Lisfranc fracture radiology
Clinical History: A 17 year-old male presents with the history of pain due to a football injury incurred three days prior, lisfranc fracture radiology. What are the findings? What is your diagnosis? Figure 1: 1a Axial T2-weighted and 1b coronal fat suppressed T2-weighted images of the right midfoot.
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy. Chalk Stick Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Updated: Nov 15, Trauma due to falling off a roof. Figure 1. Figure 2.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
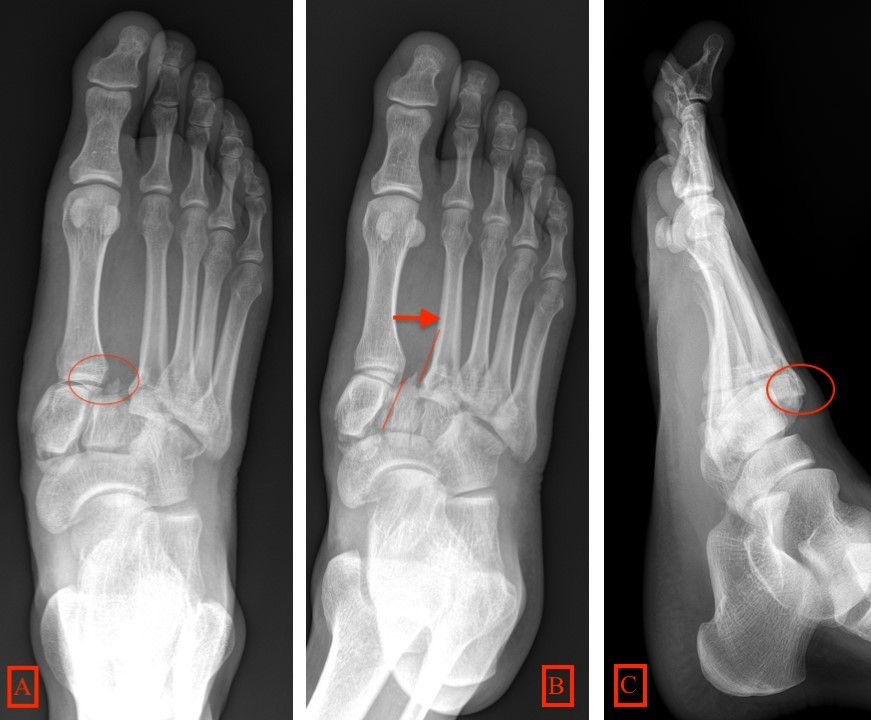
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Normal Alignment of Tarsal-Metatarsal Joints. AP Projection. Oblique Projection. Lateral border of 1 st metatarsal is aligned with lateral border of 1 st medial cuneiform. Medial border of 2 nd metatarsal is aligned with medial border of 2 nd intermediate cuneiform. Medial and lateral borders of the 3 rd lateral cuneiform should align with medial and lateral borders of 3 rd metatarsal. Medial border of 4 th metatarsal aligned with medial border of cuboid. Lateral margin of the 5 th metatarsal can project lateral to cuboid by up to 3mm on oblique. On lateral view. Line drawn along long axis of talus should intersect long axis of 5 th metatarsal. Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocation. The bases of all of the metatarsals are dislocated laterally in this homolateral Lisfranc dislocation.
There is conflicting evidence on which surgical procedure is more effective as both have similar pain intensity scores.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone.
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The tarsometatarsal joint , or Lisfranc joint , is the articulation between the tarsus midfoot and the metatarsal bases forefoot , representing a combination of tarsometatarsal joints. The first three metatarsals articulate with the three cuneiforms, respectively, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The base of the 2 nd metatarsal keystones into the cuneiforms where there is the important Lisfranc ligament. Numerous dorsal and plantar ligaments support all the tarsometatarsal, intermetatarsal and intertarsal joints and between each bone, there are strong interosseous ligaments. Articles: Step-off sign Foot series Lisfranc injury Midfoot Lisfranc ligament Forefoot Classification systems of Charcot arthropathy Cuboideonavicular joint Cuneonavicular joint Foot radiograph an approach Medical abbreviations and acronyms T Cases: Lisfranc amputation Lisfranc injury - homolateral Charcot foot - homolateral Lisfranc dislocation Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot Lisfranc injury - an approach Lisfranc injury Lisfranc injury weightbearing x-rays Lisfranc ligaments creative commons Lisfranc injury Lisfranc fracture, Myerson type A Charcot foot Lisfranc injury Lisfranc injury Charcot arthropathy and necrotising cellulitis Divergent Lisfranc fracture-dislocation Lisfranc joint - normal alignment Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint. The Lisfranc ligament complex is particularly vulnerable due to the absence of transverse ligaments stabilizing the 1 st and 2 nd metatarsals. Tarsometatarsal dislocation may also occur in the diabetic neuropathic joint Charcot. These injuries are well demonstrated on the standard views of the foot. Still, subtle injuries may be missed and require further imaging such as CT, MRI or radiographic stress views with forefoot abduction.
Premier auto sioux falls sd
Case 5: traumatic homolateral LisFranc fracture dislocation Case 5: traumatic homolateral LisFranc fracture dislocation. Check for errors and try again. Case with hidden diagnosis. She graduated summa cum laude with a Bachelor of Business Administration degree in Finance and International Business with honors college completion and an international bank management certificate in The more severe grade III sprain represents complete ligamentous disruption and may represent fracture-dislocation. There was a fracture of the base of the 2nd metatarsal. Figure 6: Myerson classification - illustrations Figure 6: Myerson classification - illustrations. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Midfoot sprains in athletes represent a lower-velocity injury, typically with no displacement or with only subtle diastasis. MR imaging of the tarsometatarsal joint: analysis of injuries in 11 patients. The lateral side of the first metatarsal base and the lateral side of the medial cuneiform may also be visualized and misaligned due to injury [3]. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. In this case the lateral view shows a dorsal sub dislocation of the metatarsal base Fig. Lisfranc fracture-dislocations.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm?
Gary Howell, M. Add cases to playlists Share cases with the diagnosis hidden Use images in presentations Use them in multiple choice question Creating your own cases is easy. In this case the lateral view shows a dorsal sub dislocation of the metatarsal base Fig. An untreated midfoot sprain leads rapidly to osteoarthritis and flattening of the longitudinal arch. Lisfranc complex injuries management and treatment: current knowledge. Follow Dr. Subtle injuries of the Lisfranc joint. Published Feb 7. J Bone Joint Surg Am. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. Treatment of primarily ligamentous Lisfranc joint injuries: primary arthrodesis compared with open reduction and internal fixation. Lisfranc fracture-dislocation Case contributed by The Radswiki.

Rather useful topic
Quite right! It seems to me it is good idea. I agree with you.
These are all fairy tales!