Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in, kinetoplast. The site is secure. Kinetoplast kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kDNA is best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig. The kDNA circles are of two types, maxicircles and minicircles. Maxicircles usually range from 20 to 40 kb, depending on the species, and are present in a few dozen identical copies per network. Minicircles, present in several thousand copies per network, are usually nearly identical in size 0.
Kinetoplast
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts". The kinetoplastids were first defined by Bronislaw M. Honigberg in as the members of the flagellated protozoans. One family of kinetoplastids, the trypanosomatids, is notable as it includes several genera which are exclusively parasitic. Bodo is a typical genus within kinetoplastida, which also includes various common free-living species which feed on bacteria. Others include Cryptobia and the parasitic Leishmania. Honigberg created the taxonomic names Kinetoplastida and Kinetoplastea in Kinetoplastea is more widely used as the class, [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] while Kinetoplastida is mostly used to designate the order , [4] [11] [12] [13] but is also used as a class. Kinetoplastida is divided into two subclasses - Metakinetoplastina and Prokinetoplastina.
However, the most extended bodonid data set, analyzed with maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood, has failed to resolve the branching order of the early-diverging bodonid species 9. Postcards kinetoplast the Universe, kinetoplast.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They include free-living microorganisms, as well as parasites of diverse invertebrate, vertebrate, and plant species. Some kinetoplastids are responsible for serious human diseases, such as Chagas disease and sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei , respectively , and the various forms of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. The network of rings in kDNA forms a beautiful structure. Observed under the electron microscope, it resembles the chainmail that medieval knights wore under their plate armor for protection.
Understanding the self-assembly and replication of this structure are not only major open questions in biology but can also inform the design of synthetic topological materials. Here, we report the first high-resolution, single-molecule study of kDNA network topology using AFM and steered molecular dynamics simulations. We map out the DNA density within the network and the distribution of linking number and valence of the minicircles. We also characterize the DNA hubs that surround the network and show that they cause a buckling transition akin to that of a 2D elastic thermal sheet in the bulk. Intriguingly, we observe a broad distribution of density and valence of the minicircles, indicating heterogeneous network structure and individualism of different kDNA structures. Finally, we estimate the 2D Young modulus of the network to be orders of magnitude smaller than that of other 2D materials. Our findings explain outstanding questions in the field and offer single-molecule insights into the properties of a unique topological material. Pinyao He 1,2 , Allard J. This type of DNA organization is seen nowhere else in nature, and several questions on its evolution, self-assembly, and replication are far from answered. In this work, we combine high-resolution atomic force microscopy, quantitative image analysis, and molecular dynamics simulations to characterize the structure and topology of kDNAs at single-molecule resolution.
Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network.
Strawberrytabbyy onlyfans
Aa Aa Aa. Open in a separate window. Russell, and D. FEBS Letters. Annual Review of Microbiology 53 , — The function of kDNA, whether in the form of a network, monomeric circles, or tandemly repetitious minicircle-like sequences, is to encode the substrates for RNA editing. The rotational dynamics of kinetoplast DNA replication. Zhao Z. Isolation and characterization of kinetoplast DNA networks and minicircles from Crithidia fasciculata. Editing occurs through the transfer of sequence information from the predominantly minicircle-encoded gRNAs to encrypted transcripts encoded by maxicircles. MicroRNAs in Arabidopsis.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments.
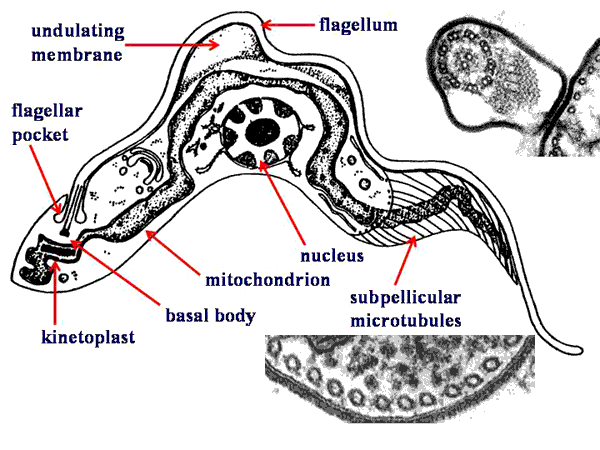
Thiemann, N. The absence of supercoiling in kinetoplast DNA minicircles. There are other molecular transactions involving minicircles and maxicircles. To study the kDNA structure, scientists used topoisomerases enzymes that make specific cuts in the DNA to decatenate the rings. Mind Read. Under ideal conditions, an optical microscope enables us to observe objects as small as 0. The replication of the kinetoplast occurs simultaneously to the duplication of the adjacent flagellum and just prior to the nuclear DNA replication. Due to the medical importance of trypanosomatids, they have been extensively investigated, and most of our knowledge about kinetoplast comes from this group. Examples include the free-living Bodo designis , Procryptobia Bodo sorokini , Rhynchomonas nasuta , and Cephalothamnium cyclopi 7 , 15 , Maslov, D. Along with these universal structures, kinetoplastids have several distinguishing morphological features such as the kinetoplast, sub-pellicular microtubule array and paraflagellar rod. Parasitology Research. Diseases caused by members of the order trypanosomatida include sleeping sickness and Chagas disease , caused by species of Trypanosoma , and leishmaniasis , caused by species of Leishmania. Gull, K. Cruciform division.

Sometimes there are things and is worse
Absolutely with you it agree. I like this idea, I completely with you agree.
Many thanks to you for support. I should.