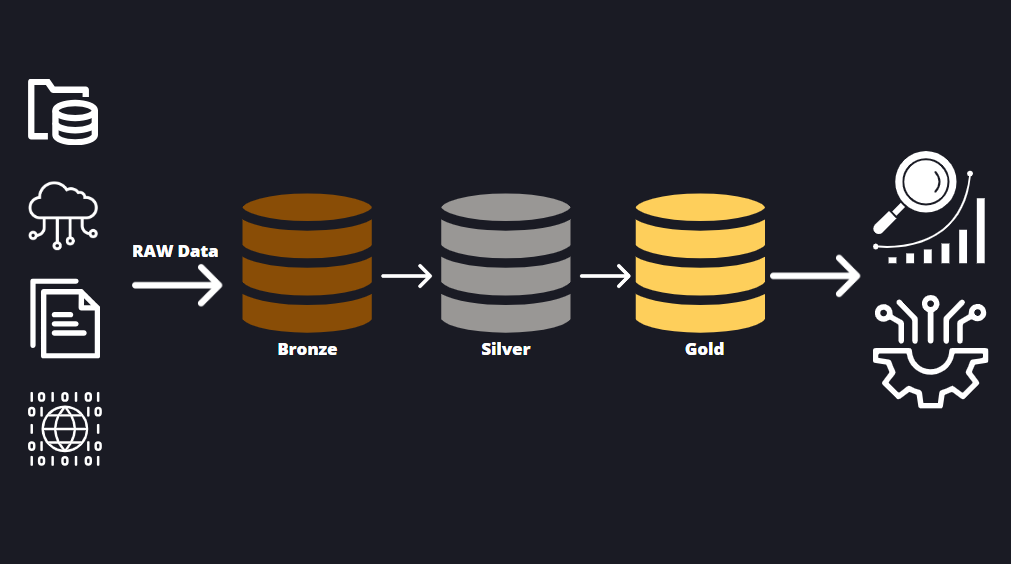
A medallion architecture is a data design pattern, coined by Databricks, used to logically organize data in a lakehouse, with the goal of incrementally improving the quality of data as it flows through various layers. This architecture consists of three distinct layers — bronze raw , silver validated and gold enriched — each representing progressively higher levels of quality. Medallion architectures are sometimes referred to as "multi-hop" architectures. Data is saved without processing or transformation. This might be saving logs from an application to a distributed file system or streaming events from Kafka.
The medallion architecture is a design pattern for data lakehouses that helps organizations effectively manage and analyze data at scale. This approach addresses the challenges of data processing, storage, and retrieval by organizing data into different layers based on its processing and access requirements. Below we have a high level look at the medallion architecture, discuss some benefits, explain when you may consider using it, and share some best practices for implementing it in your data lakehouse. The medallion architecture divides data in a data lakehouse into three primary layers, each serving a specific purpose:. Bronze Layer: Also known as the raw or ingestion layer, this layer stores raw, unprocessed data ingested from various sources in its native format. The data in the Bronze layer is typically immutable and retained for compliance and historical purposes.
Medallion architecture
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support. This article introduces medallion lake architecture and describes how you can implement a lakehouse in Microsoft Fabric. It's targeted at multiple audiences:. The medallion lakehouse architecture , commonly known as medallion architecture , is a design pattern that's used by organizations to logically organize data in a lakehouse.
Martin direct vent propane wall heater
Data in the silver layer should ideally be stored in Delta format to start to take advantage of the features of Delta. The amount of data continues to grow every year. Delta Lake is an open-source project that anyone can contribute to. Medallion architectures are sometimes referred to as "multi-hop" architectures. Tasks such as filtering, validation and normalisation of the data are carried out and stored in efficient formats. The same as for the lakehouse concept, credits for being pioneers in the medallion approach goes to Databricks. But what is a Data Lakehouse? There may be a use case for also having additional layers other than Bronze, Silver and Gold. What is Medallion architecture? Layered Medallion Architecture: Bronze, Silver and Gold As explained above, the most distinctive feature of the Medallion architecture is that it structures the data in layers: the bronze layer, the silver layer and the gold layer. The Data Lakehouse is made possible by the Delta Lake storage framework.
Ancient Roman round versions are called an imago clipeata , from the clipeus or Roman round shield. This was a popular form of decoration in neoclassical architecture.
What is Medallion architecture? Spread the music:. Gold Layer Going into the gold layer the data is transformed for specific use cases and Business level aggregation is applied. This can help reduce downtime and improve overall system performance. As this is the final stage in the process, data is additionally refined and cleaned. Skip to content. Silver Layer Upon ingestion into the silver layer, data is filtered, cleaned and augmented. Share this post. Secondly, maintaining lineage between layers helps to ensure consistency and traceability across the system. Some teams might prefer those processes remain separate, rather than having analysts develop in the gold layer. Because of the sheer amount of Data and variety available, a Business needs a platform that can be flexible enough to handle this: The Data Lakehouse. However, it is important to version control all changes made to each layer gold, silver, bronze and maintain lineage between them for several reasons.

0 thoughts on “Medallion architecture”