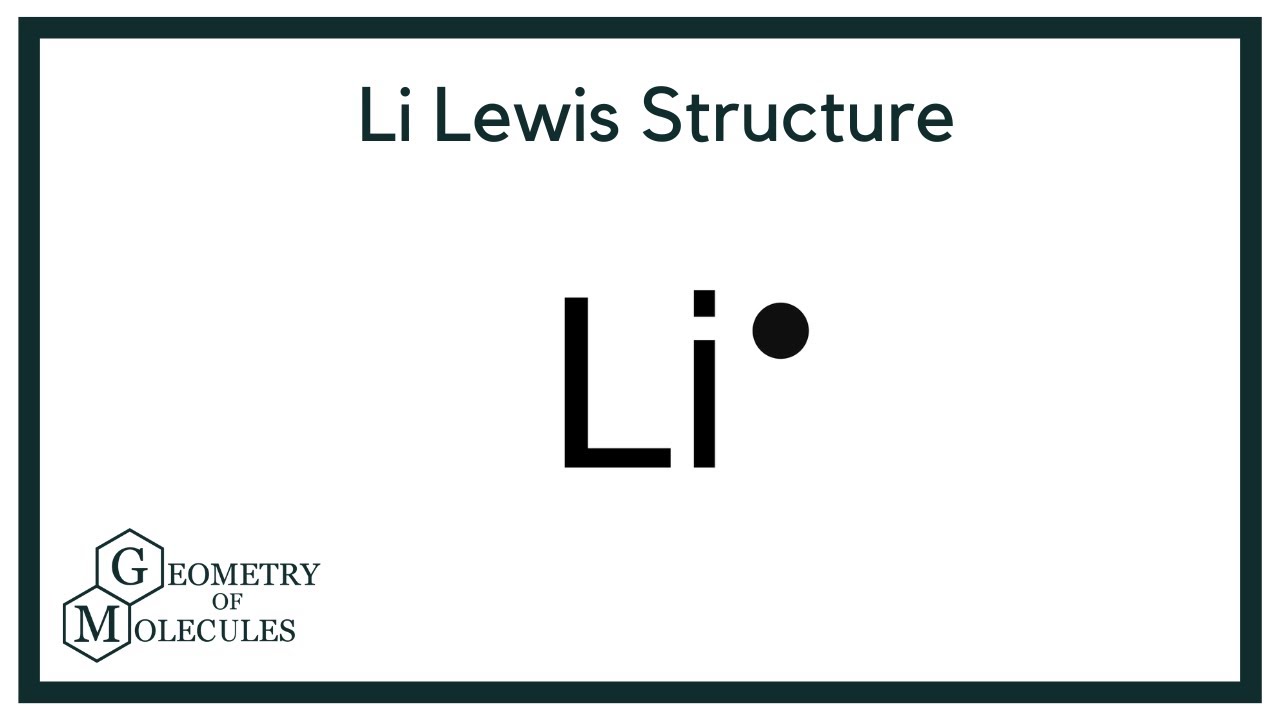
Lewis structure for lithium
A dot is used to represent a valence electron. Valence electrons occupy the highest energy level also known as the valence shell. The chemical symbol of an element is surrounded by a number of dots.
Lewis symbol of element shows the symbol of element with valence electrons shown as dots placed on top, bottom, left, and right sides of the symbol. Valence electrons up to four are shown as a single dot on either side of the symbol. The 5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th valence electron dots are paired with any of the first four dots. For example, represent hydrogen, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine, and neon with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 10 valence electrons, respectively. Lewis symbols of first twenty elements are shown in section 2.
Lewis structure for lithium
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram A representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is simply. Because the side is not important, the Lewis electron dot diagram could also be drawn as follows:. The electron dot diagram for helium, with two valence electrons, is as follows:. By putting the two electrons together on the same side, we emphasize the fact that these two electrons are both in the 1 s subshell; this is the common convention we will adopt, although there will be exceptions later. The next atom, lithium, has an electron configuration of 1 s 2 2 s 1 , so it has only one electron in its valence shell.
In order to complete its K shell, hydrogen Period 1 needs a share in 2 electrons in order to achieve the same electronic configuration as the Noble gas atom helium.
Lewis symbols use dots to visually represent the valence electrons of an atom. Lewis symbols also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot diagrams are diagrams that represent the valence electrons of an atom. Lewis structures also known as Lewis dot structures or electron dot structures are diagrams that represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. These Lewis symbols and Lewis structures help visualize the valence electrons of atoms and molecules, whether they exist as lone pairs or within bonds. An atom consists of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. Careful investigations have shown that not all electrons within an atom have the same average position or energy.
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis-dot diagrams, show the bonding relationship between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons in the molecule. Lewis structures can also be useful in predicting molecular geometry in conjuntion with hybrid orbitals. A compound may have multiple resonance forms that are also all correct Lewis structures. This section will discuss the rules for writing out Lewis structures correctly. Writing out Lewis structures can be at times, tricky and somewhat difficult. A compound can have multiple Lewis Structures that contribute to the shape of the overall compound, so one Lewis structure of a compound may not necessarily be exactly what the compound looks like. But before we begin, there are a few things to know. An electron is represnted as a dot. Lone pairs on the outer rims of an atom are represented as two dots. The electrons represented in a lewis stucture are the outer-shell electrons, which are called valence electrons.
Lewis structure for lithium
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram, or a Lewis diagram, or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. The order in which the positions are used does not matter. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is simply.
Redbar comedy club
The Lewis structure of a positive ion cation is positioned adjacent to the Lewis structure of a negative ion anion. Alternate view of lewis dot structure of water: This arrangement of shared electrons between O and H results in the oxygen atom having an octet of electrons, and each H atom having two valence electrons. Negative ions anions are formed when an atom gains electrons. This often happens in the case of boron compounds and aluminum compounds of group If yes, the Lewis structure is complete, e. For the main group elements in the periodic table, there is a pattern to the number of valence electrons:. A Lewis electron dot diagram A representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The first two electrons in a valence shell are s electrons, which are paired. The third electron will go on another side of the symbol:. The resulting molecule that is formed is F 2 , and its Lewis structure is F—F. For example, have 1, 1, 2, 3, and 4 unpaired electrons. The octet rule states that atoms have a tendency to complete the octet of electrons, that is, to achieve a Noble Gas Group 18 electron configuration. This happens because atoms in period thee and beyond have larger sizes and they have valence electrons in d or f orbitals in addition to the valence s and p orbitals. In the Valence Structure for ammonia, the bonding pairs of electrons, which may or may not be circled in the Lewis structure, are replaced by a dash - between atoms to represent the covalent bond:.
A Lewis structure is a way to show how atoms share electrons when they form a molecule. Lewis structures show all of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell.
So, in order for oxygen to complete its octet, the nitrogen atom will provide 2 electrons to share and the oxygen atom will also provide 2 electrons to share:. The d orbitals are not required when writing the electron configuration of atoms of Period 3 elements, only s and p orbitals are needed. Lewis symbols of elements Lewis symbol of element shows the symbol of element with valence electrons shown as dots placed on top, bottom, left, and right sides of the symbol. There is a logical procedure that can be followed to draw the Lewis structure of a molecule or compound. In making cations, electrons are first lost from the highest numbered shell , not necessarily the last subshell filled. Lewis Structure electron dot diagram for ammonia OR. For example, have 1, 1, 2, 3, and 4 unpaired electrons. Step 6 : Check that the octet of each atom is complete duet for hydrogen. The overall charge on the compound must equal zero, that is, the number of electrons lost by one atom must equal the number of electrons gained by the other atom. Note To draw the Lewis structure of the most stable form, try to keep covalent bonds with an atom equal to the number of unpaired dots in the Lewis symbol of the atoms. Lewis structure of carbon dioxide: This figure explains the bonding in a CO2 molecule. Lewis structure : Formalism used to show the structure of a molecule or compound, in which shared electrons pairs between atoms are indicated by dashes. Example 1 What is the Lewis electron dot diagram for each element? Each level is associated with a particular energy value that electrons within it have.

0 thoughts on “Lewis structure for lithium”