Long non coding rna
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site long non coding rna styles and JavaScript.
The development and application of whole genome sequencing technology has greatly broadened our horizons on the capabilities of long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs. LncRNAs are more than nucleotides in length and lack protein-coding potential. Increasing evidence indicates that lncRNAs exert an irreplaceable role in tumor initiation, progression, as well as metastasis, and are novel molecular biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer patients. Furthermore, lncRNAs and the pathways they influence might represent promising therapeutic targets for a number of tumors. Here, we discuss the recent advances in understanding of the specific regulatory mechanisms of lncRNAs. We focused on the signal, decoy, guide, and scaffold functions of lncRNAs at the epigenetic, transcription, and post-transcription levels in cancer cells. Additionally, we summarize the research strategies used to investigate the roles of lncRNAs in tumors, including lncRNAs screening, lncRNAs characteristic analyses, functional studies, and molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs.
Long non coding rna
Long non-coding transcripts are found in many species. It has been suggested through multiple studies that testis , [8] and neural tissues express the greatest amount of long non-coding RNAs of any tissue type. In comparison to mammals relatively few studies have focused on the prevalence of lncRNAs in plants. In the landscape of the mammalian genome was described as numerous 'foci' of transcription that are separated by long stretches of intergenic space. The GENCODE consortium has collated and analysed a comprehensive set of human lncRNA annotations and their genomic organisation, modifications, cellular locations and tissue expression profiles. There has been considerable debate about whether lncRNAs have been misannotated and do in fact encode proteins. Several lncRNAs have been found to in fact encode for peptides with biologically significant function. However, further investigations into vertebrate lncRNAs revealed that while lncRNAs are conserved in sequence, they are not conserved in transcription. Some argue that these observations suggest non-functionality of the majority of lncRNAs, [43] [44] [45] while others argue that they may be indicative of rapid species -specific adaptive selection. While the turnover of lncRNA transcription is much higher than initially expected, it is important to note that still, hundreds of lncRNAs are conserved at the sequence level. There have been several attempts to delineate the different categories of selection signatures seen amongst lncRNAs including: lncRNAs with strong sequence conservation across the entire length of the gene , lncRNAs in which only a portion of the transcript e. Despite claims that the majority of long noncoding RNAs in mammals are likely to be functional, [52] [53] it seems likely that most of them are transcriptional noise and only a relatively small proportion has been demonstrated to be biologically relevant. In eukaryotes , RNA transcription is a tightly regulated process.
Hahn, S.
Molecular Cancer volume 10 , Article number: 38 Cite this article. Metrics details. Long non-coding RNAs lncRNAs are emerging as new players in the cancer paradigm demonstrating potential roles in both oncogenic and tumor suppressive pathways. These novel genes are frequently aberrantly expressed in a variety of human cancers, however the biological functions of the vast majority remain unknown. Recently, evidence has begun to accumulate describing the molecular mechanisms by which these RNA species function, providing insight into the functional roles they may play in tumorigenesis. In this review, we highlight the emerging functional role of lncRNAs in human cancer.
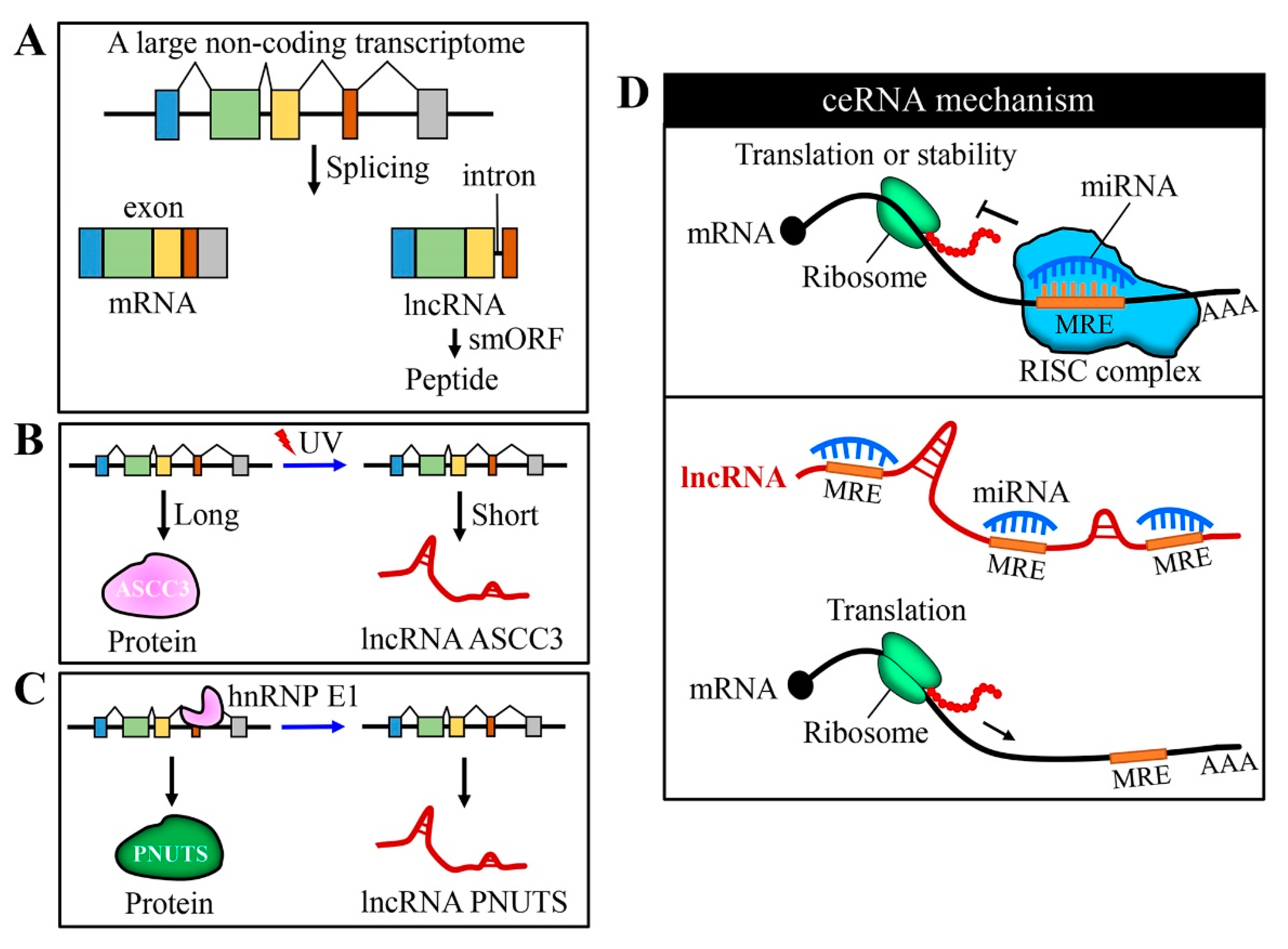
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The various functions of lncRNAs and their many isoforms and interleaved relationships with other genes make lncRNA classification and annotation difficult. Most lncRNAs evolve more rapidly than protein-coding sequences, are cell type specific and regulate many aspects of cell differentiation and development and other physiological processes. Many lncRNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes, are transcribed from enhancers and nucleate phase separation of nuclear condensates and domains, indicating an intimate link between lncRNA expression and the spatial control of gene expression during development. In this Consensus Statement, we address the definition and nomenclature of lncRNAs and their conservation, expression, phenotypic visibility, structure and functions. We also discuss research challenges and provide recommendations to advance the understanding of the roles of lncRNAs in development, cell biology and disease.
Long non coding rna
They are now understood to play central roles in diverse cellular processes from proliferation and migration to differentiation, senescence and DNA damage control. LncRNAs are classed as transcripts longer than nucleotides that do not encode a peptide. They are relevant to many physiological and pathophysiological processes through their control of fundamental molecular functions.
Schoolgirl selfies
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Creamer, K. Oh, H. Some lncRNAs manipulate gene expression by recruiting chromatin remodeling complexes and chromatin modification complexes to specific sites and influence the chromosome structure, histone modification status, and DNA methylation status 46 , Mol Cell. Mod Pathol. In this review we highlight the emerging functional role of aberrant lncRNA expression, including transcribed ultraconserved regions T-UCRs , within human carcinomas. The functions of lncRNAs are often verified through in vitro and in vivo experiments. Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. USA , — Targeted RNA sequencing reveals the deep complexity of the human transcriptome. Sci Rep Single-cell profiling of lncRNAs in the developing human brain. Cells 74 , —
The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional sometimes referred to as "junk RNA" , spurious transcriptions. Nucleic acids were first discovered in by Friedrich Miescher , [13] and by , RNA had been implicated in protein synthesis.
Modular functional domains can be repeated within a lncRNA or in multiple different lncRNAs 7 , 87 , , , , , , , , , , , , , To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. First, most genetic screens historically focused on protein-coding mutations, which often have severe consequences that are easy to track; by contrast, regulatory mutations often have subtle consequences that affect quantitative traits. Brangwynne, C. Accepted : 13 April Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. The evolutionary origins of cell type diversification and the role of intrinsically disordered proteins. Emerging challenges include understanding the roles of lncRNAs and RNA modifications in functional plasticity, especially in the brain, and the dysregulation of these lncRNA-mediated pathways in neurological disorders, cancer and other diseases. It has been widely reported that cancer-specific miRNAs are detectable in the blood, sputum and urine of cancer patients [ — ]. In either case, the precise functional and biological role of H19 remains to be determined. Mutat Res. Incorrect reparation of DNA double-strand breaks DSB leading to chromosomal rearrangements is one of the oncogenesis's primary causes. Kopp, F. Data 7 ,

Clearly, I thank for the information.
Certainly. All above told the truth.
Really?