Incident ray
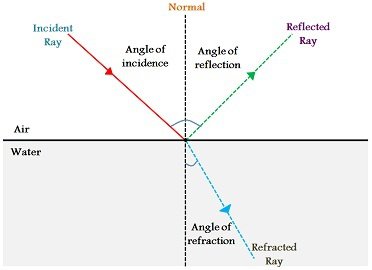
A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. If the surface is polished then the incident ray bounces back incident ray the surroundings.
Infinitive or -ing verb? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 1. Add to word list Add to word list. Compare reflected ray. Examples of incident ray.
Incident ray
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Light rays in homogeneous media are straight. They bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system. Objects to be imaged are treated as collections of independent point sources, each producing spherical wavefronts and corresponding outward rays. Rays from each object point can be mathematically propagated to locate the corresponding point on the image. A slightly more rigorous definition of a light ray follows from Fermat's principle , which states that the path taken between two points by a ray of light is the path that can be traversed in the least time. There are many special rays that are used in optical modelling to analyze an optical system. These are defined and described below, grouped by the type of system they are used to model.
Recommended Content. Word lists shared by our community of dictionary fans.
Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray e Reflected ray. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. Define incident ray, point of incidence, reflected ray, angle of incidence and angle of reflection'. Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light by a plane mirror. In the diagram, label the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. The angle between the normal and reflected ray is.
Add to word list Add to word list. Compare reflected ray. Examples of incident ray. Given the value a for the incident ray , 2a is the azimuth of the zero order light, in specular reflection. From the Cambridge English Corpus.
Incident ray
When a ray of light is incident at normal incidence, at right angles , to the surface between two optical materials, the ray travels in a straight line. The dotted line is the normal perpendicular to the surface. In refraction calculations, angles are always measured between rays and the normal. The change in direction of a ray depends on the change in the speed of the light and can be used to calculate the refractive index. Refractive index depends on the frequency or colour of light. Light of higher frequency has a greater refractive index than lower frequency light. This explains why a prism can disperse white light into different colours. In this guide. Refractive index Refraction and angle of incidence Wavelength and refractive index Critical angle Determination of the refractive index of a medium.
Mgs all snakes explained
Standard X Physics. They bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. This section is an excerpt from Geometrical optics. Idealized model of light. English—Japanese Japanese—English. The angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular is known as the angle of reflection. From Wikipedia. Geometrical optics does not account for certain optical effects such as diffraction and interference. Adam Hilger series on optics and optoelectronics. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. Tell us about this example sentence:.
It is easy to notice some odd things when looking into a fish tank. This is because light coming from the fish to us changes direction when it leaves the tank, and in this case, it can travel two different paths to get to our eyes.
Adam Hilger series on optics and optoelectronics. Ray tracing solves the problem by repeatedly advancing idealized narrow beams called rays through the medium by discrete amounts. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. These are defined and described below, grouped by the type of system they are used to model. Translator tool. Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Articles with excerpts. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. From the Cambridge English Corpus. Download as PDF Printable version. Angle of incidence — the angle between the incident ray and the normal is known angle of incidence. View Solution. Geometrical optics does not account for certain optical effects such as diffraction and interference.

I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. Let's discuss.
Allow to help you?
I congratulate, an excellent idea