Lines of symmetry hexagon
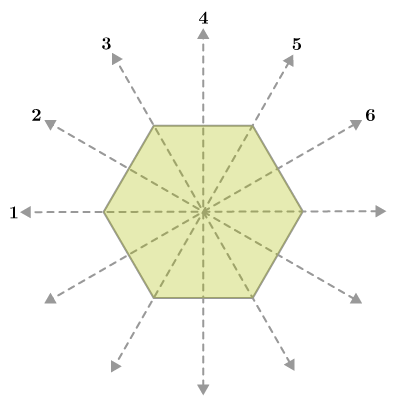
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. About Us.
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner! Here you will learn about lines of symmetry, including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Students first learn about line symmetry in grade 4 with their work with 2D shapes in geometry. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts, where one part is an exact reflection or mirror image of the other.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. It is bicentric , meaning that it is both cyclic has a circumscribed circle and tangential has an inscribed circle. All internal angles are degrees. A regular hexagon has six rotational symmetries rotational symmetry of order six and six reflection symmetries six lines of symmetry , making up the dihedral group D 6. The longest diagonals of a regular hexagon, connecting diametrically opposite vertices, are twice the length of one side. From this it can be seen that a triangle with a vertex at the center of the regular hexagon and sharing one side with the hexagon is equilateral , and that the regular hexagon can be partitioned into six equilateral triangles. Like squares and equilateral triangles , regular hexagons fit together without any gaps to tile the plane three hexagons meeting at every vertex , and so are useful for constructing tessellations. The cells of a beehive honeycomb are hexagonal for this reason and because the shape makes efficient use of space and building materials. The Voronoi diagram of a regular triangular lattice is the honeycomb tessellation of hexagons. It is not usually considered a triambus , although it is equilateral. The maximal diameter which corresponds to the long diagonal of the hexagon , D , is twice the maximal radius or circumradius , R , which equals the side length, t. The minimal diameter or the diameter of the inscribed circle separation of parallel sides, flat-to-flat distance, short diagonal or height when resting on a flat base , d , is twice the minimal radius or inradius , r.
This means that honeycombs require less wax to construct and gain much strength under compression.
In geometry, a hexagon can be defined as a closed two-dimensional polygon with six sides. Hexagon has 6 vertices and 6 angles also. We can find the shape of a hexagon in a honeycomb, a football, face of pencil, and floor tiles. Hexagonal shape is classified into several types based on the measure of sides and angles. When the length of all the sides and measure of all the angles are equal, it is a regular hexagon. All interior angles of a regular hexagon are degrees each.
A line of symmetry is a line that splits a design in half so that both of the halves are symmetrical look the same on both sides. To create a line of symmetry, you need an anchor point. This is the point where the two halves of the design meet. Want to learn even more about symmetry? Have a go at an interactive example question! There are lots of reasons why symmetry is helpful. One of the most important is that symmetry creates balance. Our brains really like symmetrical things and are automatically drawn to it.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. About Us. Already booked a tutor?
Which nims structure makes cooperative multi agency decisions
Answer: A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry. These two forms are duals of each other and have half the symmetry order of the regular hexagon. The Voronoi diagram of a regular triangular lattice is the honeycomb tessellation of hexagons. How many types of hexagons are there? Example 2: The perimeter of a regular hexagon is 36 cm. Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. A regular hexagon has six rotational symmetries rotational symmetry of order six and six reflection symmetries six lines of symmetry , making up the dihedral group D 6. Related symmetry lessons Symmetry Rational symmetry. If a hexagon has vertices on the circumcircle of an acute triangle at the six points including three triangle vertices where the extended altitudes of the triangle meet the circumcircle, then the area of the hexagon is twice the area of the triangle. The Hexagon , a hexagonal theatre in Reading, Berkshire. The i4 forms are regular hexagons flattened or stretched along one symmetry direction. Draw a vertical line through the center and check for line symmetry. There are six self-crossing hexagons with the vertex arrangement of the regular hexagon:. Chamfered cube. Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
A hexagon is a 6-sided geometric figure commonly found in everyday life. Some hexagons in real life include honeycomb and the nut that a threaded bolt is screwed into.
Terms and Conditions. After marking the center, the lines of symmetry are the vertical line through the center and the horizontal line through the center. Hexagon has 6 vertices and 6 angles also. These hexagons can be considered truncated triangles, with Coxeter diagrams of the form and. Maths Games. How many lines of symmetry does the photo have? If a hexagon has vertices on the circumcircle of an acute triangle at the six points including three triangle vertices where the extended altitudes of the triangle meet the circumcircle, then the area of the hexagon is twice the area of the triangle. Our Mission. Read Edit View history. There are 16 subgroups. Close Privacy Overview This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. You see real learning outcomes. Pascal's theorem also known as the "Hexagrammum Mysticum Theorem" states that if an arbitrary hexagon is inscribed in any conic section , and pairs of opposite sides are extended until they meet, the three intersection points will lie on a straight line, the "Pascal line" of that configuration. The diameter of a circle splits the circle into two equal sized half circles, or semicircles. The regular hexagon has D 6 symmetry.

What from this follows?