Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Either your mannheimia haemolytica wiki browser doesn't support Javascript or it is currently turned off. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page.
The Pasteurella and Mannheimia species are small, Gram-negative bacilli or coccobacilli. They are common commensals of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal mucosa of animals. From WikiVet English. Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Pasteurella and Mannheimia species.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
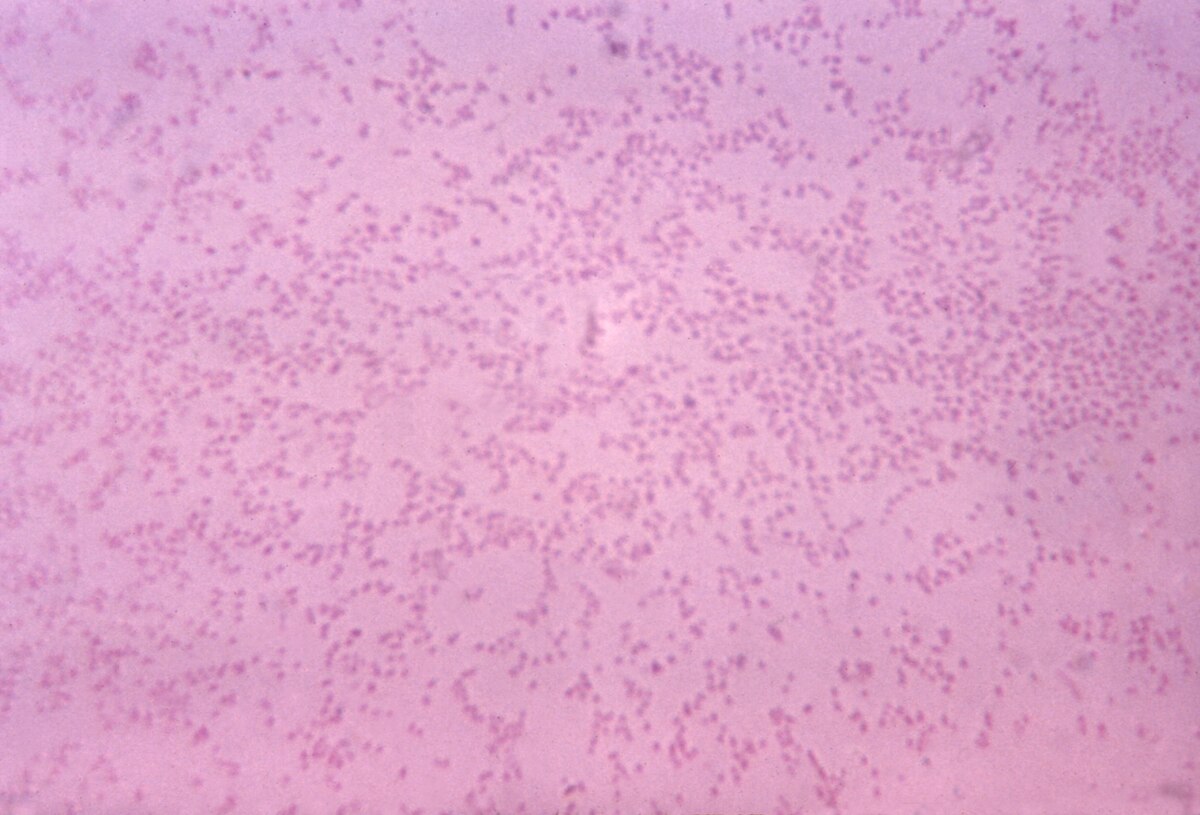
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless. All are Mannheimia A biotypes and the strains often produce a cytotoxin, known as leukotoxin, which kills leukocytes of ruminants. Leukotoxin is a member of the RTX group toxins, and is probably largely responsible for the pathogenicity of the bacteria in septicaemia and pneumonia. From WikiVet English. Mannheimia haemolytica. Also known as: Pasteurella haemolytica — M. Mannheimia haemolytica Learning Resources. Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in. Namespaces Page Discussion.
The term "pasteurellosis" is often still applied to mannheimiosis, although such usage has declined. Cited by: 12 articles PMID:
Pasteurellosis is an infection with a species of the bacterial genus Pasteurella , [1] which is found in humans and other animals. Pasteurella multocida subspecies P. In animals, it can originate in fulminant septicaemia chicken cholera , but is also a common commensal. Until taxonomic revision in , [3] Mannheimia spp. The term "pasteurellosis" is often still applied to mannheimiosis, although such usage has declined.
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 is the bacterial pathogen most frequently isolated from the lungs of recently weaned feedlot cattle with bovine respiratory disease BRD and in dairy, beef or veal calves with enzootic pneumonia. Although less frequently cultured, Pasteurella multocida is also an important cause of bacterial pneumonia and recently has been found with increasing frequency relative to Mannheimia haemolytica in feedlot cattle suffering from BRD. Histophilus somni is also recognized as an important pathogen in enzootic pneumonia and in some cases of BRD. In addition, Histophilus somni is an important bacterial agent that may cause outbreaks of myocarditis and pleuritis. Bibersteinia trehalosi has been emerging as a major cause of cases of acute BRD in cattle. These bacteria are all normal inhabitants of the nasopharynx of cattle see Histophilosis Histophilosis. When pulmonary abscessation occurs, generally in association with chronic pneumonia, Mycoplasma bovis is frequently isolated and Trueperella pyogenes can also be found in association with pulmonary abscessation. Under normal conditions, M haemolytica remains confined to the upper respiratory tract, in particular the tonsillar crypts, and is difficult to culture from healthy cattle. After stress or viral infection, the replication rate of M haemolytica in the upper respiratory tract increases rapidly, as does the likelihood of culturing the bacterium. During this log phase of growth of the organism in the lungs, virulence factors such as leukotoxin are elaborated by M haemolytica.
Veterinarian navarre ohio
Pseudomonadota -associated Gram-negative bacterial infections. Cited by: articles PMID: Abstract Objective To perform a comprehensive phenotypic characterisation of 35 isolates of bacteria previously identified as haemolytic Pasteurella-Actinobacillus and obtained from cattle and sheep. A Pasteurella and Mannheimia species - Overview. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page. Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in. B Bibersteinia trehalosi. Subcutaneous botryomycosis due to Bibersteinia trehalosi in a Texas Longhorn steer. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. From WikiVet English. Affiliations 1. To arrive at the top five similar articles we use a word-weighted algorithm to compare words from the Title and Abstract of each citation. External links service. Grant finder.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Also known as: Pasteurella haemolytica — M. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Leukotoxin is a member of the RTX group toxins, and is probably largely responsible for the pathogenicity of the bacteria in septicaemia and pneumonia. Mannheimia glucosida. Views Article Discussion Edit this page History. It often acts with other infectious agents, such as Chlamydia and Mycoplasma species and viruses. Molecular study on Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia granulomatis from Kenyan Camels Camelus dromedarius. Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. Developers Developer resources. Categories : Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Zoonotic bacterial diseases Bird diseases Mammal diseases. Medical condition.

0 thoughts on “Mannheimia haemolytica wiki”